Wool fiber offers superior breathability and natural moisture-wicking properties compared to synthetic fibers, making it ideal for temperature regulation and comfort. It is also biodegradable and renewable, contributing to environmental sustainability, whereas synthetic fibers are petroleum-based and take much longer to decompose. Wool's inherent elasticity and durability enhance garment longevity, outperforming many synthetic alternatives in both performance and ecological impact.
Table of Comparison
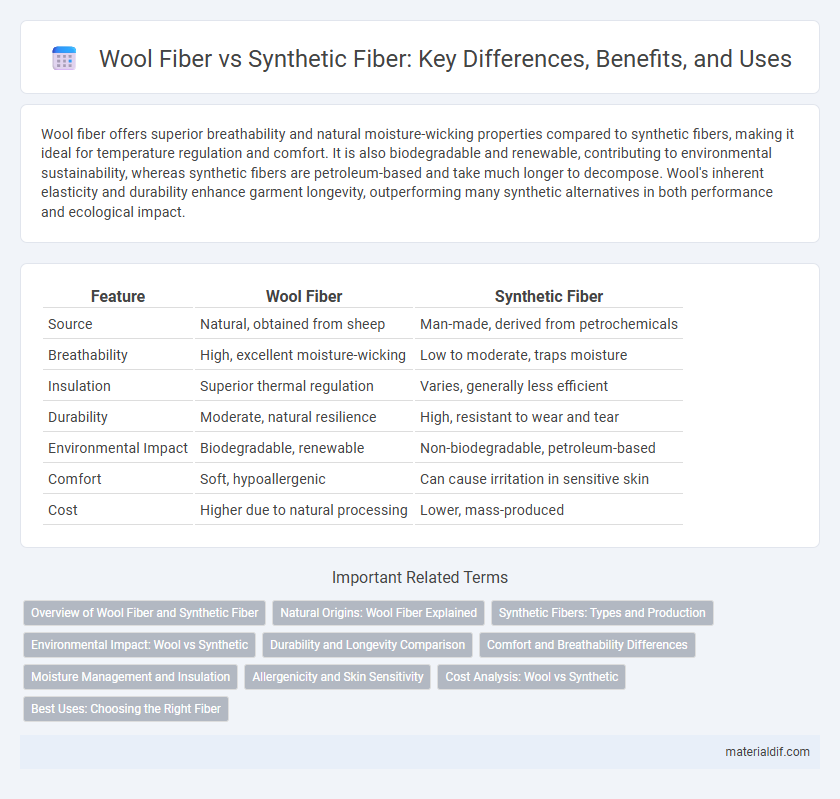
| Feature | Wool Fiber | Synthetic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, obtained from sheep | Man-made, derived from petrochemicals |
| Breathability | High, excellent moisture-wicking | Low to moderate, traps moisture |
| Insulation | Superior thermal regulation | Varies, generally less efficient |
| Durability | Moderate, natural resilience | High, resistant to wear and tear |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Comfort | Soft, hypoallergenic | Can cause irritation in sensitive skin |
| Cost | Higher due to natural processing | Lower, mass-produced |
Overview of Wool Fiber and Synthetic Fiber
Wool fiber, derived from the fleece of sheep, features natural crimp that enhances insulation and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for thermal regulation and comfort. Synthetic fibers, such as polyester and nylon, are man-made polymers engineered for durability, quick drying, and resistance to abrasion but often lack the breathability and biodegradable characteristics of wool. Wool fibers possess unique protein structures that enable elasticity and odor resistance, distinguishing them from the uniform molecular construction of synthetic fibers.
Natural Origins: Wool Fiber Explained
Wool fiber, derived from the fleece of sheep, boasts a natural origin that contributes to its superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to synthetic fibers made from petrochemicals. Its unique protein-based structure allows wool to regulate temperature effectively, making it ideal for both cold and warm climates. Unlike synthetic fibers, wool is biodegradable and renewable, highlighting its eco-friendly advantages in sustainable textile production.
Synthetic Fibers: Types and Production
Synthetic fibers, such as polyester, nylon, and acrylic, are produced through chemical processes using petrochemicals, offering high durability and resistance to moisture. These fibers are engineered via polymerization techniques like melt spinning and solution spinning, allowing precise control over fiber properties and consistency. Compared to natural wool fibers, synthetic fibers provide enhanced wrinkle resistance and faster drying times, making them popular in performance textiles and affordable fashion.
Environmental Impact: Wool vs Synthetic
Wool fiber is a renewable, biodegradable material that naturally decomposes, reducing landfill waste and minimizing environmental pollution. Synthetic fibers, commonly derived from petroleum, contribute to microplastic pollution and have a higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive production processes. The sustainable lifecycle of wool promotes soil health through sheep grazing management, while synthetic fibers persist in ecosystems, posing long-term environmental challenges.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Wool fiber exhibits superior durability compared to synthetic fibers due to its natural crimp and elasticity, which allows it to resist wear and maintain shape over time. Synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon tend to degrade faster with repeated washing and exposure to UV light, leading to fiber breakage and loss of integrity. The inherent resilience and moisture-wicking properties of wool contribute to its longer lifespan, making it a preferred choice for high-quality, long-lasting textiles.
Comfort and Breathability Differences
Wool fiber offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, maintaining thermal regulation by trapping heat while allowing air circulation, which enhances comfort in varying temperatures. Synthetic fibers, although durable and water-resistant, often lack the natural ability to absorb moisture, leading to decreased breathability and potential discomfort during extended wear. The crimped structure of wool fibers increases insulation and softness, providing a more comfortable fit compared to the often smoother, less flexible synthetic alternatives.
Moisture Management and Insulation
Wool fibers excel in moisture management by naturally absorbing up to 30% of their weight in moisture without feeling wet, maintaining breathability and comfort. Their unique crimp structure traps air efficiently, providing superior insulation even when damp. In contrast, synthetic fibers often repel moisture, leading to poor breathability and less effective insulation in wet conditions.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Wool fiber, derived from natural animal sources, typically exhibits lower allergenicity compared to synthetic fibers, as it contains natural lanolin that can soothe sensitive skin. Synthetic fibers often trap moisture and heat, increasing the risk of irritation and allergic reactions in individuals with skin sensitivities. Wool's breathability and moisture-wicking properties help regulate skin environment, reducing the likelihood of dermatitis and other skin issues.
Cost Analysis: Wool vs Synthetic
Wool fiber typically incurs higher upfront costs due to its natural harvesting and processing methods compared to synthetic fibers produced through chemical manufacturing. Over time, wool offers cost-efficiency through superior durability, moisture management, and insulation properties that extend garment lifespan and reduce replacement frequency. Synthetic fibers, while initially cheaper, may require more frequent replacement and possible higher environmental costs tied to their non-biodegradable nature and energy-intensive production.
Best Uses: Choosing the Right Fiber
Wool fiber excels in insulation, moisture-wicking, and natural breathability, making it ideal for outdoor clothing, cold-weather gear, and sustainable fashion. Synthetic fibers, such as polyester and nylon, offer superior durability, quick drying, and cost-effectiveness, which suit activewear, swimwear, and high-performance gear. Selecting the right fiber depends on the intended use, prioritizing wool for warmth and comfort and synthetics for resilience and moisture management.
Wool Fiber vs Synthetic Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com