Engineered bamboo offers enhanced durability and uniformity compared to natural bamboo, making it ideal for construction and flooring applications. It undergoes processes like lamination and compression, which improve strength and resistance to moisture and pests. Natural bamboo, while eco-friendly and renewable, varies in quality and is more susceptible to environmental damage and decay.
Table of Comparison
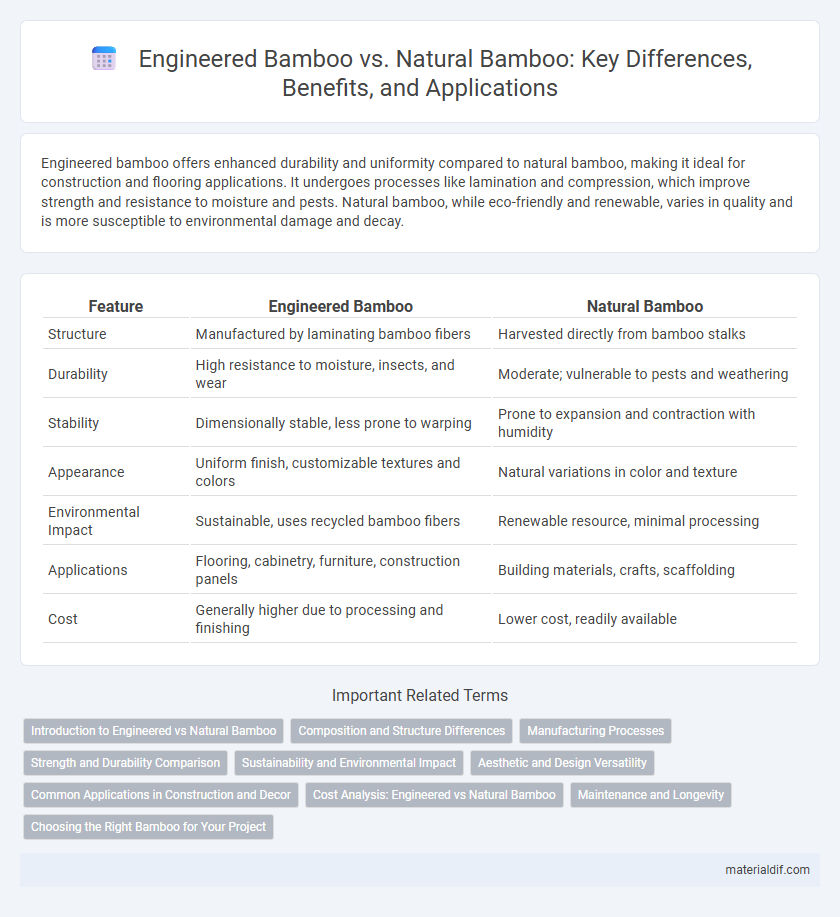
| Feature | Engineered Bamboo | Natural Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Manufactured by laminating bamboo fibers | Harvested directly from bamboo stalks |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture, insects, and wear | Moderate; vulnerable to pests and weathering |
| Stability | Dimensionally stable, less prone to warping | Prone to expansion and contraction with humidity |
| Appearance | Uniform finish, customizable textures and colors | Natural variations in color and texture |
| Environmental Impact | Sustainable, uses recycled bamboo fibers | Renewable resource, minimal processing |
| Applications | Flooring, cabinetry, furniture, construction panels | Building materials, crafts, scaffolding |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing and finishing | Lower cost, readily available |
Introduction to Engineered vs Natural Bamboo
Engineered bamboo is manufactured by processing natural bamboo fibers into composite materials, offering enhanced strength, durability, and uniformity compared to natural bamboo. Natural bamboo grows rapidly and exhibits variable properties influenced by species, climate, and growth conditions, leading to inconsistencies in performance. The distinction between engineered and natural bamboo lies in engineered products' controlled quality and tailored applications versus the organic variability found in natural bamboo culms.
Composition and Structure Differences
Engineered bamboo consists of compressed bamboo fibers bonded with adhesives, creating uniform panels with enhanced strength and stability, while natural bamboo retains its hollow cylindrical structure with segmented nodes. The composition of engineered bamboo alters the natural lignin and cellulose alignment through the lamination process, resulting in improved resistance to moisture and deformation. Natural bamboo's cellular structure provides flexibility and lightweight characteristics, but engineered bamboo offers consistent density and durability for construction and furniture applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Engineered bamboo undergoes a controlled manufacturing process involving the slicing, boiling, and laminating of bamboo strips, which enhances durability and uniformity compared to natural bamboo. Natural bamboo is harvested and used in its raw form, preserving its organic structure but displaying variable strength and density. The engineered process improves resistance to moisture, pests, and deformation, making it suitable for construction and furniture applications that demand consistent performance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Engineered bamboo offers enhanced strength and durability compared to natural bamboo due to its manufacturing process, which involves laminating multiple bamboo layers for uniform density and reduced defects. Natural bamboo, while inherently strong with a tensile strength comparable to steel, is more susceptible to environmental factors such as moisture, pests, and UV exposure, leading to faster degradation. Engineered bamboo's controlled composition improves resistance to warping, splitting, and insect damage, making it a superior choice for long-lasting construction and flooring applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Engineered bamboo offers enhanced sustainability by utilizing bamboo fibers in a way that maximizes material efficiency and reduces waste compared to natural bamboo harvesting. Its production reduces deforestation pressure, as engineered bamboo can be derived from faster-growing, lower-grade stalks unsuitable for traditional uses. The environmental impact of engineered bamboo includes lower carbon emissions and energy consumption during processing, making it a greener alternative to both natural bamboo and conventional timber.
Aesthetic and Design Versatility
Engineered bamboo offers greater aesthetic consistency and design versatility compared to natural bamboo, featuring uniform grain patterns and customizable finishes that suit modern architectural trends. Natural bamboo showcases unique variations in color and texture, imparting an organic, rustic charm ideal for traditional or eco-centric designs. The adaptability of engineered bamboo enhances its application in intricate design projects, while natural bamboo remains favored for its authentic, natural appeal.
Common Applications in Construction and Decor
Engineered bamboo offers enhanced strength and uniformity, making it ideal for structural elements like flooring, decking, and load-bearing panels in construction. Natural bamboo retains its organic texture and flexibility, commonly used in decorative applications such as wall coverings, furniture, and artisan crafts. Both types leverage bamboo's sustainability, but engineered bamboo is favored for precision and durability while natural bamboo is prized for aesthetic authenticity.
Cost Analysis: Engineered vs Natural Bamboo
Engineered bamboo generally incurs higher initial costs compared to natural bamboo due to processing, adhesive materials, and manufacturing technology involved in its production. Natural bamboo is more affordable as it is harvested and used with minimal treatment, but it may require more frequent maintenance and replacement over time. Long-term cost analysis often favors engineered bamboo for its durability and stability, reducing expenses related to repairs and replacements in construction or flooring applications.
Maintenance and Longevity
Engineered bamboo offers enhanced durability and lower maintenance compared to natural bamboo due to its processed and stabilized composition. Natural bamboo requires regular sealing and protection against moisture and pests to prevent decay and warping. Engineered bamboo products typically have a longer lifespan, resisting environmental damage more effectively than untreated natural bamboo.
Choosing the Right Bamboo for Your Project
Engineered bamboo offers enhanced durability, uniformity, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for flooring and structural applications where consistency is crucial. Natural bamboo provides a more organic aesthetic with unique grain patterns and is suitable for decorative purposes or projects emphasizing eco-friendly materials. Selecting the right bamboo depends on project requirements, balancing performance needs with visual appeal and environmental impact.
Engineered bamboo vs natural bamboo Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com