Brittle clay is characterized by its low plasticity, causing it to crack easily when dried or fired due to a lack of flexibility and moisture content. Plastic clay, on the other hand, exhibits high plasticity, allowing it to be easily shaped and molded without cracking, as it contains fine particles and adequate water. Understanding the difference between brittle and plastic clay is crucial for artists and potters to select the appropriate material for their specific crafting needs.
Table of Comparison
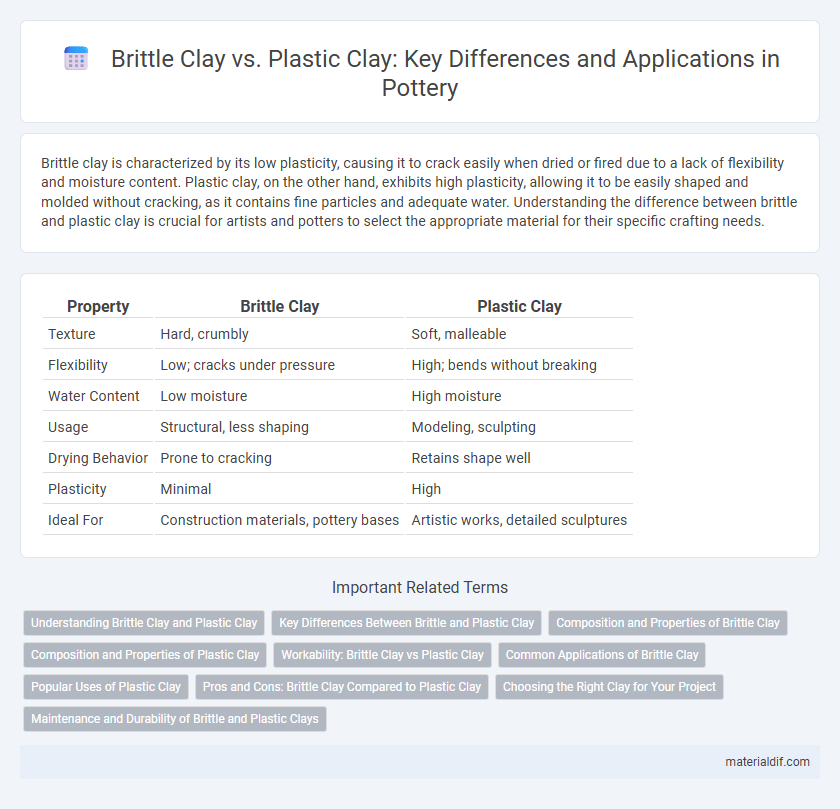
| Property | Brittle Clay | Plastic Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Hard, crumbly | Soft, malleable |
| Flexibility | Low; cracks under pressure | High; bends without breaking |
| Water Content | Low moisture | High moisture |
| Usage | Structural, less shaping | Modeling, sculpting |
| Drying Behavior | Prone to cracking | Retains shape well |
| Plasticity | Minimal | High |
| Ideal For | Construction materials, pottery bases | Artistic works, detailed sculptures |
Understanding Brittle Clay and Plastic Clay
Brittle clay is characterized by its low moisture content and high rigidity, causing it to crack easily when manipulated. Plastic clay contains higher moisture levels and exhibits malleability, allowing for smooth shaping and stretching without breaking. Understanding the differences between brittle and plastic clay is essential for selecting the right type for pottery, sculpture, or construction applications.
Key Differences Between Brittle and Plastic Clay
Brittle clay exhibits low plasticity, causing it to crack and break easily under stress, while plastic clay offers high plasticity, allowing it to be molded and shaped without breaking. The mineral composition and moisture content primarily influence these properties; brittle clay often has less water and a higher concentration of rigid mineral particles, whereas plastic clay contains more water and fine particles that aid in flexibility. Understanding these differences is crucial for applications in ceramics, construction, and pottery, as each clay type responds differently to shaping, drying, and firing processes.
Composition and Properties of Brittle Clay
Brittle clay typically consists of high amounts of silica and alumina, resulting in a rigid, less malleable structure with low plasticity. Its composition causes it to crack or fracture easily under stress, distinguishing it from plastic clay, which contains higher organic matter and water content that enhance flexibility. Properties of brittle clay include high shrinkage rates when drying, poor workability, and a tendency to lose moisture quickly, making it unsuitable for shaping or molding applications.
Composition and Properties of Plastic Clay
Plastic clay contains higher proportions of water and fine-grained particles such as kaolinite and montmorillonite, which enhance its malleability and workability compared to brittle clay. Its composition allows for greater plasticity, elasticity, and resistance to cracking during shaping and drying processes. These properties make plastic clay ideal for sculpting, pottery, and modeling applications requiring flexibility and smooth surface finishes.
Workability: Brittle Clay vs Plastic Clay
Brittle clay demonstrates limited workability due to its low moisture content and tendency to crack or break under pressure, making it challenging for detailed modeling or shaping. Plastic clay offers superior workability, characterized by high moisture levels and flexibility, allowing artists and potters to easily manipulate, mold, and form intricate designs without the risk of crumbling. This enhanced plasticity results from the clay's mineral composition and water retention capacity, which directly influence its malleability and drying behavior.
Common Applications of Brittle Clay
Brittle clay, characterized by low plasticity and high rigidity, is commonly used in applications such as pottery making for decorative items, where precise shapes and fine detail are crucial. It is also preferred in ceramic tile production and sculpting models that require minimal deformation during drying and firing processes. Its fast drying properties make it ideal for prototypes and art pieces that do not need significant flexibility.
Popular Uses of Plastic Clay
Plastic clay is widely used in pottery, sculpture, and ceramic arts due to its malleability and ability to retain shape during forming. Its high moisture content allows artists to create intricate details and smooth surfaces, making it ideal for hand-building and wheel-throwing techniques. Unlike brittle clay, plastic clay reduces the risk of cracking during drying and firing, which enhances its popularity in both amateur and professional ceramics.
Pros and Cons: Brittle Clay Compared to Plastic Clay
Brittle clay offers higher rigidity and holds detailed shapes better than plastic clay, making it ideal for fine sculptures requiring sharp edges. However, brittle clay is prone to cracking and breaking during drying and firing, whereas plastic clay provides greater flexibility and durability throughout the sculpting process. Despite plastic clay's versatility and ease of use, brittle clay's limited workability restricts its applications to projects needing minimal manipulation after shaping.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Project
Brittle clay, known for its low plasticity and rigidity, suits projects requiring detailed, delicate structures that hold sharp edges without deformation. Plastic clay offers higher flexibility and workability, ideal for sculpting and modeling complex shapes that need smooth manipulation without cracking. Selecting the right clay hinges on the project's demands for texture, strength, and drying behavior to ensure durability and desired finish.
Maintenance and Durability of Brittle and Plastic Clays
Brittle clay requires frequent monitoring and careful handling to prevent cracking and breakage due to its rigid structure and low moisture retention, which reduces its overall durability in long-term use. Plastic clay, with higher plasticity and moisture content, offers greater flexibility and resilience, making it easier to maintain and less prone to damage during shaping and firing processes. Proper storage and controlled humidity levels are essential for both types to preserve their workability and extend their lifespan.
Brittle Clay vs Plastic Clay Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com