Safety glass is engineered to minimize injury by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, making it ideal for environments requiring enhanced protection. Decorative glass prioritizes aesthetic appeal with various designs, textures, and colors but may not possess the same level of impact resistance or safety features. Choosing between safety glass and decorative glass depends on the specific balance needed between functionality and visual elegance.
Table of Comparison
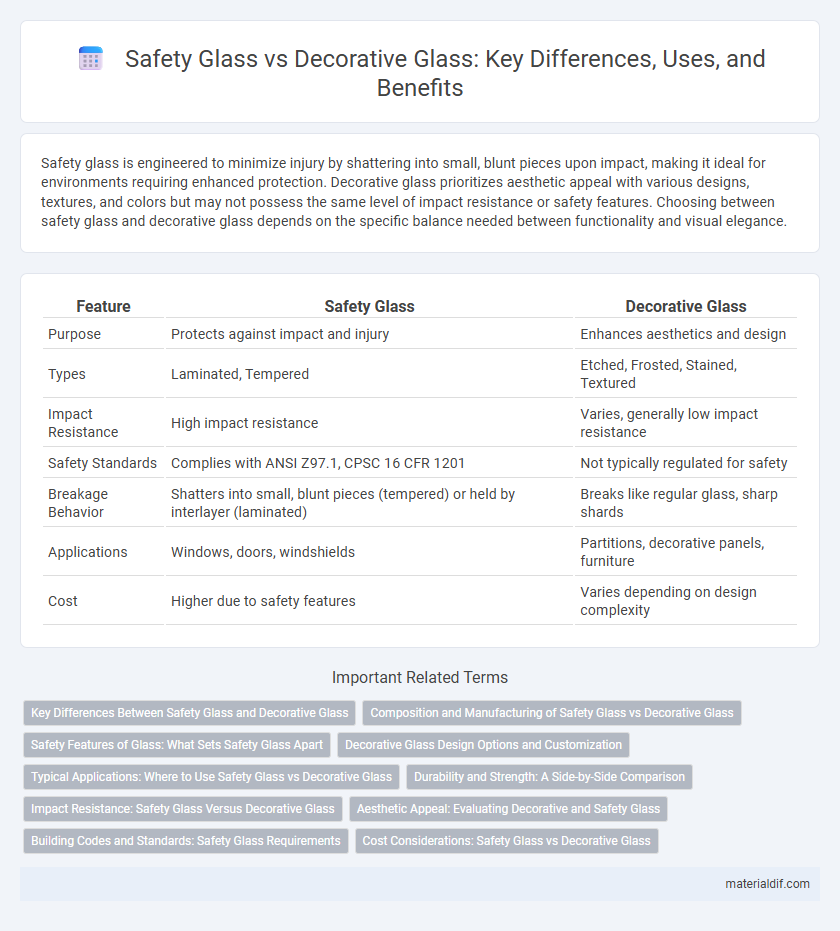
| Feature | Safety Glass | Decorative Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects against impact and injury | Enhances aesthetics and design |
| Types | Laminated, Tempered | Etched, Frosted, Stained, Textured |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance | Varies, generally low impact resistance |
| Safety Standards | Complies with ANSI Z97.1, CPSC 16 CFR 1201 | Not typically regulated for safety |
| Breakage Behavior | Shatters into small, blunt pieces (tempered) or held by interlayer (laminated) | Breaks like regular glass, sharp shards |
| Applications | Windows, doors, windshields | Partitions, decorative panels, furniture |
| Cost | Higher due to safety features | Varies depending on design complexity |
Key Differences Between Safety Glass and Decorative Glass
Safety glass is designed to minimize injury by shattering into small, blunt pieces or remaining intact with a plastic interlayer, commonly used in automotive windows and building facades for impact resistance. Decorative glass prioritizes aesthetic appeal with various textures, colors, and patterns, often lacking the structural strength and shatterproof qualities of safety glass. Key differences include impact resistance, fragmentation behavior, and primary use cases, where safety glass ensures protection while decorative glass enhances visual design.
Composition and Manufacturing of Safety Glass vs Decorative Glass
Safety glass is typically composed of laminated or tempered glass, where layers of glass are bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or toughened through controlled thermal processing to enhance strength and prevent shattering. Decorative glass often involves coated, etched, or printed treatments on annealed glass, focusing on aesthetics rather than impact resistance. Manufacturing safety glass includes processes like heat soaking and lamination, whereas decorative glass production emphasizes surface finishing techniques for visual appeal.
Safety Features of Glass: What Sets Safety Glass Apart
Safety glass, including tempered and laminated glass, is engineered to reduce injury risks by either shattering into small, blunt pieces or holding together upon impact, unlike decorative glass which prioritizes aesthetics over protection. Tempered safety glass undergoes thermal or chemical treatment to enhance strength up to five times that of regular glass, making it resistant to breakage from sudden force. Laminated safety glass consists of multiple layers bonded with a durable interlayer, preventing shards from dispersing and maintaining structural integrity during impacts.
Decorative Glass Design Options and Customization
Decorative glass offers a wide range of design options including frosted, etched, stained, and textured finishes that enhance aesthetic appeal while providing privacy. Customization allows for intricate patterns, colors, and layering techniques tailored to specific architectural or interior design needs. Unlike safety glass primarily focused on strength and impact resistance, decorative glass emphasizes artistic expression and personalized style in both residential and commercial spaces.
Typical Applications: Where to Use Safety Glass vs Decorative Glass
Safety glass is essential in high-risk environments such as automotive windshields, building windows near doors, and shower enclosures due to its impact resistance and shatterproof properties. Decorative glass is ideal for enhancing aesthetic appeal in interior applications like cabinet doors, partitions, and decorative panels, where safety requirements are minimal. Selecting safety glass ensures compliance with building codes in safety-critical areas, while decorative glass is preferred for visual enhancement and design flexibility.
Durability and Strength: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Safety glass, including tempered and laminated varieties, offers superior strength and impact resistance, reducing the risk of shattering into dangerous shards. Decorative glass, such as frosted or stained glass, prioritizes aesthetics but generally lacks the enhanced durability and breakage protection found in safety glass. For applications requiring robust safety features and structural integrity, safety glass outperforms decorative glass in durability and strength.
Impact Resistance: Safety Glass Versus Decorative Glass
Safety glass, such as tempered or laminated glass, offers superior impact resistance compared to decorative glass due to its ability to withstand strong forces without shattering into sharp pieces. Decorative glass prioritizes aesthetics and may include materials like frosted or stained glass, which are more prone to breaking upon impact and do not provide the same level of protection. Building codes and safety standards often require safety glass in areas subject to human impact, emphasizing its critical role in injury prevention and structural safety.
Aesthetic Appeal: Evaluating Decorative and Safety Glass
Decorative glass offers a wide range of aesthetic options, including stained, frosted, and textured designs that enhance visual appeal in interior and exterior applications. Safety glass, such as tempered or laminated glass, prioritizes durability and shatter resistance, often with limited decorative features but available in tinted or patterned variations for subtle enhancement. Combining both types can achieve a balance between aesthetic appeal and functional safety in architectural projects.
Building Codes and Standards: Safety Glass Requirements
Safety glass complies with stringent building codes and standards such as ANSI Z97.1 and CPSC 16 CFR 1201, ensuring it resists impact and minimizes injury risk in buildings. Decorative glass typically does not meet these safety requirements unless specifically treated or laminated to comply with these certifications. Building codes mandate the use of safety glass in critical areas like doors, windows near floors, and shower enclosures to enhance occupant safety.
Cost Considerations: Safety Glass vs Decorative Glass
Safety glass typically incurs higher costs due to specialized manufacturing processes like tempering or lamination, enhancing its strength and impact resistance. Decorative glass varies widely in price depending on design complexity, materials used, and customization, often resulting in lower baseline costs but potential increases for intricate patterns or finishes. Budget decisions should weigh the premium of enhanced safety features against the aesthetic value and customization potential of decorative options.
Safety glass vs Decorative glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com