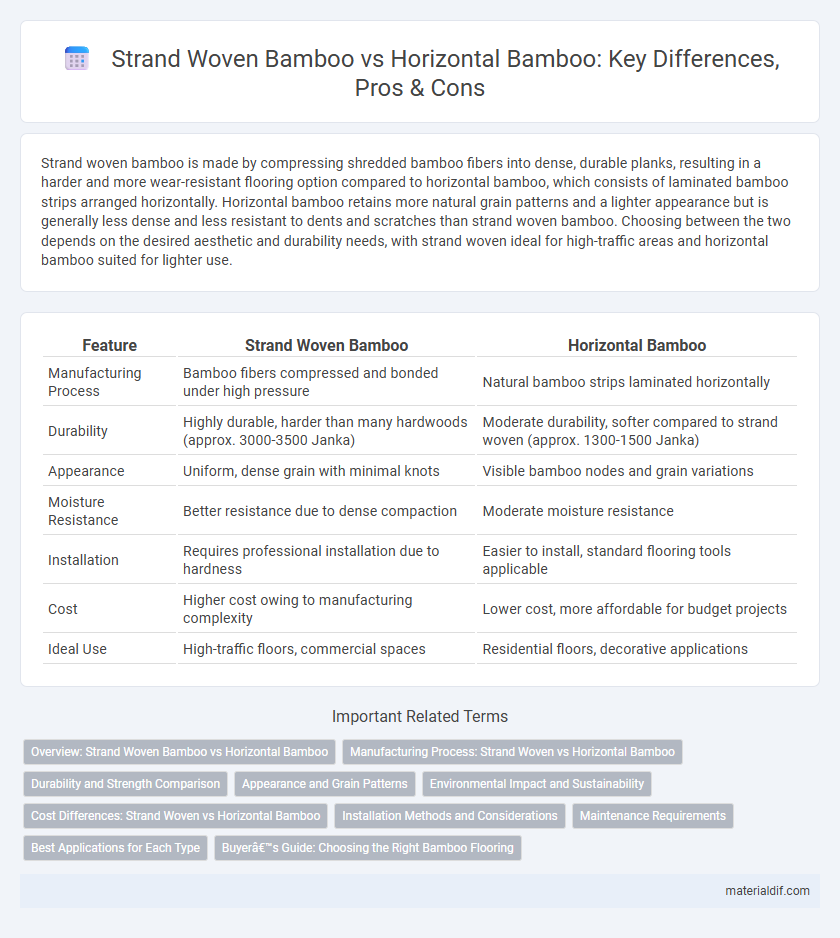
Strand woven bamboo is made by compressing shredded bamboo fibers into dense, durable planks, resulting in a harder and more wear-resistant flooring option compared to horizontal bamboo, which consists of laminated bamboo strips arranged horizontally. Horizontal bamboo retains more natural grain patterns and a lighter appearance but is generally less dense and less resistant to dents and scratches than strand woven bamboo. Choosing between the two depends on the desired aesthetic and durability needs, with strand woven ideal for high-traffic areas and horizontal bamboo suited for lighter use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Strand Woven Bamboo | Horizontal Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Bamboo fibers compressed and bonded under high pressure | Natural bamboo strips laminated horizontally |
| Durability | Highly durable, harder than many hardwoods (approx. 3000-3500 Janka) | Moderate durability, softer compared to strand woven (approx. 1300-1500 Janka) |
| Appearance | Uniform, dense grain with minimal knots | Visible bamboo nodes and grain variations |
| Moisture Resistance | Better resistance due to dense compaction | Moderate moisture resistance |
| Installation | Requires professional installation due to hardness | Easier to install, standard flooring tools applicable |
| Cost | Higher cost owing to manufacturing complexity | Lower cost, more affordable for budget projects |
| Ideal Use | High-traffic floors, commercial spaces | Residential floors, decorative applications |
Overview: Strand Woven Bamboo vs Horizontal Bamboo
Strand woven bamboo is manufactured by compressing shredded bamboo fibers under high heat and pressure, resulting in an exceptionally durable and dense flooring material with high resistance to scratches and dents. Horizontal bamboo is created by flattening whole bamboo stalks into strips and layering them horizontally, offering a distinct, natural grain appearance but with lower density and durability compared to strand woven bamboo. Both types provide eco-friendly flooring options, yet strand woven bamboo is preferred for high-traffic areas due to its superior hardness and longevity.
Manufacturing Process: Strand Woven vs Horizontal Bamboo
Strand woven bamboo undergoes a manufacturing process where bamboo fibers are shredded, soaked, and then compressed under high heat and pressure to form dense, durable planks. In contrast, horizontal bamboo is produced by stacking and laminating whole bamboo strips side by side, typically glued and pressed into boards without fiber alteration. The strand woven method results in stronger, more dimensionally stable flooring compared to the less dense, more natural appearance of horizontal bamboo.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Strand woven bamboo exhibits superior durability and strength compared to horizontal bamboo due to its manufacturing process, which involves compressing bamboo fibers under high pressure to create a dense, hard surface. This results in strand woven bamboo having higher Janka hardness ratings, often exceeding 3000, making it more resistant to dents and wear than horizontal bamboo, which typically ranges around 1300 to 1400. The dense composition and enhanced structural integrity of strand woven bamboo make it ideal for high-traffic flooring and structural applications, whereas horizontal bamboo is better suited for decorative or light-use purposes.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Strand woven bamboo features a dense, interwoven grain pattern with a uniform, linear appearance that enhances durability and visual depth. Horizontal bamboo showcases distinct nodes and natural variations, highlighting a more organic, striped grain structure that emphasizes the bamboo's natural growth rings. The visual difference between strand woven and horizontal bamboo significantly impacts design aesthetics, with strand woven offering a contemporary look and horizontal bamboo providing a traditional, textured appeal.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Strand woven bamboo offers superior environmental benefits compared to horizontal bamboo due to its production from shredded bamboo fibers, which utilizes more extensive raw material and reduces waste. This manufacturing process results in a denser, more durable product that reduces the frequency of replacement and associated resource consumption. Horizontal bamboo, while still sustainable as a rapidly renewable resource, generally involves less intensive processing and may have a shorter lifespan, potentially leading to higher long-term environmental impact.
Cost Differences: Strand Woven vs Horizontal Bamboo
Strand woven bamboo generally costs more than horizontal bamboo due to its complex manufacturing process, which involves compressing bamboo fibers under high pressure to create a denser, more durable product. Horizontal bamboo is typically less expensive because it retains the bamboo's natural structure with laminated strips, requiring less processing. The higher price of strand woven bamboo reflects its superior hardness and resistance to wear, making it a preferred choice for high-traffic flooring despite the initial investment.
Installation Methods and Considerations
Strand woven bamboo requires adhesive installation or floating floor methods due to its dense, compressed structure, ensuring strong bonding and stability. Horizontal bamboo typically utilizes tongue-and-groove planks, allowing for easier nail-down or staple installation on subfloors. Consider moisture levels and substrate conditions carefully for both types to prevent warping and ensure long-term durability.
Maintenance Requirements
Strand woven bamboo flooring requires less maintenance compared to horizontal bamboo due to its dense composition, which enhances its durability and resistance to scratches and moisture. Horizontal bamboo, with its layered grain structure, is more susceptible to dents and water damage, necessitating regular sealing and prompt cleaning to maintain its appearance. Proper care for strand woven bamboo typically involves simple sweeping and occasional damp mopping, while horizontal bamboo demands more frequent refinishing to preserve its finish.
Best Applications for Each Type
Strand woven bamboo, known for its superior density and hardness, is ideal for high-traffic flooring and outdoor decking where durability is crucial. Horizontal bamboo, featuring visible nodes and a softer texture, suits interior wall paneling, ceiling treatments, and furniture where aesthetic appeal and flexibility are prioritized. Choosing the right type depends on balancing structural strength needs with design preferences for residential or commercial spaces.
Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the Right Bamboo Flooring
Strand woven bamboo flooring offers exceptional durability and resistance to dents, making it ideal for high-traffic areas, while horizontal bamboo provides a traditional, natural grain appearance preferred for aesthetic appeal. Buyers should consider the level of foot traffic, intended room use, and desired visual style when choosing between these options to ensure the best fit for their home or commercial space. Understanding the manufacturing process and hardness ratings can further guide purchasing decisions for long-lasting, stylish bamboo flooring solutions.
strand woven bamboo vs horizontal bamboo Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com