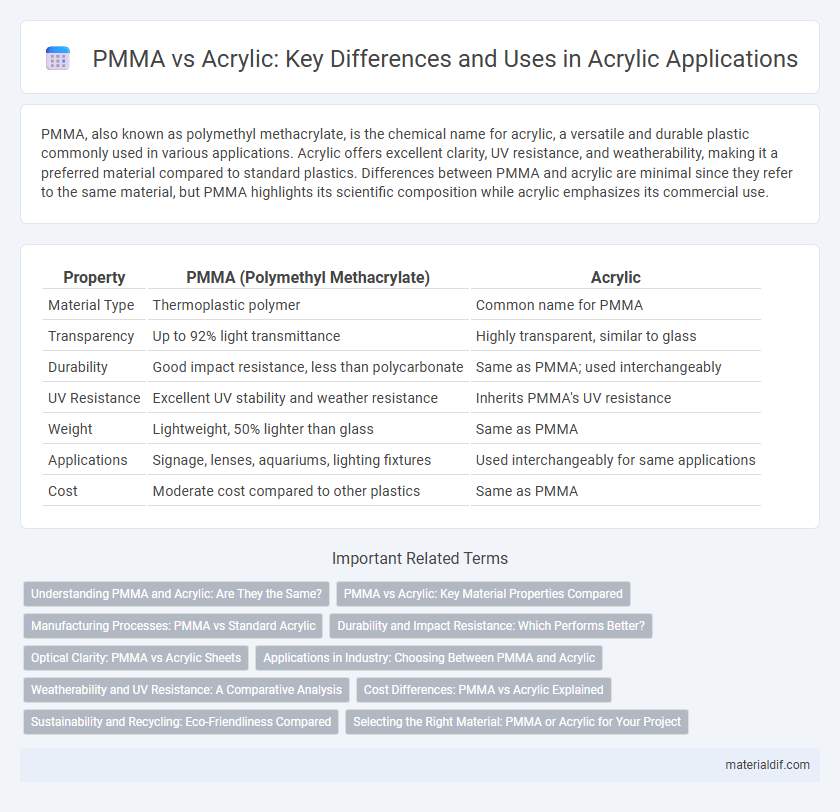
PMMA, also known as polymethyl methacrylate, is the chemical name for acrylic, a versatile and durable plastic commonly used in various applications. Acrylic offers excellent clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, making it a preferred material compared to standard plastics. Differences between PMMA and acrylic are minimal since they refer to the same material, but PMMA highlights its scientific composition while acrylic emphasizes its commercial use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Common name for PMMA |
| Transparency | Up to 92% light transmittance | Highly transparent, similar to glass |
| Durability | Good impact resistance, less than polycarbonate | Same as PMMA; used interchangeably |
| UV Resistance | Excellent UV stability and weather resistance | Inherits PMMA's UV resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight, 50% lighter than glass | Same as PMMA |
| Applications | Signage, lenses, aquariums, lighting fixtures | Used interchangeably for same applications |
| Cost | Moderate cost compared to other plastics | Same as PMMA |
Understanding PMMA and Acrylic: Are They the Same?
PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, is a specific type of acrylic known for its transparency, durability, and resistance to UV light, commonly used in windows and displays. Acrylic refers to a broader category of synthetic polymers including PMMA, but the term is often used interchangeably with PMMA in commercial contexts. Understanding that PMMA is a subset of acrylic helps clarify their relationship while highlighting PMMA's distinct chemical composition and properties.
PMMA vs Acrylic: Key Material Properties Compared
PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, is a type of acrylic known for its superior optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability compared to general acrylic materials. It offers higher tensile strength and better impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and transparency. While standard acrylic can vary in quality and properties, PMMA consistently provides enhanced performance characteristics critical for automotive, medical, and lighting industries.
Manufacturing Processes: PMMA vs Standard Acrylic
PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, is manufactured primarily through casting and extrusion processes, offering superior optical clarity and durability compared to standard acrylic produced via bulk polymerization. Casting PMMA involves pouring liquid monomer into molds, resulting in sheets with enhanced mechanical properties and minimal internal stress. Standard acrylic, often made through a continuous extrusion process, is cost-effective but typically exhibits lower clarity and greater susceptibility to environmental stress cracking.
Durability and Impact Resistance: Which Performs Better?
PMMA, commonly known as acrylic, offers excellent clarity and weather resistance but is more prone to cracking under high impact compared to other acrylic variants. Acrylic materials like polycarbonate surpass PMMA in impact resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring greater durability and toughness. Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting materials for environments exposed to mechanical stress or harsh conditions.
Optical Clarity: PMMA vs Acrylic Sheets
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) and Acrylic sheets both offer exceptional optical clarity, with light transmittance reaching up to 92%, making them ideal for applications requiring clear visibility. PMMA is often preferred due to its superior scratch resistance and better UV stability compared to generic acrylic sheets, ensuring long-lasting transparency. Optical quality differences become more pronounced in outdoor or high-exposure environments, where PMMA maintains clarity without yellowing or degrading.
Applications in Industry: Choosing Between PMMA and Acrylic
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) and acrylic are often used interchangeably in industry, but PMMA specifically refers to the chemical composition, providing superior optical clarity and weather resistance essential for automotive lighting and medical devices. Acrylic sheets, derived from PMMA, serve well in signage, displays, and architectural glazing due to their lightweight and impact resistance. Industries prioritize PMMA when transparency and UV stability are critical, while acrylic sheets are favored for cost-effective applications where durability and ease of fabrication matter.
Weatherability and UV Resistance: A Comparative Analysis
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) and Acrylic are often used interchangeably, yet PMMA specifically excels in weatherability and UV resistance due to its molecular structure that minimizes degradation under prolonged sun exposure. PMMA maintains clarity and mechanical properties longer than general acrylic variants, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as signage and glazing. UV-resistant grades of PMMA provide superior protection against yellowing and brittleness, ensuring durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Differences: PMMA vs Acrylic Explained
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) and acrylic are often used interchangeably, but PMMA is a specific type of acrylic material known for its durability and clarity. Cost differences arise because PMMA typically undergoes higher manufacturing standards, resulting in a higher price compared to general acrylic sheets. Choosing between PMMA and acrylic depends on application requirements, with PMMA offering better performance at a premium cost while generic acrylic presents a more budget-friendly alternative.
Sustainability and Recycling: Eco-Friendliness Compared
PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, and acrylic both refer to the same thermoplastic material widely used for its clarity and durability, with PMMA being the chemical name. From a sustainability perspective, PMMA is recyclable through processes like depolymerization, allowing monomers to be recovered and reused, thereby reducing waste and energy consumption. Acrylic's eco-friendliness is enhanced by its recyclability and relatively lower environmental impact during production compared to other plastics, making it a more sustainable choice for clear plastic applications.
Selecting the Right Material: PMMA or Acrylic for Your Project
Choosing between PMMA and acrylic depends on project requirements such as clarity, strength, and weather resistance. PMMA, also known as polymethyl methacrylate, offers superior optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor displays and lenses. Acrylic, being a lower-cost alternative, provides good durability and ease of fabrication for indoor applications where high impact resistance is less critical.
PMMA vs Acrylic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com