Core-spun fiber features a strong core wrapped with fibers, providing enhanced durability and flexibility ideal for high-stress applications in PET manufacturing. Covered fiber, on the other hand, consists of a central filament entirely enveloped by a protective outer layer, offering superior resistance to abrasion and chemicals. Choosing between core-spun and covered fibers depends on the specific requirements for strength, flexibility, and durability in fiber PET products.
Table of Comparison
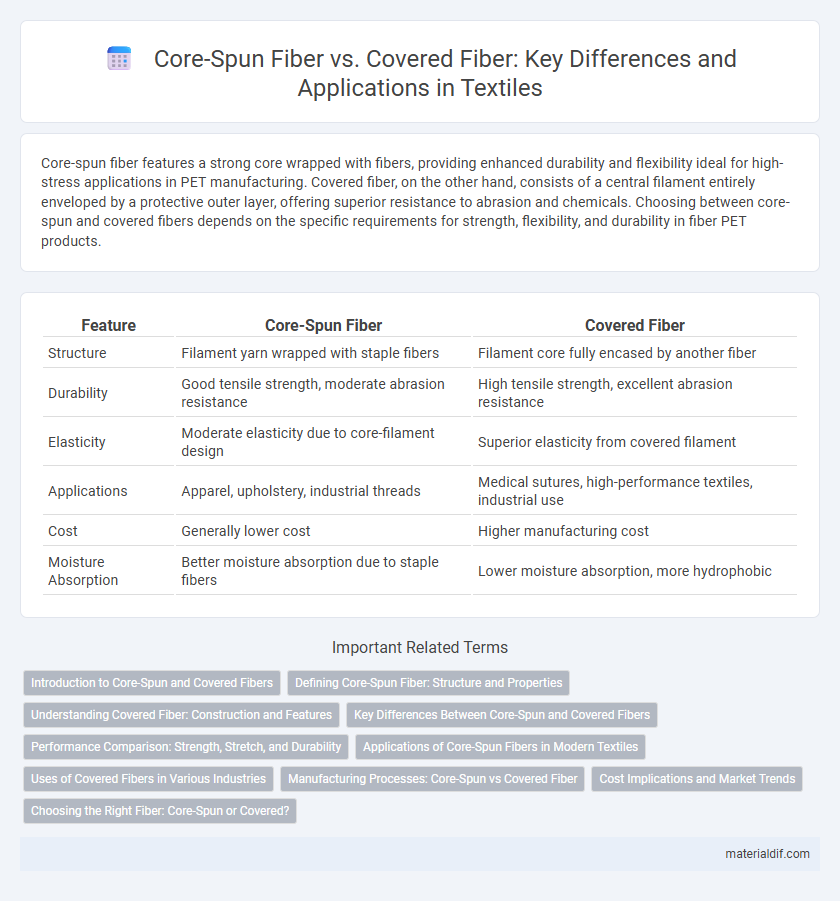
| Feature | Core-Spun Fiber | Covered Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Filament yarn wrapped with staple fibers | Filament core fully encased by another fiber |
| Durability | Good tensile strength, moderate abrasion resistance | High tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity due to core-filament design | Superior elasticity from covered filament |
| Applications | Apparel, upholstery, industrial threads | Medical sutures, high-performance textiles, industrial use |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Moisture Absorption | Better moisture absorption due to staple fibers | Lower moisture absorption, more hydrophobic |
Introduction to Core-Spun and Covered Fibers
Core-spun fibers consist of a central core of one material wrapped by another fiber, combining strength and comfort in a single yarn. Covered fibers feature a filament yarn enclosed by a staple fiber sheath, enhancing durability and elasticity. Both fiber types are widely used in textiles for their unique structural properties that optimize performance.
Defining Core-Spun Fiber: Structure and Properties
Core-spun fiber features a central core of high-strength filaments wrapped with a softer, usually spun yarn, combining the durability of synthetic fibers with the comfort of natural fibers. This structure enhances tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance while maintaining a lightweight and flexible profile ideal for advanced textile applications. The composite nature of core-spun fibers delivers superior performance in garments and industrial fabrics compared to conventional covered fibers, which typically involve wrapping one fiber type around a core without integration of properties.
Understanding Covered Fiber: Construction and Features
Covered fiber consists of a central filament completely surrounded by a protective sheath, enhancing durability and resistance to abrasion compared to core-spun fiber, which has fibers twisted around a central core. This construction provides covered fiber with superior tensile strength and improved flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and resistance to environmental factors. The outer covering also enables better control over the fiber's surface properties, such as texture and color retention.
Key Differences Between Core-Spun and Covered Fibers
Core-spun fibers consist of a central core yarn wrapped tightly with a different fiber, combining strength and softness for enhanced durability and comfort. Covered fibers are created by helically wrapping filament yarn around a core, providing elasticity and resistance to abrasion, ideal for applications requiring stretch and resilience. The primary distinction lies in their structural composition and performance characteristics, with core-spun fibers offering better moisture absorption and covered fibers excelling in elasticity and abrasion resistance.
Performance Comparison: Strength, Stretch, and Durability
Core-spun fiber combines a strong synthetic core with a natural fiber sheath, delivering superior tensile strength and enhanced durability compared to covered fiber, which uses a core wrapped tightly by another fiber. Core-spun fibers exhibit better stretch recovery and resist deformation under repeated stress, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring sustained elasticity. Covered fibers provide moderate strength and wear resistance but generally lag behind core-spun fibers in maintaining structural integrity over extended use.
Applications of Core-Spun Fibers in Modern Textiles
Core-spun fibers are widely used in modern textiles for enhanced durability and comfort, particularly in activewear and industrial fabrics where strength and flexibility are critical. Their unique structure, combining a strong core with a soft outer sheath, makes them ideal for applications requiring abrasion resistance and improved moisture management. Core-spun fibers also find significant use in technical textiles, such as upholstery and automotive interiors, due to their ability to maintain shape and withstand heavy wear.
Uses of Covered Fibers in Various Industries
Covered fibers find extensive applications in industries such as automotive, where enhanced durability and resistance to abrasion are essential for seat belts and airbags. In the medical field, covered fibers are used for surgical sutures and catheters, offering biocompatibility and flexibility. The textile industry employs covered fibers in high-performance sportswear and protective clothing to provide added strength and weather resistance.
Manufacturing Processes: Core-Spun vs Covered Fiber
Core-spun fiber manufacturing involves wrapping staple fibers around a central filament core, creating a composite yarn that combines strength and comfort. Covered fiber production entails spirally wrapping an elastomeric filament with a sheath of spun yarn, enhancing elasticity and durability. These distinct processes impact the yarn's performance characteristics, with core-spun fibers offering enhanced softness and covered fibers providing superior stretch and recovery.
Cost Implications and Market Trends
Core-spun fiber typically offers a cost-effective alternative to covered fiber by combining a core of synthetic filaments wrapped with staple fibers, reducing overall material expenses while maintaining strength. Covered fiber, often made by coating a core with protective materials, incurs higher production costs but provides superior durability and resistance, appealing to premium market segments. Market trends indicate growing demand for core-spun fibers in cost-sensitive industries such as textiles and composites, while covered fibers dominate specialized applications requiring high performance.
Choosing the Right Fiber: Core-Spun or Covered?
Core-spun fiber combines a strong filament core with a soft outer fiber, offering enhanced durability and comfort, ideal for applications requiring abrasion resistance and elasticity. Covered fiber features a central filament completely encased by another fiber layer, providing superior protection against friction and improving overall tensile strength. Choosing the right fiber depends on balancing strength, flexibility, and comfort needs specific to textile or industrial use cases.
Core-Spun Fiber vs Covered Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com