Alkali-lime glass, commonly used in windows and bottles, offers durability and affordability due to its composition of silica, soda, and lime. Lead glass, also known as lead crystal, contains lead oxide, which enhances its refractive index and weight, making it highly prized for decorative items and fine glassware. The key difference lies in lead glass's superior brilliance and clarity compared to the more utilitarian alkali-lime glass.
Table of Comparison
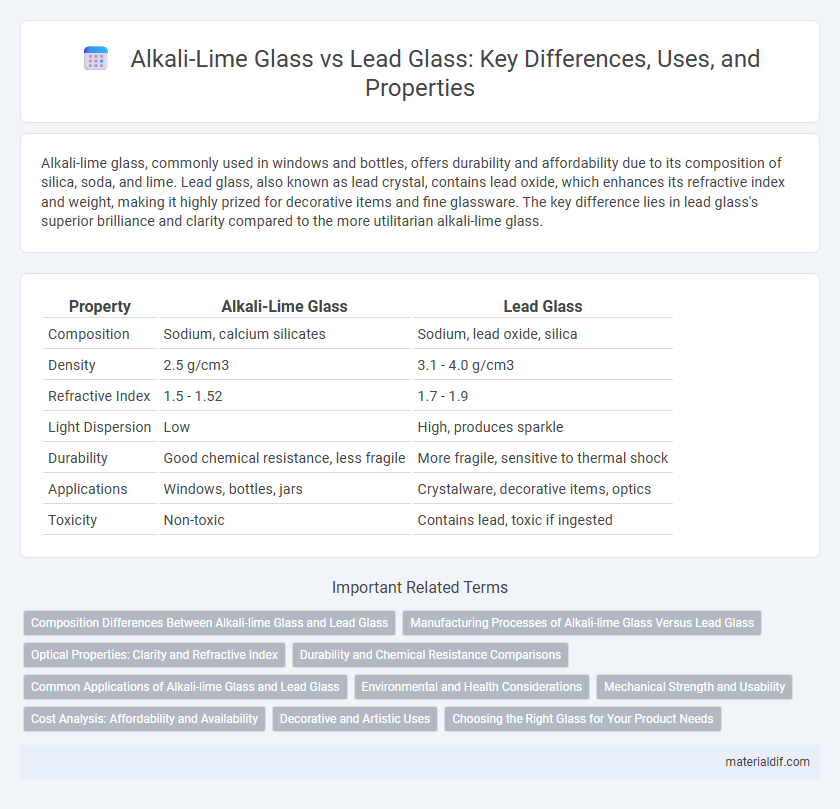
| Property | Alkali-Lime Glass | Lead Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium, calcium silicates | Sodium, lead oxide, silica |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 3.1 - 4.0 g/cm3 |
| Refractive Index | 1.5 - 1.52 | 1.7 - 1.9 |
| Light Dispersion | Low | High, produces sparkle |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, less fragile | More fragile, sensitive to thermal shock |
| Applications | Windows, bottles, jars | Crystalware, decorative items, optics |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic | Contains lead, toxic if ingested |
Composition Differences Between Alkali-lime Glass and Lead Glass
Alkali-lime glass primarily consists of silica (SiO2), soda (Na2O), and lime (CaO), which provides durability and chemical stability, whereas lead glass contains a significant proportion of lead oxide (PbO) that increases its density and refractive index. The higher lead content in lead glass lowers its melting point, making it easier to shape and polish for decorative purposes, while alkali-lime glass is more commonly used in windows and bottles due to its strength and lower cost. Differences in composition influence optical properties, with lead glass exhibiting superior brilliance and clarity compared to the typically more utilitarian alkali-lime glass.
Manufacturing Processes of Alkali-lime Glass Versus Lead Glass
Alkali-lime glass is produced by melting silica with soda ash and limestone at temperatures around 1500degC, resulting in a stable, durable material primarily used in windows and containers. Lead glass manufacturing involves adding lead oxide to the molten mixture, which lowers the melting point to about 1200degC and increases the glass's refractive index, enhancing brilliance and weight, ideal for decorative items and optical lenses. The alkali-lime process emphasizes cost-effectiveness and structural strength, whereas the lead glass process prioritizes optical clarity and density.
Optical Properties: Clarity and Refractive Index
Alkali-lime glass exhibits moderate clarity with a refractive index around 1.52, making it suitable for everyday applications such as windows and bottles. Lead glass offers superior optical clarity and a higher refractive index, typically between 1.7 and 1.8, resulting in enhanced brilliance and sparkle often utilized in fine glassware and optical instruments. The increased refractive index of lead glass also contributes to its greater dispersion, producing vivid color separation and light refraction effects.
Durability and Chemical Resistance Comparisons
Alkali-lime glass exhibits moderate durability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for everyday applications but vulnerable to alkaline substances. Lead glass offers superior durability and enhanced chemical resistance, especially against water and acids, due to the incorporation of lead oxide, which increases density and decreases corrosion. These properties make lead glass more resistant to scratching and chemical degradation compared to alkali-lime glass in laboratory and decorative uses.
Common Applications of Alkali-lime Glass and Lead Glass
Alkali-lime glass is predominantly used in windows, bottles, and everyday glassware due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. Lead glass, known for its high refractive index and brilliance, is commonly employed in decorative items, optical lenses, and radiation shielding. Each type serves specialized roles based on its chemical composition and physical properties.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Alkali-lime glass is environmentally favorable due to its lower energy consumption during production and absence of toxic lead content, making it safer for recycling and disposal. Lead glass, containing lead oxide, poses significant health risks through lead leaching and requires careful handling to avoid environmental contamination. Proper management of lead glass waste is essential to prevent soil and water pollution, emphasizing the ecological advantages of alkali-lime glass in sustainable applications.
Mechanical Strength and Usability
Alkali-lime glass features moderate mechanical strength and excellent chemical durability, making it ideal for everyday applications such as windows and bottles. Lead glass, containing lead oxide, offers superior mechanical strength and enhanced optical clarity, commonly used in decorative items and radiation shielding. The higher density and refractive index of lead glass improve its usability in precision optics, while alkali-lime glass remains preferred for cost-effective, mass-produced glass products.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Availability
Alkali-lime glass offers significant cost advantages due to its widespread availability of raw materials like silica, soda ash, and limestone, making it more affordable for mass production. Lead glass, containing lead oxide, incurs higher material costs and stricter environmental regulations, driving up overall expenses. This cost disparity affects affordability and accessibility, with alkali-lime glass dominating markets where budget and volume requirements are critical.
Decorative and Artistic Uses
Alkali-lime glass is widely used for decorative and artistic applications due to its affordability and ease of shaping, making it ideal for mass-produced ornaments and stained glass windows. Lead glass, with its high refractive index and superior clarity, is preferred for luxury decorative items such as crystal vases, chandeliers, and fine glassware, enhancing brilliance and aesthetic appeal. The unique optical properties of lead glass allow intricate cutting and engraving, elevating artistic craftsmanship in collectible and high-end decorative pieces.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Product Needs
Alkali-lime glass offers excellent chemical durability and affordability, making it ideal for everyday containers and windows, while lead glass provides superior brilliance, weight, and refractive index, perfect for decorative items and specialized optics. Consider alkali-lime glass for budget-friendly, lightweight applications requiring moderate thermal resistance, whereas lead glass suits products demanding high clarity and enhanced light dispersion. Evaluate product needs based on factors like durability, aesthetics, cost, and safety regulations to select the optimal glass type.
Alkali-lime glass vs Lead glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com