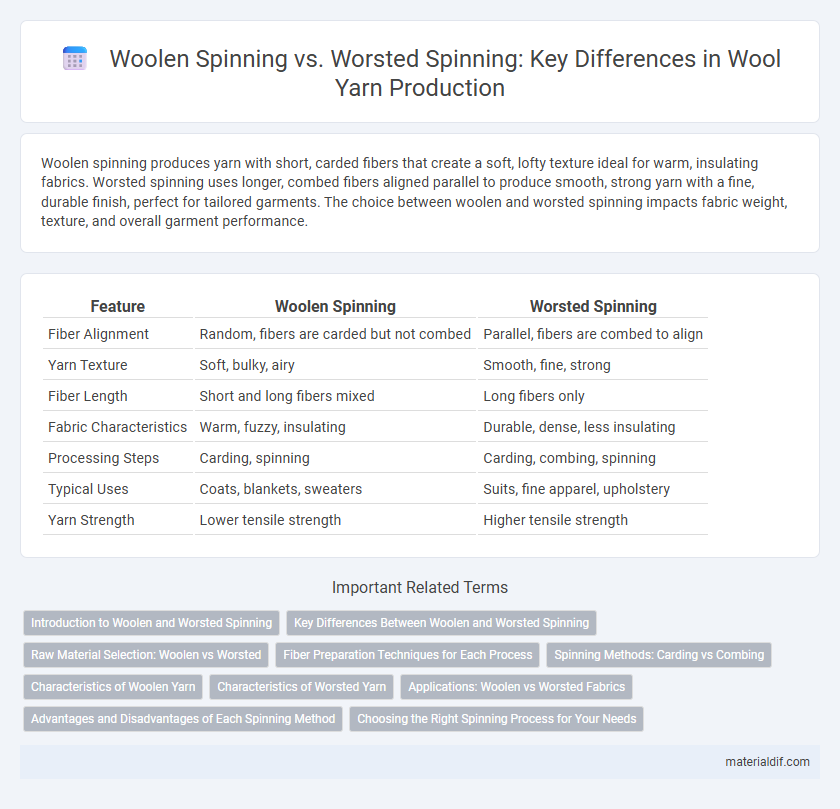
Woolen spinning produces yarn with short, carded fibers that create a soft, lofty texture ideal for warm, insulating fabrics. Worsted spinning uses longer, combed fibers aligned parallel to produce smooth, strong yarn with a fine, durable finish, perfect for tailored garments. The choice between woolen and worsted spinning impacts fabric weight, texture, and overall garment performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Woolen Spinning | Worsted Spinning |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Alignment | Random, fibers are carded but not combed | Parallel, fibers are combed to align |
| Yarn Texture | Soft, bulky, airy | Smooth, fine, strong |
| Fiber Length | Short and long fibers mixed | Long fibers only |
| Fabric Characteristics | Warm, fuzzy, insulating | Durable, dense, less insulating |
| Processing Steps | Carding, spinning | Carding, combing, spinning |
| Typical Uses | Coats, blankets, sweaters | Suits, fine apparel, upholstery |
| Yarn Strength | Lower tensile strength | Higher tensile strength |
Introduction to Woolen and Worsted Spinning
Woolen spinning produces yarn from carded fibers that are short and airy, resulting in a soft, warm, and bulky fabric ideal for insulation. Worsted spinning uses combed, longer fibers aligned parallel to create a smooth, fine, and strong yarn suited for durable, high-quality textiles. The fundamental difference lies in fiber preparation and alignment, directly impacting the texture and performance of the final woolen or worsted fabric.
Key Differences Between Woolen and Worsted Spinning
Woolen spinning produces yarns with shorter, carded fibers that create a soft, bulky, and insulating fabric, ideal for warm clothing. Worsted spinning uses longer, combed fibers aligned parallel, resulting in smooth, strong, and fine yarns suited for durable, lightweight textiles. The fundamental difference lies in fiber preparation and alignment, affecting texture, strength, and fabric density.
Raw Material Selection: Woolen vs Worsted
Woolen spinning uses shorter staple fibers from coarser wool grades, favoring raw materials with more natural crimp and lanolin content to create loftier yarns with better insulation. Worsted spinning requires long, fine staple fibers that have been carefully combed to align fibers parallel, resulting in smoother, stronger yarns ideal for fine suiting fabrics. The raw material selection for worsted focuses on top-quality merino or similar wools with minimal vegetable matter to ensure high yarn uniformity and durability.
Fiber Preparation Techniques for Each Process
Woolen spinning involves carding fibers to create a loose, airy web of fibers that retains natural crimps and generates a soft, bulky yarn ideal for insulation. Worsted spinning requires combing fibers to align them parallel and remove short fibers, producing a smooth, strong, and fine yarn with a sleek finish. The distinct fiber preparation techniques directly affect the texture, strength, and appearance of the final wool fabric in each spinning process.
Spinning Methods: Carding vs Combing
Woolen spinning uses carding to align fibers in a loose, airy formation, producing a soft, warm yarn with a fuzzy texture ideal for insulating garments. Worsted spinning employs combing to parallelize fibers tightly, removing short staples and creating smooth, strong yarn with a fine, sleek finish preferred for tailored clothing. The choice between carding and combing directly influences the yarn's fiber alignment, strength, and fabric texture, making spinning methods critical in wool processing.
Characteristics of Woolen Yarn
Woolen spinning produces yarn that is soft, bulky, and highly insulating due to the shorter, carded fibers being aligned in a random manner, creating air pockets that trap heat. Woolen yarn is characterized by its fuzzy texture and elasticity, making it ideal for warm, cozy fabrics like blankets and sweaters. Unlike worsted yarn, which is smooth and tightly spun with longer fibers aligned parallel, woolen yarn offers superior loft and resilience suited for thermal insulation.
Characteristics of Worsted Yarn
Worsted yarn is characterized by its smooth, strong, and fine texture, achieved through a combing process that aligns fibers parallel and removes short fibers, contrasting with the fuzzier appearance of woolen yarn. This spinning method produces a dense, tightly twisted yarn with higher tensile strength, making it ideal for durable, high-quality fabrics like suiting and fine knitwear. Worsted yarn's uniformity and reduced elasticity contribute to its crisp hand feel and excellent stitch definition in textiles.
Applications: Woolen vs Worsted Fabrics
Woolen spinning produces soft, warm, and fuzzy fabrics ideal for insulation in sweaters, blankets, and heavy outerwear, whereas worsted spinning creates smooth, tightly twisted fibers suited for durable, fine-textured garments like suits, trousers, and uniforms. Woolen fabrics excel in casual wear and cold-weather accessories due to their loft and warmth, while worsted fabrics are preferred in formal and tailored apparel for their strength and crisp appearance. The choice between woolen and worsted fabrics directly impacts garment performance, comfort, and style in various textile applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Spinning Method
Woolen spinning produces soft, bulky yarn with excellent insulation properties due to its short, carded fibers, ideal for warm, cozy fabrics but lacks smoothness and strength compared to worsted spinning. Worsted spinning aligns long fibers tightly, resulting in smooth, strong, and durable yarn suitable for fine, high-quality garments but offers less warmth and elasticity. The choice depends on desired fabric characteristics: woolen for comfort and warmth, worsted for durability and a polished appearance.
Choosing the Right Spinning Process for Your Needs
Woolen spinning produces soft, warm, and airy yarn by carding fibers into a loose, tangled mass ideal for cozy sweaters and insulating fabrics, while worsted spinning aligns fibers parallel for smooth, strong, and durable yarn suited to tailored garments and fine textiles. Selecting woolen or worsted spinning depends on the desired fabric characteristics, with woolen best for warmth and softness and worsted for strength and smoothness. Understanding fiber preparation, yarn texture, and end-use applications ensures the optimal spinning process matches your project requirements.
Woolen spinning vs Worsted spinning Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com