Aliphatic foam offers superior UV resistance and color stability, making it ideal for outdoor and long-term applications, while aromatic foam provides excellent cost-effectiveness and mechanical strength for general indoor use. The chemical structure of aliphatic foam results in lower susceptibility to yellowing and degradation, whereas aromatic foam tends to darken and become brittle over time when exposed to sunlight. Choosing between aliphatic and aromatic foam depends on the specific performance requirements, environmental exposure, and budget considerations of the project.
Table of Comparison
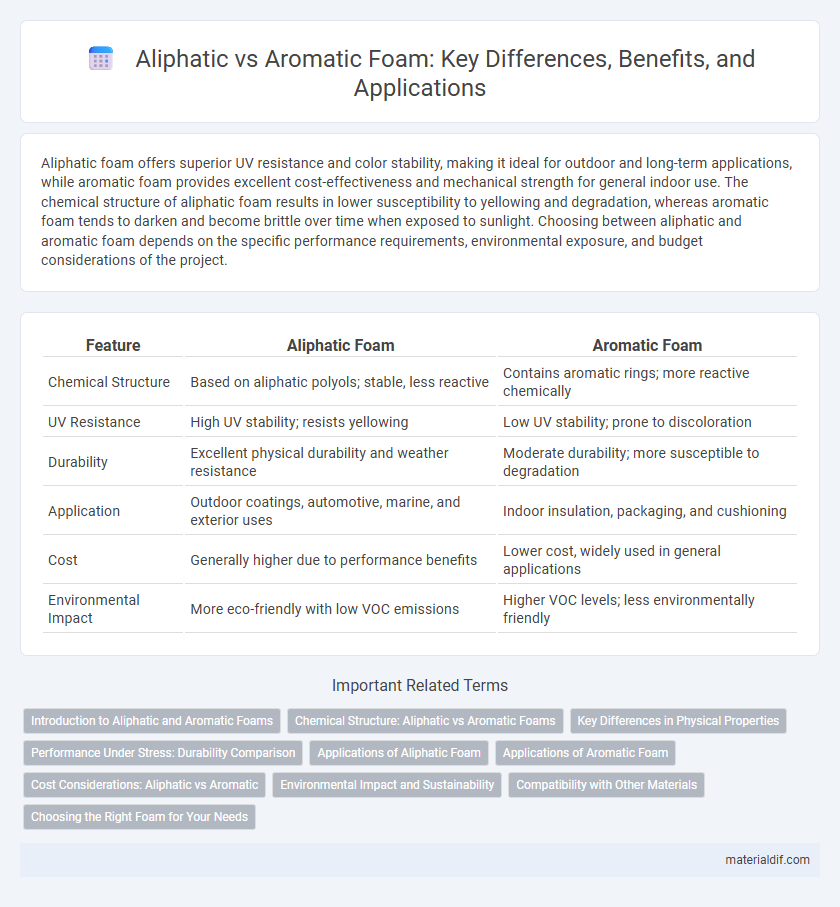
| Feature | Aliphatic Foam | Aromatic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Based on aliphatic polyols; stable, less reactive | Contains aromatic rings; more reactive chemically |
| UV Resistance | High UV stability; resists yellowing | Low UV stability; prone to discoloration |
| Durability | Excellent physical durability and weather resistance | Moderate durability; more susceptible to degradation |
| Application | Outdoor coatings, automotive, marine, and exterior uses | Indoor insulation, packaging, and cushioning |
| Cost | Generally higher due to performance benefits | Lower cost, widely used in general applications |
| Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly with low VOC emissions | Higher VOC levels; less environmentally friendly |
Introduction to Aliphatic and Aromatic Foams
Aliphatic foam is characterized by its UV resistance and superior weathering properties, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as insulation and roofing. Aromatic foam, derived from aromatic isocyanates, offers excellent mechanical strength and thermal insulation but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure. Understanding these fundamental differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate foam type based on environmental durability and application requirements.
Chemical Structure: Aliphatic vs Aromatic Foams
Aliphatic foams are primarily composed of straight or branched carbon chains resulting in enhanced UV resistance and flexibility, making them ideal for outdoor applications. Aromatic foams contain benzene rings within their chemical structure, which provides higher rigidity and thermal stability but reduces durability under prolonged sun exposure. This fundamental chemical difference influences their performance characteristics, with aliphatic foams favored for weatherability and aromatic foams preferred for mechanical strength.
Key Differences in Physical Properties
Aliphatic foam exhibits superior UV resistance and color stability compared to aromatic foam, which tends to yellow and degrade faster when exposed to sunlight. Aromatic foam generally offers higher rigidity and better thermal insulation, but its chemical structure makes it less resistant to environmental factors. In contrast, aliphatic foam's enhanced durability and flexibility make it ideal for applications requiring long-term exposure and aesthetic retention.
Performance Under Stress: Durability Comparison
Aliphatic foam exhibits superior UV resistance and color stability, maintaining structural integrity under prolonged environmental stress, unlike aromatic foam which tends to degrade and yellow over time. Aromatic foam offers excellent initial mechanical strength but shows reduced durability when exposed to harsh conditions such as moisture and temperature fluctuations. The enhanced performance of aliphatic foam under stress makes it preferable for outdoor and demanding industrial applications where long-term resilience is critical.
Applications of Aliphatic Foam
Aliphatic foam is widely used in outdoor and UV-exposed applications due to its superior resistance to sunlight, weathering, and chemical degradation compared to aromatic foam. It is commonly applied in automotive parts, coatings, and sealants where durability and color stability are critical. The enhanced longevity and clarity of aliphatic foam make it ideal for protective layers in construction and electronics industries.
Applications of Aromatic Foam
Aromatic foam is widely used in insulation, packaging, and cushioning due to its cost-effectiveness and excellent thermal properties. It is preferred in construction for wall and roof insulation, as well as in refrigerated transport and cold storage facilities for temperature control. Despite lower UV resistance compared to aliphatic foam, aromatic foam remains popular in applications where budget constraints and insulation efficiency are prioritized.
Cost Considerations: Aliphatic vs Aromatic
Aliphatic foam typically costs more than aromatic foam due to its enhanced UV resistance and durability, making it ideal for outdoor applications despite the higher initial investment. Aromatic foam, while more economical, lacks long-term weathering stability and often requires additional coatings or maintenance, increasing overall expenses over time. Choosing between the two depends on balancing upfront costs with lifecycle expenditure based on application requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aliphatic foam is favored for its superior environmental profile, offering greater UV resistance and lower emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which reduces air pollution and health risks during production and use. Aromatic foam, while often more cost-effective, tends to release higher levels of hazardous chemicals and has limited biodegradability, contributing to long-term environmental persistence and waste management challenges. Prioritizing aliphatic foam supports sustainability goals by enhancing recyclability and minimizing ecological harm, making it a better choice for eco-conscious construction and insulation projects.
Compatibility with Other Materials
Aliphatic foam exhibits superior compatibility with UV-sensitive substrates and coatings, maintaining its integrity and appearance in outdoor applications. Aromatic foam, while cost-effective, tends to degrade under UV exposure and may cause discoloration or chemical interactions when paired with certain plastics or adhesives. Selecting aliphatic foam ensures enhanced material stability and extended service life in composite assemblies.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Aliphatic foam offers superior UV resistance and color stability, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as roofing and insulation where long-term durability is essential. Aromatic foam provides cost-effective thermal insulation and soundproofing but tends to degrade faster under sunlight exposure, suitable for indoor environments. Evaluating factors like exposure conditions, budget, and performance requirements ensures selecting the right foam type that maximizes efficiency and longevity.
Aliphatic foam vs Aromatic foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com