Engobe and slip are both liquid clay coatings used in pottery to alter surface texture and color before firing. Engobe typically contains a higher amount of fluxes and pigments, allowing it to produce more vibrant and durable finishes compared to slip, which is usually a simpler clay slurry used primarily for joining pieces or surface decoration. Understanding the differences in composition and application helps ceramic artists achieve desired aesthetic effects and functional qualities in their clay projects.
Table of Comparison
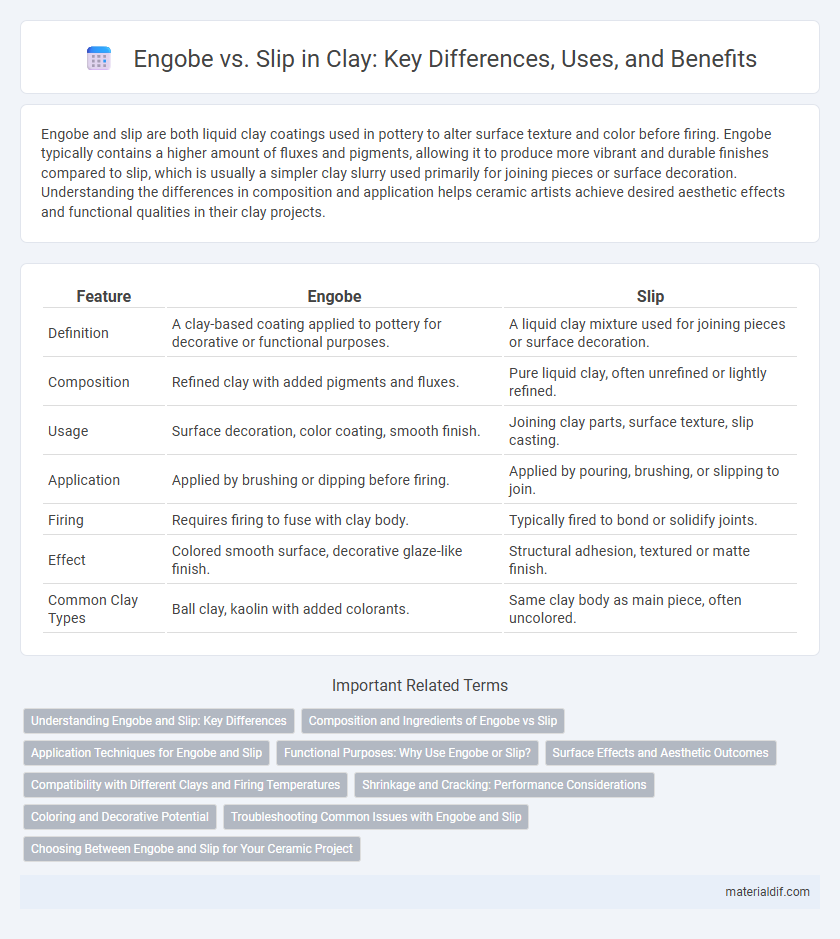
| Feature | Engobe | Slip |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A clay-based coating applied to pottery for decorative or functional purposes. | A liquid clay mixture used for joining pieces or surface decoration. |
| Composition | Refined clay with added pigments and fluxes. | Pure liquid clay, often unrefined or lightly refined. |
| Usage | Surface decoration, color coating, smooth finish. | Joining clay parts, surface texture, slip casting. |
| Application | Applied by brushing or dipping before firing. | Applied by pouring, brushing, or slipping to join. |
| Firing | Requires firing to fuse with clay body. | Typically fired to bond or solidify joints. |
| Effect | Colored smooth surface, decorative glaze-like finish. | Structural adhesion, textured or matte finish. |
| Common Clay Types | Ball clay, kaolin with added colorants. | Same clay body as main piece, often uncolored. |
Understanding Engobe and Slip: Key Differences
Engobe is a refined clay slip that is applied to pottery before firing to create a smooth, colored surface, often thinner and more consistent than traditional slip. Slip consists of liquid clay used primarily for decorating or joining clay pieces, typically thicker and less refined than engobe. Understanding the differences lies in their composition, texture, and finishing effects, with engobe offering a more controlled, decorative surface and slip serving functional or basic decorative purposes.
Composition and Ingredients of Engobe vs Slip
Engobe is a liquid clay mixture primarily composed of clay, water, and fluxes, often containing additional colorants or oxides to enhance surface decoration. Slip consists mainly of finely ground clay particles suspended in water without significant additives, used for joining or decorating ceramics. While engobe's composition is tailored for specific finishes and textures, slip maintains a basic formula aimed at consistency and adhesion.
Application Techniques for Engobe and Slip
Engobe and slip are both liquid clay mixtures applied to pottery surfaces for decorative or functional purposes, but their application techniques differ slightly. Engobe is typically applied with brushes or by dipping, allowing for precise layering and intricate designs due to its thinner consistency and controlled texture. Slip, being thicker and more fluid, is commonly poured or trailed onto the clay surface, enabling dynamic patterns and thicker coatings that enhance texture and color variations.
Functional Purposes: Why Use Engobe or Slip?
Engobe and slip serve distinct functional purposes in ceramics: engobe is primarily used for surface decoration and creating a smooth, colored layer that adheres well to the clay body, enhancing both aesthetics and texture. Slip, a liquid clay mixture, functions as a bonding agent for joining clay pieces and can also be used for decorating or creating different textures before firing. Choosing between engobe and slip depends on whether the goal is decorative surface treatment or structural joining in pottery.
Surface Effects and Aesthetic Outcomes
Engobe, a refined clay slip, creates a smoother and more polished surface, enhancing intricate designs and decorative details with vibrant colors, while slip provides a thicker layer that adds texture and depth but may obscure fine patterns. Engobe's fine particle size allows for precise application and subtle shading, promoting a uniform finish suitable for detailed artistic work. Slip's coarser texture offers a more rustic, tactile quality, contributing to expressive, three-dimensional aesthetics on ceramic surfaces.
Compatibility with Different Clays and Firing Temperatures
Engobe and slip both serve as decorative clay coatings but differ in their compatibility with various clay bodies and firing temperatures. Engobe typically contains finer particles and fluxes, ensuring better adherence and color stability on stoneware and porcelain clays fired at mid to high temperatures (cone 5-10). Slip, often thicker and unrefined, suits lower-fired earthenware clays but may cause defects such as peeling or cracking if mismatched with high-temperature firings or incompatible clay bodies.
Shrinkage and Cracking: Performance Considerations
Engobe generally has lower shrinkage rates compared to slip, reducing the risk of cracking during the drying and firing processes. Slip, often composed of similar clay bodies as the base ware, tends to shrink at a closer rate to the underlying clay, which can help maintain surface integrity and minimize stress-induced cracks. Selecting between engobe and slip depends on balancing shrinkage compatibility and desired surface texture to enhance overall ceramic performance.
Coloring and Decorative Potential
Engobe offers a more refined, opaque coloring suitable for smooth, uniform surfaces, providing a matte finish that enhances intricate decorative details. Slip, being thinner and more fluid, allows for versatile painting and marbling techniques but results in a more translucent color layer that emphasizes texture beneath. Both materials expand the decorative potential in ceramics by enabling varied surface effects, with engobe excelling in solid hues and slip in dynamic, layered designs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Engobe and Slip
Engobe and slip, both clay-based coatings used for surface decoration, can present common issues such as cracking, peeling, or uneven application. Troubleshooting engobe involves adjusting the consistency and moisture content to prevent cracking during drying, while slip problems often require refining particle size and mixing techniques to avoid separation or bubbling. Proper layering techniques and controlled drying conditions are essential for both to ensure strong adhesion and smooth finishes on ceramic pieces.
Choosing Between Engobe and Slip for Your Ceramic Project
Engobe and slip both serve as surface treatments in ceramics, but engobe is typically a colored, refined clay applied for decoration or texture, while slip is a more fluid mixture used mainly for joining or layering clay. Choosing engobe over slip enhances visual appeal with vibrant, opaque colors and smooth finishes, ideal for detailed designs. Slip is preferable when needing structural adhesion or creating slip-cast forms, making the choice dependent on whether aesthetics or function is the project's priority.
Engobe vs Slip Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com