Biodegradable cellophane offers a sustainable alternative to conventional plastic by decomposing naturally without releasing harmful microplastics into the environment. Unlike traditional plastic, which can persist for hundreds of years, cellophane made from renewable cellulose breaks down efficiently in composting conditions. This eco-friendly material significantly reduces pollution and supports a circular economy by minimizing plastic waste accumulation.
Table of Comparison
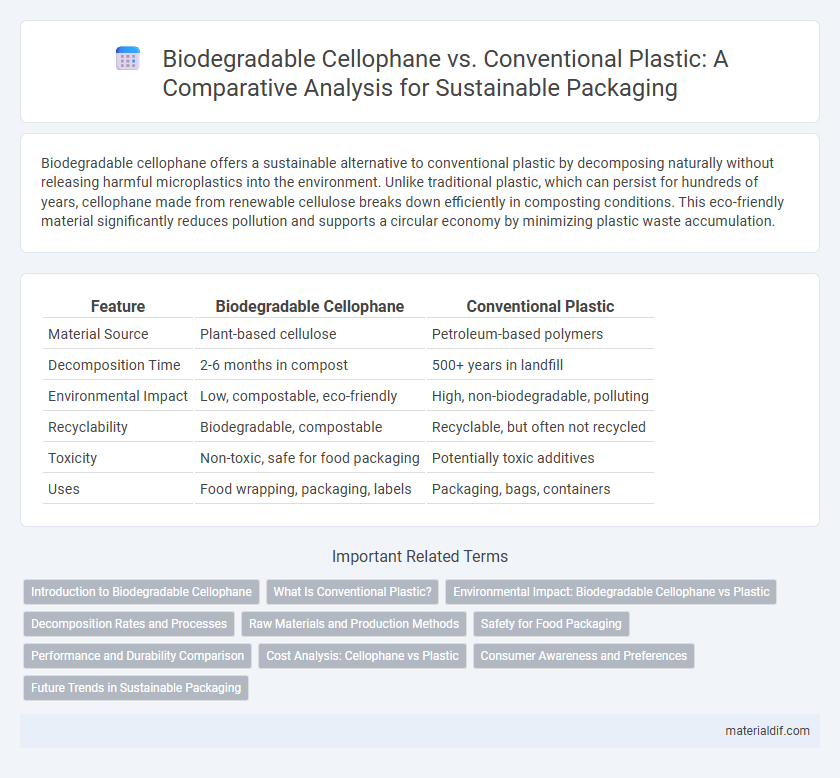
| Feature | Biodegradable Cellophane | Conventional Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Plant-based cellulose | Petroleum-based polymers |
| Decomposition Time | 2-6 months in compost | 500+ years in landfill |
| Environmental Impact | Low, compostable, eco-friendly | High, non-biodegradable, polluting |
| Recyclability | Biodegradable, compostable | Recyclable, but often not recycled |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, safe for food packaging | Potentially toxic additives |
| Uses | Food wrapping, packaging, labels | Packaging, bags, containers |
Introduction to Biodegradable Cellophane
Biodegradable cellophane is made from regenerated cellulose derived from wood pulp, making it a sustainable alternative to conventional plastic films produced from petrochemicals. This material decomposes naturally through microbial activity within weeks to months, reducing environmental pollution associated with plastic waste. Its transparency, flexibility, and compostability position biodegradable cellophane as an eco-friendly packaging solution in various industries.
What Is Conventional Plastic?
Conventional plastic is a synthetic polymer derived primarily from petrochemicals such as crude oil and natural gas, widely used for packaging due to its durability and low cost. Unlike biodegradable cellophane, conventional plastic is non-biodegradable, persisting in the environment for hundreds of years and contributing significantly to pollution and landfill waste. Its resistance to natural degradation processes makes it a major challenge for waste management and environmental sustainability efforts.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradable Cellophane vs Plastic
Biodegradable cellophane, made from cellulose, decomposes naturally within weeks, significantly reducing landfill waste and microplastic pollution compared to conventional plastic, which can persist for centuries. Its production requires fewer fossil fuels and emits lower greenhouse gases, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. The environmental impact of biodegradable cellophane is markedly less harmful, promoting sustainable packaging solutions that mitigate plastic pollution and help protect ecosystems.
Decomposition Rates and Processes
Biodegradable cellophane decomposes within weeks to months through natural microbial activity, breaking down into water, carbon dioxide, and biomass without leaving harmful residues. In contrast, conventional plastic can take hundreds of years to degrade, fragmenting into microplastics that persist in the environment and pose ecological risks. The accelerated decomposition rate of biodegradable cellophane significantly reduces landfill volume and environmental pollution compared to conventional plastic waste.
Raw Materials and Production Methods
Biodegradable cellophane is derived from renewable cellulose sources such as wood pulp or cotton fibers, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastic, which is primarily produced from petroleum-based polymers like polyethylene and polypropylene. The production of biodegradable cellophane involves dissolving cellulose in a solvent to form a film that is compostable and breaks down naturally, whereas conventional plastic manufacturing relies on polymerization processes that result in persistent materials resistant to degradation. These fundamental differences in raw materials and production methods significantly impact the environmental footprint, with cellophane offering reduced carbon emissions and improved sustainability compared to conventional plastics.
Safety for Food Packaging
Biodegradable cellophane, derived from cellulose, offers a safer alternative to conventional plastic by being non-toxic and free from harmful chemicals like BPA and phthalates, which are often found in plastic food packaging. Its natural composition reduces the risk of chemical leaching into food, ensuring higher safety standards for consumers. Unlike conventional plastic, biodegradable cellophane also supports eco-friendly disposal, breaking down into harmless organic compounds without releasing hazardous substances.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Biodegradable cellophane exhibits strong tensile strength and moisture resistance comparable to conventional plastic, offering effective protection for food packaging while reducing environmental impact. Unlike traditional plastics, cellophane decomposes naturally within weeks to months under composting conditions, significantly minimizing persistent waste. However, conventional plastic often surpasses cellophane in long-term durability and chemical resistance, making it more suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring extended shelf life.
Cost Analysis: Cellophane vs Plastic
Biodegradable cellophane, derived from cellulose, typically incurs higher upfront production costs compared to conventional plastic due to raw material expenses and specialized manufacturing processes. Despite these initial costs, cellophane offers potential savings in waste management and environmental compliance fees, which are rising globally with stricter regulations on plastic pollution. Over time, the total cost of biodegradable cellophane can be more competitive when factoring in lifecycle benefits and reduced ecological impact compared to petroleum-based plastic alternatives.
Consumer Awareness and Preferences
Biodegradable cellophane, made from natural cellulose, offers an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastic, attracting environmentally conscious consumers who prioritize sustainability. Consumer awareness about the environmental impact of plastic waste has surged, driving a significant shift in preferences toward biodegradable packaging options like cellophane. Market research indicates that transparency in product labeling and education about biodegradability substantially influence purchasing decisions, fostering increased demand for cellophane over traditional plastic films.
Future Trends in Sustainable Packaging
Biodegradable cellophane, derived from cellulose, offers a renewable and compostable alternative to conventional plastic packaging that relies on petroleum-based polymers. Future trends in sustainable packaging emphasize the integration of biodegradable cellophane to reduce plastic pollution and enhance circular economy models. Innovations aim to improve the material's barrier properties and scalability, driving wider adoption across food and consumer goods industries.
Biodegradable Cellophane vs Conventional Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com