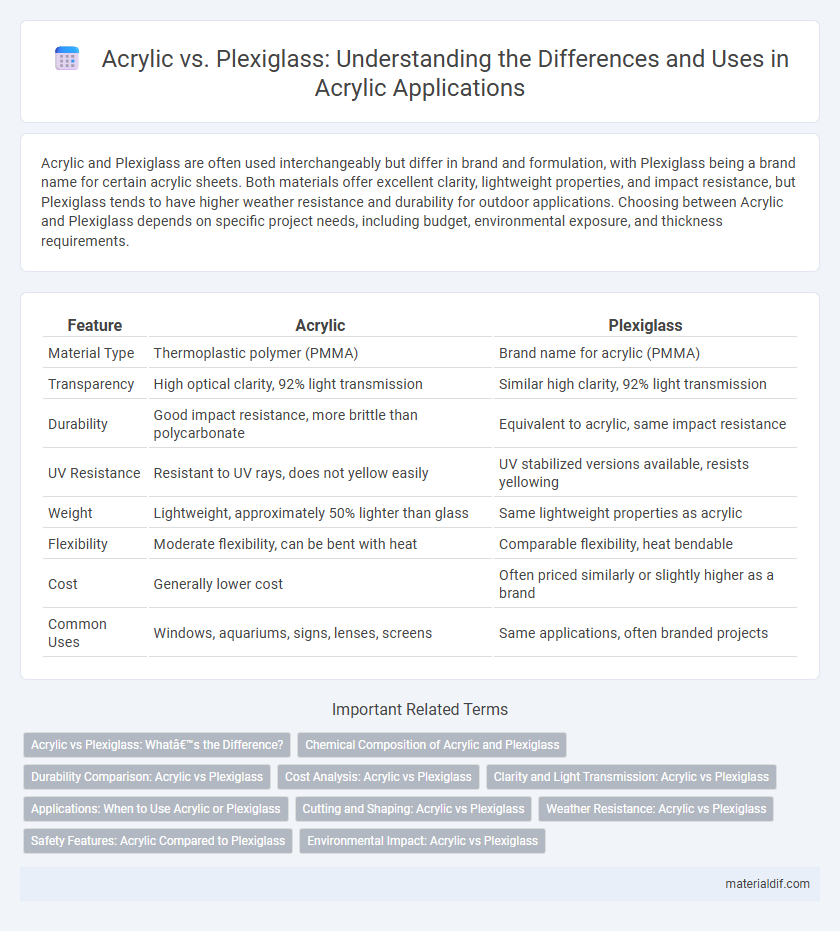
Acrylic and Plexiglass are often used interchangeably but differ in brand and formulation, with Plexiglass being a brand name for certain acrylic sheets. Both materials offer excellent clarity, lightweight properties, and impact resistance, but Plexiglass tends to have higher weather resistance and durability for outdoor applications. Choosing between Acrylic and Plexiglass depends on specific project needs, including budget, environmental exposure, and thickness requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acrylic | Plexiglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer (PMMA) | Brand name for acrylic (PMMA) |
| Transparency | High optical clarity, 92% light transmission | Similar high clarity, 92% light transmission |
| Durability | Good impact resistance, more brittle than polycarbonate | Equivalent to acrylic, same impact resistance |
| UV Resistance | Resistant to UV rays, does not yellow easily | UV stabilized versions available, resists yellowing |
| Weight | Lightweight, approximately 50% lighter than glass | Same lightweight properties as acrylic |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, can be bent with heat | Comparable flexibility, heat bendable |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Often priced similarly or slightly higher as a brand |
| Common Uses | Windows, aquariums, signs, lenses, screens | Same applications, often branded projects |
Acrylic vs Plexiglass: What’s the Difference?
Acrylic and Plexiglass are often used interchangeably, but Plexiglass is actually a brand name for acrylic sheets. Both materials share similar properties such as clarity, lightweight nature, and impact resistance, making them ideal for windows, displays, and signage. The primary difference lies in branding and pricing, with Plexiglass sometimes being slightly more expensive due to its brand recognition and quality assurances.
Chemical Composition of Acrylic and Plexiglass
Acrylic and Plexiglass share the same chemical composition, primarily polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), a transparent thermoplastic polymer known for its clarity and durability. Both materials are synthesized through polymerization of methyl methacrylate monomers, giving them similar physical properties and chemical resistance. Differences in brand formulations and manufacturing processes can slightly affect their strength and UV resistance, but chemically they remain nearly identical.
Durability Comparison: Acrylic vs Plexiglass
Acrylic and Plexiglass, often used interchangeably, are actually the same material, both made from polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), which offers excellent durability and resistance to impact compared to glass. This lightweight, shatter-resistant plastic maintains clarity and strength over time, making it highly suitable for applications requiring long-term durability and weather resistance. Its resistance to UV light and environmental factors ensures Plexiglass remains clear and structurally sound, outperforming many alternative transparent materials.
Cost Analysis: Acrylic vs Plexiglass
Acrylic and Plexiglass, both popular transparent thermoplastics, differ in cost primarily due to brand and quality variations, with Plexiglass often being a trademarked variant of acrylic. On average, acrylic sheets tend to be slightly more affordable, priced around $10 to $20 per square foot, while Plexiglass can range from $15 to $25 per square foot depending on thickness and clarity. Cost analysis should factor in not only the base price but also durability, UV resistance, and application-specific performance to determine the best value for projects requiring transparent plastic materials.
Clarity and Light Transmission: Acrylic vs Plexiglass
Acrylic and Plexiglass both offer superior clarity and high light transmission, typically around 92%. Acrylic sheets are known for their exceptional optical clarity and minimal yellowing over time, maintaining transparency better in UV-exposed environments. Plexiglass, a branded form of acrylic, matches these properties with excellent light transmission and clarity, making both materials ideal for applications requiring clear, bright visibility.
Applications: When to Use Acrylic or Plexiglass
Acrylic and Plexiglass are essentially the same material, both being clear, shatter-resistant alternatives to glass used in applications such as windows, displays, and protective barriers. Acrylic excels in outdoor applications due to its superior UV resistance and weather durability, while Plexiglass is commonly used in indoor signage, picture frames, and aquarium tanks where clarity and ease of shaping are important. Choosing between acrylic and Plexiglass depends on factors like exposure to sunlight, impact resistance requirements, and the need for precision cutting or polishing.
Cutting and Shaping: Acrylic vs Plexiglass
Acrylic and Plexiglass are essentially the same material, with Plexiglass being a brand name for acrylic sheets, sharing identical properties in cutting and shaping. Both materials can be easily cut with laser cutters, saws, and scored for clean edges, offering high precision in fabrication processes. Their thermoforming capabilities allow for bending and molding into complex shapes without cracking, making them ideal for custom designs and detailed projects.
Weather Resistance: Acrylic vs Plexiglass
Acrylic and Plexiglass are essentially the same material, both known for excellent weather resistance, making them ideal for outdoor applications. Acrylic resists UV rays and does not yellow or degrade when exposed to sunlight over time, maintaining clarity and strength. Plexiglass shares these properties, offering durable, weatherproof performance suitable for signage, windows, and protective barriers.
Safety Features: Acrylic Compared to Plexiglass
Acrylic and Plexiglass are essentially the same material, both being transparent thermoplastic sheets used as alternatives to glass, with "Plexiglass" being a popular brand name of acrylic. Acrylic offers excellent safety features due to its impact resistance, which is about 10-24 times greater than glass, reducing the risk of shattering into sharp pieces. This makes acrylic ideal for applications requiring durability and safety, such as protective barriers, windows, and displays.
Environmental Impact: Acrylic vs Plexiglass
Acrylic and Plexiglass, both derived from polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), have similar environmental footprints due to their non-biodegradable nature and production processes involving fossil fuels. Recycling options for acrylic products are limited compared to other plastics, resulting in longer degradation periods in landfills. Innovations in bio-based acrylic alternatives aim to reduce carbon emissions and environmental impact relative to conventional Plexiglass materials.
Acrylic vs Plexiglass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com