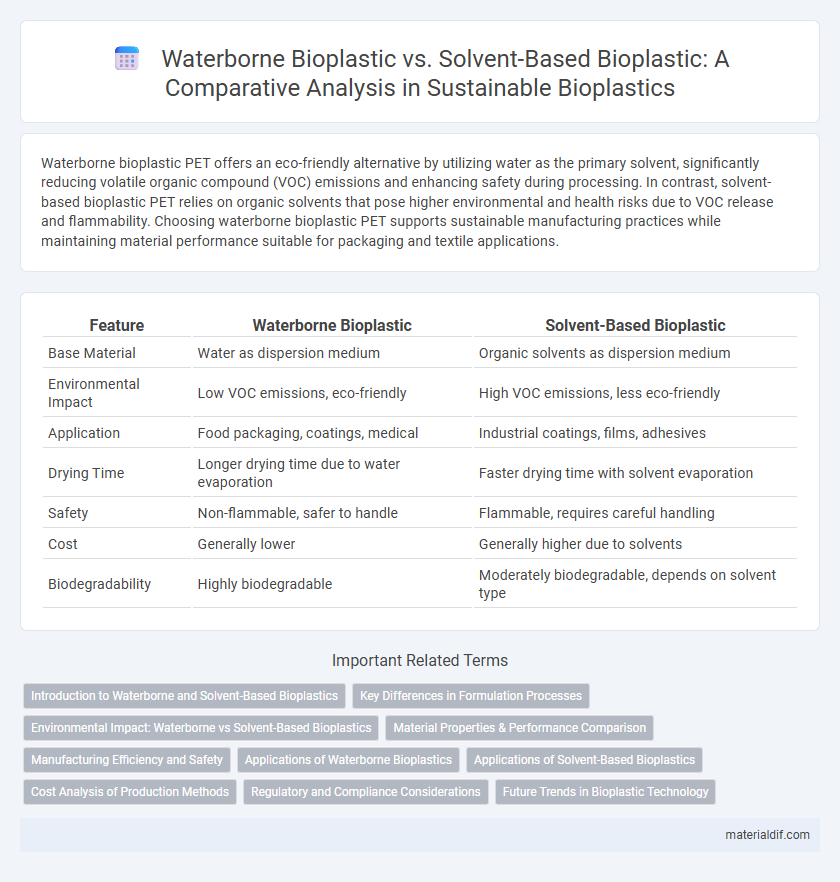
Waterborne bioplastic PET offers an eco-friendly alternative by utilizing water as the primary solvent, significantly reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and enhancing safety during processing. In contrast, solvent-based bioplastic PET relies on organic solvents that pose higher environmental and health risks due to VOC release and flammability. Choosing waterborne bioplastic PET supports sustainable manufacturing practices while maintaining material performance suitable for packaging and textile applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Waterborne Bioplastic | Solvent-Based Bioplastic |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Water as dispersion medium | Organic solvents as dispersion medium |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC emissions, eco-friendly | High VOC emissions, less eco-friendly |
| Application | Food packaging, coatings, medical | Industrial coatings, films, adhesives |
| Drying Time | Longer drying time due to water evaporation | Faster drying time with solvent evaporation |
| Safety | Non-flammable, safer to handle | Flammable, requires careful handling |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher due to solvents |
| Biodegradability | Highly biodegradable | Moderately biodegradable, depends on solvent type |
Introduction to Waterborne and Solvent-Based Bioplastics
Waterborne bioplastics utilize water as the primary solvent, offering eco-friendly advantages such as reduced volatile organic compounds (VOC) emissions and lower toxicity, making them ideal for sustainable packaging and coatings. Solvent-based bioplastics rely on organic solvents, providing superior mechanical properties and faster drying times, but pose environmental and health concerns due to solvent emissions. Understanding the differences in formulation chemistry and environmental impact is essential for selecting the appropriate bioplastic type for specific industrial applications.
Key Differences in Formulation Processes
Waterborne bioplastics utilize water as the primary solvent, resulting in lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and enhanced environmental safety compared to solvent-based bioplastics. Solvent-based bioplastics rely on organic solvents such as toluene or acetone, which facilitate faster drying times but contribute to higher toxicity and environmental hazards. The formulation process of waterborne bioplastics emphasizes eco-friendly additives and dispersion techniques, while solvent-based bioplastic production prioritizes solvent compatibility and film-forming properties.
Environmental Impact: Waterborne vs Solvent-Based Bioplastics
Waterborne bioplastics significantly reduce the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to solvent-based bioplastics, minimizing air pollution and human health risks. Their formulation primarily uses water as a carrier, enhancing biodegradability and lowering environmental toxicity. In contrast, solvent-based bioplastics rely on organic solvents that contribute to hazardous emissions and increased carbon footprints during production and disposal.
Material Properties & Performance Comparison
Waterborne bioplastics exhibit superior environmental compatibility with low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and enhanced biodegradability compared to solvent-based bioplastics, which often rely on toxic organic solvents that contribute to environmental pollution. Material performance shows that waterborne bioplastics generally provide improved flexibility, adhesion, and reduced flammability, whereas solvent-based bioplastics tend to offer higher mechanical strength and longer durability under harsh conditions. The choice between waterborne and solvent-based bioplastics depends on the application's specific requirements for sustainability, mechanical resilience, and regulatory compliance.
Manufacturing Efficiency and Safety
Waterborne bioplastics offer enhanced manufacturing efficiency due to lower energy consumption in drying processes and reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to solvent-based bioplastics. They provide a safer production environment by minimizing exposure to hazardous solvents, decreasing fire risks and health hazards for workers. Manufacturing facilities benefit from simplified regulatory compliance and reduced costs associated with solvent handling and disposal.
Applications of Waterborne Bioplastics
Waterborne bioplastics are widely applied in coatings, adhesives, and biomedical devices due to their low toxicity and environmental compatibility, making them ideal for sensitive applications like food packaging and medical implants. Their water-based formulation enhances biodegradability and reduces volatile organic compounds (VOCs), supporting sustainable manufacturing processes in industries such as automotive and electronics. These bioplastics offer superior performance in surface adhesion and flexibility, driving their preference in eco-friendly product development and regulatory-compliant applications.
Applications of Solvent-Based Bioplastics
Solvent-based bioplastics are extensively used in packaging, automotive parts, and medical devices due to their excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Their ability to form durable, moisture-resistant films makes them ideal for flexible and rigid packaging applications where barrier properties are critical. Furthermore, solvent-based bioplastics are favored in coating and adhesive formulations, providing enhanced performance in industrial and consumer products.
Cost Analysis of Production Methods
Waterborne bioplastic production typically incurs lower costs due to reduced solvent usage and simplified waste management, enhancing environmental compliance and lowering disposal expenses. In contrast, solvent-based bioplastic manufacturing demands expensive, volatile organic solvents and intricate recovery systems, increasing operational and capital expenditures. Cost analysis reveals waterborne bioplastics offer more economical scalability and sustainability compared to solvent-based alternatives.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Waterborne bioplastics exhibit lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, aligning with stringent environmental regulations like EPA standards and REACH compliance, making them favorable for eco-friendly applications. Solvent-based bioplastics face more rigorous scrutiny due to higher VOC content and potential hazardous air pollutants, often requiring extensive permits and monitoring under OSHA and local environmental agencies. Regulatory frameworks increasingly incentivize waterborne bioplastics in manufacturing processes to reduce air pollution and occupational health risks.
Future Trends in Bioplastic Technology
Waterborne bioplastics exhibit enhanced environmental compatibility due to lower VOC emissions and increased biodegradability compared to solvent-based bioplastics. Emerging innovations focus on improving waterborne formulations with bio-based additives to enhance mechanical properties and durability. Future trends indicate a shift towards scalable waterborne bioplastic production driven by stricter environmental regulations and demand for sustainable packaging solutions.
Waterborne bioplastic vs Solvent-based bioplastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com