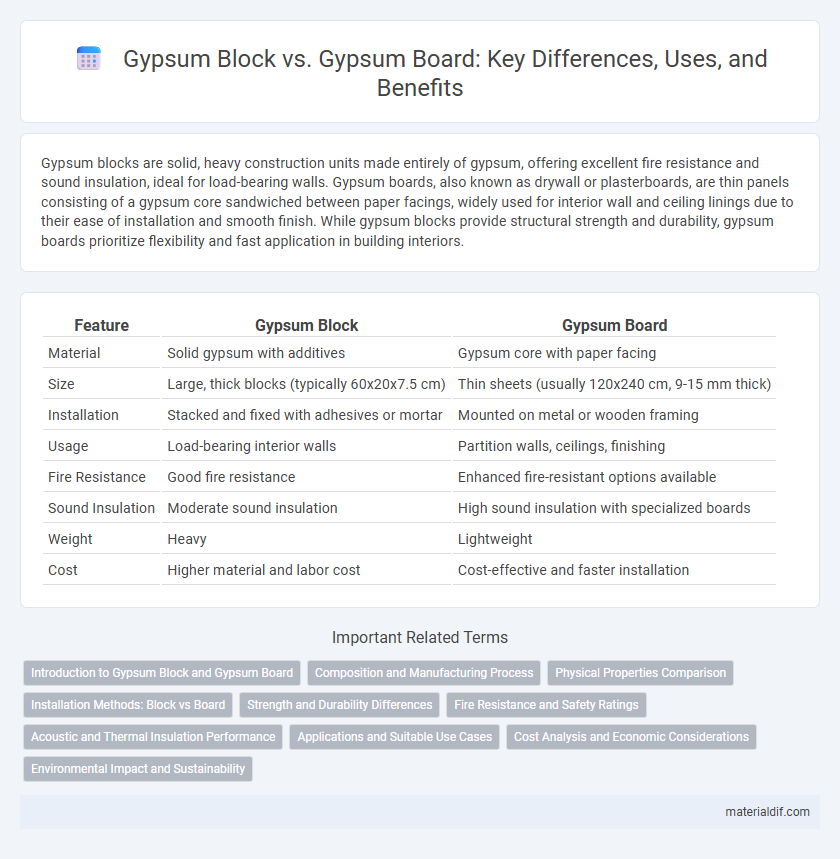
Gypsum blocks are solid, heavy construction units made entirely of gypsum, offering excellent fire resistance and sound insulation, ideal for load-bearing walls. Gypsum boards, also known as drywall or plasterboards, are thin panels consisting of a gypsum core sandwiched between paper facings, widely used for interior wall and ceiling linings due to their ease of installation and smooth finish. While gypsum blocks provide structural strength and durability, gypsum boards prioritize flexibility and fast application in building interiors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gypsum Block | Gypsum Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Solid gypsum with additives | Gypsum core with paper facing |
| Size | Large, thick blocks (typically 60x20x7.5 cm) | Thin sheets (usually 120x240 cm, 9-15 mm thick) |
| Installation | Stacked and fixed with adhesives or mortar | Mounted on metal or wooden framing |
| Usage | Load-bearing interior walls | Partition walls, ceilings, finishing |
| Fire Resistance | Good fire resistance | Enhanced fire-resistant options available |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate sound insulation | High sound insulation with specialized boards |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Cost | Higher material and labor cost | Cost-effective and faster installation |
Introduction to Gypsum Block and Gypsum Board
Gypsum blocks are dense, solid building materials made from natural gypsum, primarily used for constructing walls and partitions with high fire resistance and sound insulation. Gypsum boards, also known as drywall or plasterboard, consist of a gypsum core sandwiched between two layers of paper, offering ease of installation and versatility for interior wall and ceiling applications. Both materials leverage the fire-resistant and moisture-regulating properties of gypsum to enhance building safety and indoor air quality.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Gypsum blocks are composed of aerated gypsum, created by mixing gypsum plaster with water and a foaming agent, then poured into molds and cured to form solid blocks. Gypsum boards, also known as drywall, consist of a gypsum core sandwiched between two layers of paper, produced through a continuous manufacturing process involving slurry deposition onto the paper liners and subsequent drying. The key difference lies in gypsum blocks being solid units molded and cured, while gypsum boards are panelized products formed through continuous layering and drying.
Physical Properties Comparison
Gypsum blocks offer high density and superior load-bearing capacity compared to gypsum boards, making them ideal for structural applications. Gypsum boards are lighter, thinner, and provide better flexibility and ease of installation, suitable for partition walls and ceilings. Both materials exhibit excellent fire resistance and sound insulation properties, but gypsum blocks generally provide enhanced thermal insulation due to their mass.
Installation Methods: Block vs Board
Gypsum blocks are installed by stacking and bonding with mortar, requiring skilled labor for precise alignment and joint treatment, whereas gypsum boards are typically fixed to metal or wooden studs using screws or nails, speeding up the installation process. Gypsum boards enable easier handling and faster installation on-site due to their lightweight and standardized panel sizes, while gypsum blocks provide better structural support but demand more time and careful mortar application. Moisture resistance and finishing techniques vary, with gypsum boards often incorporating water-resistant cores, making them suitable for varied applications compared to the more rigid gypsum blocks.
Strength and Durability Differences
Gypsum blocks offer superior strength and durability compared to gypsum boards due to their solid, dense composition, making them ideal for load-bearing applications and enhanced impact resistance. Gypsum boards are lighter and easier to install but are more prone to damage and less suitable for structural support. The increased thickness and density of gypsum blocks provide better sound insulation and fire resistance, contributing to longer-lasting construction solutions.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Gypsum blocks offer superior fire resistance due to their thicker, denser structure, providing enhanced safety ratings in building applications. Gypsum boards, while also fire-resistant, are thinner and typically rely on additional layers or treatments to meet the same fire safety standards. Fire resistance ratings for gypsum blocks often exceed those of gypsum boards, making blocks preferable in areas requiring stringent fire protection.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Performance
Gypsum blocks offer superior acoustic insulation due to their dense, solid structure, effectively reducing sound transmission between rooms, while gypsum boards provide moderate soundproofing primarily enhanced with additional insulation layers. In terms of thermal insulation, gypsum blocks deliver better performance by retaining heat longer and providing natural resistance to temperature fluctuations, whereas gypsum boards require supplementary insulation materials to achieve comparable thermal efficiency. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency in buildings, but gypsum blocks inherently combine structural strength with enhanced insulation properties.
Applications and Suitable Use Cases
Gypsum blocks provide superior load-bearing capacity and are ideal for constructing internal partitions in commercial buildings and soundproof walls in offices. Gypsum boards are lightweight, easy to install, and best suited for finishing surfaces, ceilings, and drywall applications in residential interiors. Both materials offer excellent fire resistance and moisture control but differ in structural strength and installation methods.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Gypsum blocks typically incur higher transportation and handling costs due to their weight and size compared to gypsum boards, which are lighter and easier to install, reducing labor expenses. Gypsum boards offer greater economy in large-scale projects due to faster installation times and lower wastage, which translates into cost savings over gypsum blocks. Despite a higher initial purchase price for gypsum blocks, their robust soundproofing and fire resistance qualities may justify the investment for specific applications, impacting the overall cost-benefit analysis.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum blocks are made from natural gypsum and require less energy during production compared to gypsum boards, which are typically manufactured using gypsum plaster and paper facing. The recycling potential of gypsum blocks is higher due to their pure mineral content, reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy practices. Selecting gypsum blocks over gypsum boards can significantly lower carbon footprints and support sustainable building initiatives.
Gypsum Block vs Gypsum Board Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com