Acrylic lamination involves bonding a clear acrylic layer to a surface to enhance durability and clarity, providing a thicker and more protective barrier than acrylic coating. Acrylic coating is a thin liquid layer applied to surfaces for scratch resistance and UV protection, offering easier application but less impact resistance than lamination. Choosing between acrylic lamination and acrylic coating depends on the desired level of protection, aesthetic finish, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
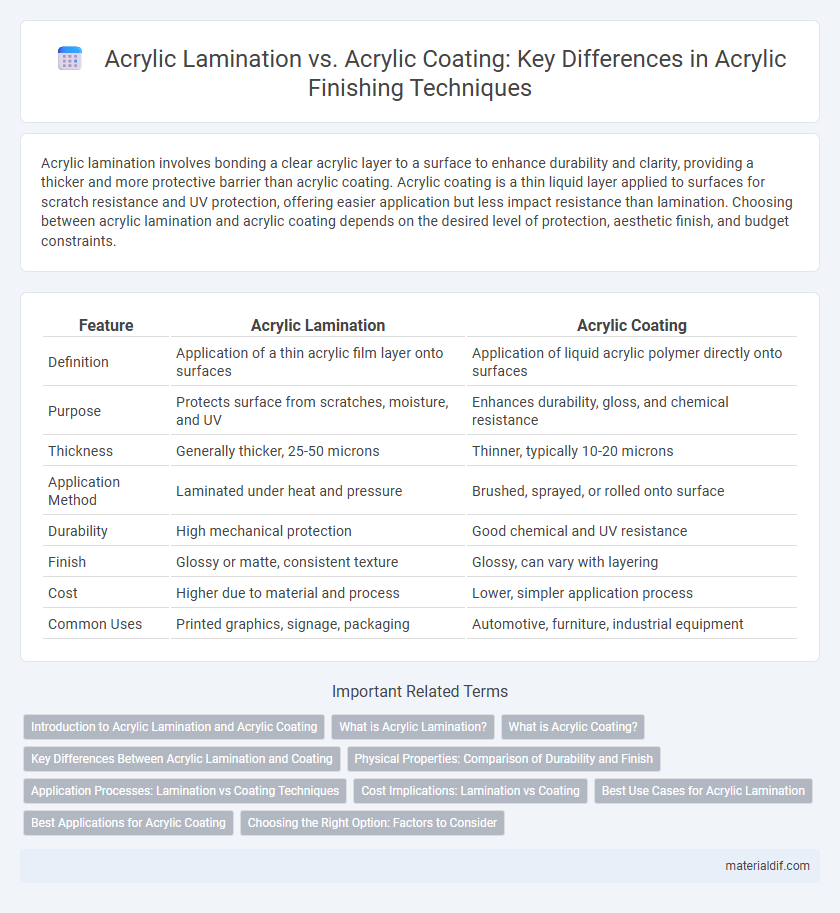
| Feature | Acrylic Lamination | Acrylic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Application of a thin acrylic film layer onto surfaces | Application of liquid acrylic polymer directly onto surfaces |
| Purpose | Protects surface from scratches, moisture, and UV | Enhances durability, gloss, and chemical resistance |
| Thickness | Generally thicker, 25-50 microns | Thinner, typically 10-20 microns |
| Application Method | Laminated under heat and pressure | Brushed, sprayed, or rolled onto surface |
| Durability | High mechanical protection | Good chemical and UV resistance |
| Finish | Glossy or matte, consistent texture | Glossy, can vary with layering |
| Cost | Higher due to material and process | Lower, simpler application process |
| Common Uses | Printed graphics, signage, packaging | Automotive, furniture, industrial equipment |
Introduction to Acrylic Lamination and Acrylic Coating
Acrylic lamination involves bonding acrylic sheets to surfaces for enhanced durability, impact resistance, and aesthetic appeal, commonly used in protective displays and signage. Acrylic coating refers to the application of a thin acrylic layer, providing surfaces with UV protection, scratch resistance, and moisture barrier properties. Both processes improve material longevity but differ in thickness, function, and application methods, with lamination focusing on structural reinforcement and coating emphasizing surface protection.
What is Acrylic Lamination?
Acrylic lamination involves bonding a thin acrylic film to a surface to enhance durability, UV resistance, and clarity, often used in signage and displays. This process provides a protective layer that resists scratches, moisture, and yellowing, extending the lifespan of printed materials. Unlike acrylic coating, which is a liquid application creating a thin protective surface, lamination results in a thicker, more robust shield with improved impact resistance.
What is Acrylic Coating?
Acrylic coating is a protective layer applied to surfaces to enhance durability, UV resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Unlike acrylic lamination, which involves bonding a plastic film to a substrate, acrylic coating forms a thin, transparent film through a liquid application process. This coating is commonly used in automotive finishes, signage, and architectural elements to prevent scratches, fading, and weathering.
Key Differences Between Acrylic Lamination and Coating
Acrylic lamination involves bonding a thin acrylic film onto a surface to provide enhanced durability and UV resistance, while acrylic coating applies a liquid acrylic layer directly onto the substrate, forming a protective and glossy finish. Lamination typically offers superior scratch resistance and thickness, making it ideal for high-traffic applications, whereas coating allows for more flexible application on irregular surfaces and easier touch-ups. Differences in application methods, thickness, durability, and visual effects distinctly separate acrylic lamination from acrylic coating in industrial and decorative uses.
Physical Properties: Comparison of Durability and Finish
Acrylic lamination offers superior durability with enhanced resistance to scratches, chemicals, and UV exposure compared to acrylic coating, making it ideal for high-traffic or outdoor applications. The lamination process provides a thicker, more robust protective layer that preserves the surface's clarity and gloss over time, while acrylic coating typically delivers a thinner finish that is more prone to wear and fading. Both finishes enhance aesthetic appeal, but lamination ensures longer-lasting protection and a consistently smooth, glossy surface.
Application Processes: Lamination vs Coating Techniques
Acrylic lamination involves bonding a clear acrylic film onto a substrate using heat and pressure to enhance durability and clarity, making it ideal for signage and protective surfaces. Acrylic coating entails applying a liquid acrylic polymer directly onto surfaces through spraying or brushing, providing a smooth, protective finish that resists UV damage and weathering. The lamination process offers a thicker, more impact-resistant layer, whereas acrylic coating emphasizes flexibility and ease of reapplication.
Cost Implications: Lamination vs Coating
Acrylic lamination typically incurs higher upfront costs due to the multi-layer application process and specialized equipment, while acrylic coating offers a more economical option with simpler application methods and lower material expenses. Over time, lamination provides superior durability and scratch resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs compared to acrylic coating. Budget considerations often favor acrylic coating for short-term projects, whereas lamination is a cost-effective investment for extended product longevity.
Best Use Cases for Acrylic Lamination
Acrylic lamination provides a durable, transparent protective layer ideal for preserving printed materials, photographs, and artwork, making it the best choice for high-traffic or frequently handled items. It enhances resistance to moisture, UV rays, and physical damage, ensuring longevity and vibrant color retention in documents or displays. Unlike acrylic coating, which is typically a thinner surface finish, acrylic lamination offers robust protection suitable for portable or outdoor applications requiring long-term preservation.
Best Applications for Acrylic Coating
Acrylic coating offers superior durability and UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as automotive finishes, signage, and architectural surfaces. Unlike acrylic lamination, acrylic coating provides a thin, protective layer that enhances gloss and scratch resistance without altering the substrate's texture. This makes acrylic coating the best choice for preserving the original appearance while delivering long-lasting protection.
Choosing the Right Option: Factors to Consider
Selecting between acrylic lamination and acrylic coating depends on factors such as durability, aesthetic requirements, and environmental exposure. Acrylic lamination provides a thicker, protective layer ideal for high-traffic surfaces needing impact resistance, while acrylic coating offers a thinner, more flexible finish suited for enhancing gloss and color vibrancy. Consider the substrate type, intended use, and maintenance demands to determine the most effective option for long-term performance and visual appeal.
Acrylic Lamination vs Acrylic Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com