Paper clay combines traditional clay with cellulose fibers, enhancing its strength and flexibility compared to traditional clay. This hybrid material allows for thinner, lighter, and more delicate creations that are less prone to cracking during drying and firing. Artists favor paper clay for its improved workability and ability to easily join pieces, streamlining the sculpting process.
Table of Comparison
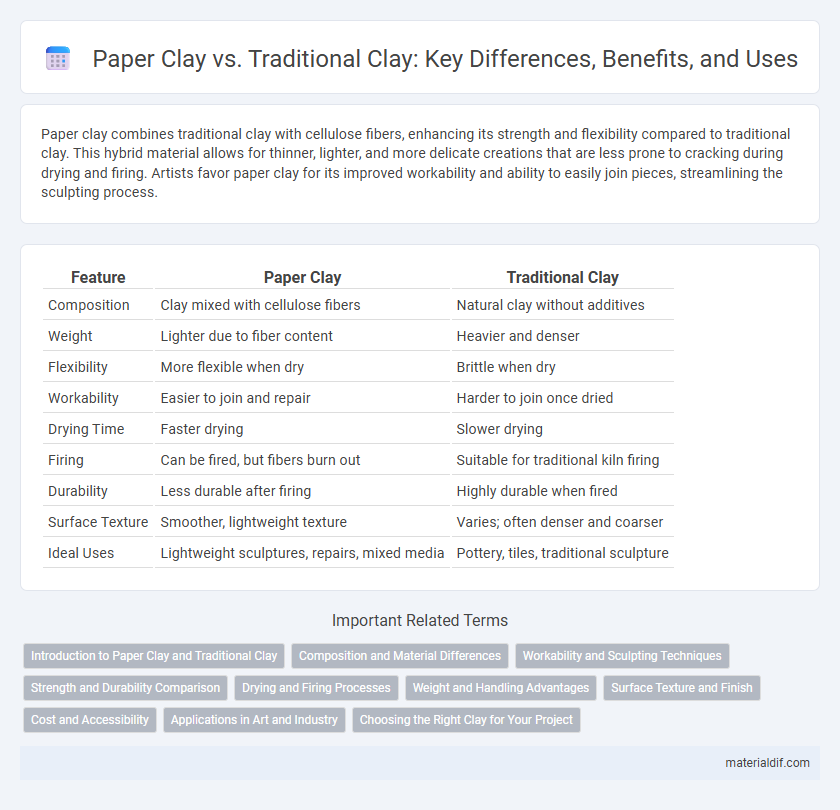
| Feature | Paper Clay | Traditional Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay mixed with cellulose fibers | Natural clay without additives |
| Weight | Lighter due to fiber content | Heavier and denser |
| Flexibility | More flexible when dry | Brittle when dry |
| Workability | Easier to join and repair | Harder to join once dried |
| Drying Time | Faster drying | Slower drying |
| Firing | Can be fired, but fibers burn out | Suitable for traditional kiln firing |
| Durability | Less durable after firing | Highly durable when fired |
| Surface Texture | Smoother, lightweight texture | Varies; often denser and coarser |
| Ideal Uses | Lightweight sculptures, repairs, mixed media | Pottery, tiles, traditional sculpture |
Introduction to Paper Clay and Traditional Clay
Paper clay combines traditional clay with cellulose fiber, enhancing its strength and reducing drying time compared to traditional clay, which consists solely of natural minerals like kaolin or ball clay. This fusion improves workability and allows for thinner, lighter sculptures that are less prone to cracking during drying or firing. Traditional clay remains favored for its plasticity and ability to hold fine details, but paper clay introduces versatility for artists seeking durability and ease of repair.
Composition and Material Differences
Paper clay contains cellulose fibers blended with traditional clay, enhancing flexibility and reducing cracking during drying. Traditional clay is primarily composed of natural minerals like kaolinite, quartz, and feldspar, offering a denser and less porous texture. The inclusion of paper fibers in paper clay improves workability and allows for thinner, lighter sculptures compared to heavier, more brittle traditional clay.
Workability and Sculpting Techniques
Paper clay offers enhanced workability compared to traditional clay due to its lightweight composition and added cellulose fibers, making it easier to mold and shape without cracking. Its increased tensile strength allows artists to create intricate details and delicate forms that hold well during drying and firing processes. Traditional clay, while versatile, often requires more careful moisture control and may be less forgiving for fine sculpting techniques, especially for beginners.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Paper clay contains cellulose fibers that enhance strength and reduce cracking during drying compared to traditional clay. Its lightweight composition allows for greater flexibility and resistance to breakage, making it more durable in thin or delicate forms. Traditional clay tends to be denser but may become more brittle and prone to chipping over time, especially without proper firing.
Drying and Firing Processes
Paper clay dries faster than traditional clay due to its fibrous composition, reducing the risk of cracks during the drying phase. The inclusion of cellulose fibers in paper clay enhances its structural integrity, allowing for thinner and more intricate designs without compromising durability. During firing, paper clay typically requires lower temperatures and shorter firing times, resulting in energy savings and less warping compared to traditional clay.
Weight and Handling Advantages
Paper clay is significantly lighter than traditional clay due to its fiber content, making it easier to handle and shape for extended periods without fatigue. Its lightweight nature reduces the overall mass of finished pieces, allowing for larger sculptures with less structural support. Drying times are faster and less prone to cracking, enhancing its practical advantages for artists and potters.
Surface Texture and Finish
Paper clay offers a smoother surface texture compared to traditional clay due to the incorporation of cellulose fibers, which reduce cracking and improve workability. Traditional clay tends to have a denser, more porous finish that can show imperfections more readily after drying and firing. The fiber blend in paper clay allows for finer detailing and a more refined, consistent finish ideal for delicate sculptural work.
Cost and Accessibility
Paper clay generally costs more than traditional clay due to the added materials like cellulose fibers, which enhance its flexibility and reduce drying time. Traditional clay is widely available and often less expensive, making it accessible for beginners and large-scale projects. Despite the higher cost, paper clay's increased workability and reduced risk of cracking can result in cost savings by minimizing material waste.
Applications in Art and Industry
Paper clay incorporates cellulose fibers, making it lightweight and more flexible than traditional clay, which enhances its use in detailed sculpting and mixed-media art projects. Traditional clay, often preferred in industrial ceramics, offers superior durability and is better suited for functional pottery and mass production processes. Artists favor paper clay for its ease of sanding and repairability, while industrial applications rely on traditional clay's high firing strength and consistent texture.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Project
Paper clay offers enhanced flexibility and lightweight properties due to its cellulose fiber content, making it ideal for intricate sculpting and delicate details. Traditional clay provides superior plasticity and durability for functional pottery and firing strength, suitable for wheel throwing and high-temperature kiln work. Selecting the right clay depends on project requirements such as desired texture, drying time, firing temperature, and final use.
Paper Clay vs Traditional Clay Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com