Bamboo fiber is derived from the long, strong strands of the bamboo plant and is used primarily in textile production for its durability and softness. Bamboo pulp, on the other hand, is a processed form of bamboo cellulose typically used in paper manufacturing and as a raw material for viscose or rayon fabric. Understanding the distinction between bamboo fiber and bamboo pulp is essential for choosing sustainable materials in both clothing and paper industries.
Table of Comparison
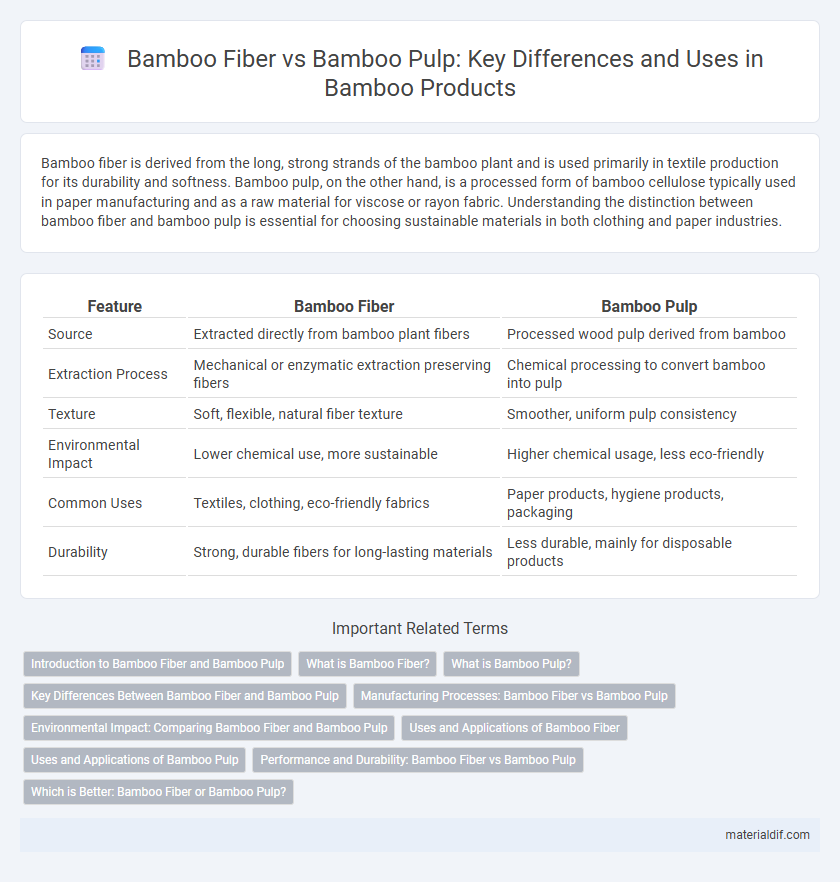
| Feature | Bamboo Fiber | Bamboo Pulp |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted directly from bamboo plant fibers | Processed wood pulp derived from bamboo |
| Extraction Process | Mechanical or enzymatic extraction preserving fibers | Chemical processing to convert bamboo into pulp |
| Texture | Soft, flexible, natural fiber texture | Smoother, uniform pulp consistency |
| Environmental Impact | Lower chemical use, more sustainable | Higher chemical usage, less eco-friendly |
| Common Uses | Textiles, clothing, eco-friendly fabrics | Paper products, hygiene products, packaging |
| Durability | Strong, durable fibers for long-lasting materials | Less durable, mainly for disposable products |
Introduction to Bamboo Fiber and Bamboo Pulp
Bamboo fiber is a natural textile material derived from the cellulose strands within bamboo plants, known for its softness, breathability, and durability in fabric production. Bamboo pulp is the processed raw material, obtained by mechanically or chemically breaking down bamboo plant fibers into a slurry, which serves as the base for producing bamboo viscose, rayon, or paper products. Understanding the distinction between bamboo fiber and bamboo pulp is essential for evaluating the sustainability, manufacturing methods, and end-use applications in the textile and paper industries.
What is Bamboo Fiber?
Bamboo fiber is a natural textile material derived directly from the bamboo plant's cellulose through mechanical processing, preserving its strength and sustainability. Unlike bamboo pulp, which is chemically processed into viscose or rayon, bamboo fiber retains its antibacterial and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly clothing and textiles. This natural fiber supports biodegradable and renewable fabric production, promoting environmentally responsible manufacturing.
What is Bamboo Pulp?
Bamboo pulp is a raw material derived from the chemical or mechanical processing of bamboo plants, used primarily to manufacture paper and viscose fibers. Unlike bamboo fiber, which refers to the naturally extracted long fibers from bamboo stalks, bamboo pulp consists of short cellulose fibers separated and purified to create a soft, fine material suitable for industrial applications. Synthesizing bamboo pulp involves breaking down the lignin and hemicellulose components to isolate cellulose, enhancing its usability in textiles and paper production.
Key Differences Between Bamboo Fiber and Bamboo Pulp
Bamboo fiber is a natural textile material derived from the long cellulose strands extracted mechanically from bamboo plants, characterized by strength, softness, and breathability. Bamboo pulp, on the other hand, is chemically processed from bamboo to produce a soft, biodegradable material primarily used in paper manufacturing and viscose rayon production. Key differences include bamboo fiber's retention of natural properties suitable for eco-friendly fabrics, whereas bamboo pulp undergoes chemical treatments resulting in a less sustainable, often less durable product.
Manufacturing Processes: Bamboo Fiber vs Bamboo Pulp
Bamboo fiber is extracted through mechanical or chemical processes that separate cellulose fibers from the bamboo stalk, resulting in long, durable strands used in textiles and composites. Bamboo pulp, created by chemically breaking down bamboo into a slurry, serves as the primary raw material for paper production and rayon manufacturing. The manufacturing of bamboo fiber emphasizes retaining fiber strength and length, while bamboo pulp production focuses on achieving a uniform, processable cellulose material.
Environmental Impact: Comparing Bamboo Fiber and Bamboo Pulp
Bamboo fiber production generates less chemical waste and consumes less water compared to bamboo pulp processing, which often involves harsh chemicals in the pulping process. The mechanical extraction methods used for bamboo fiber preserve more of the plant's natural properties, resulting in a lower carbon footprint and reduced environmental pollution. Bamboo pulp, primarily used in paper manufacturing, typically requires intensive energy and chemical inputs, increasing its overall environmental impact.
Uses and Applications of Bamboo Fiber
Bamboo fiber is primarily used in the textile industry to create soft, breathable fabrics for clothing, upholstery, and home textiles due to its natural antibacterial and moisture-wicking properties. Bamboo pulp, on the other hand, is mainly utilized in paper production, including tissues, napkins, and specialty papers, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional wood pulp. The versatility of bamboo fiber extends to biodegradable composites and eco-friendly packaging materials, enhancing sustainable product manufacturing.
Uses and Applications of Bamboo Pulp
Bamboo pulp, derived from raw bamboo through chemical processing, is primarily used in the production of paper, textiles, and biodegradable packaging materials due to its high cellulose content and eco-friendly properties. Unlike bamboo fiber, which is often used in fabric manufacturing for clothing and home textiles, bamboo pulp serves as a sustainable raw material in the paper industry for products like tissue paper, printing paper, and disposable hygiene products. The versatility of bamboo pulp extends to eco-conscious industries aiming to replace wood pulp with renewable and fast-growing bamboo sources.
Performance and Durability: Bamboo Fiber vs Bamboo Pulp
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior performance and durability compared to bamboo pulp due to its long, strong cellulose strands, which enhance tensile strength and resistance to wear. Bamboo pulp, often chemically processed, tends to have shorter fibers, resulting in lower mechanical strength and faster degradation over time. Products made from bamboo fiber maintain structural integrity and softness longer than those derived solely from bamboo pulp.
Which is Better: Bamboo Fiber or Bamboo Pulp?
Bamboo fiber is derived from mechanically processed bamboo, resulting in strong, durable, and breathable fabric, while bamboo pulp is chemically processed to create viscose or rayon, offering a softer but less eco-friendly option. Bamboo fiber retains more natural antibacterial properties and moisture-wicking capabilities compared to bamboo pulp, making it better for sustainable textiles and activewear. Choosing bamboo fiber over bamboo pulp ensures a product with superior durability, environmental benefits, and performance in comfort and hygiene.
bamboo fiber vs bamboo pulp Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com