Worsted and woolen fabrics differ primarily in their fiber preparation and texture, with worsted fibers being combed to align parallel and produce a smooth, dense fabric ideal for suits and formal wear. Woolen fabrics use shorter fibers that are carded rather than combed, resulting in a softer, fluffier material prized for warmth and insulation. Understanding these distinctions helps in choosing the right wool fabric based on the desired durability, texture, and warmth.
Table of Comparison
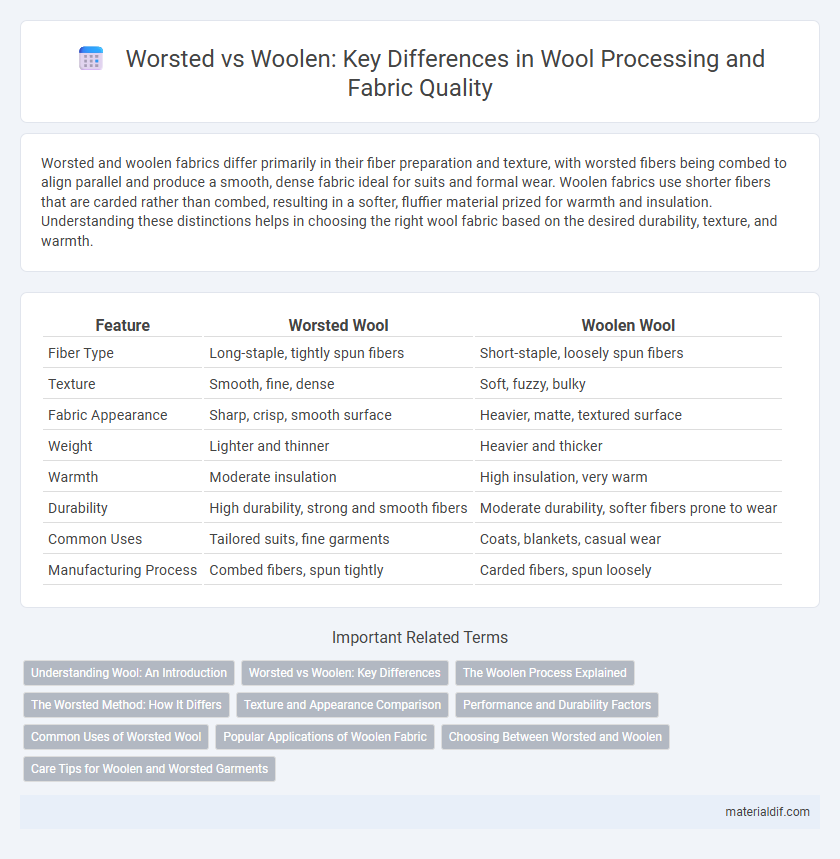
| Feature | Worsted Wool | Woolen Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Long-staple, tightly spun fibers | Short-staple, loosely spun fibers |
| Texture | Smooth, fine, dense | Soft, fuzzy, bulky |
| Fabric Appearance | Sharp, crisp, smooth surface | Heavier, matte, textured surface |
| Weight | Lighter and thinner | Heavier and thicker |
| Warmth | Moderate insulation | High insulation, very warm |
| Durability | High durability, strong and smooth fibers | Moderate durability, softer fibers prone to wear |
| Common Uses | Tailored suits, fine garments | Coats, blankets, casual wear |
| Manufacturing Process | Combed fibers, spun tightly | Carded fibers, spun loosely |
Understanding Wool: An Introduction
Worsted wool features tightly spun, long fibers that create a smooth, durable fabric ideal for tailored garments and formal wear. Woolen fabric, made from shorter, loosely spun fibers, offers a softer, warmer texture suited for casual clothing and insulation. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the appropriate wool type based on texture, durability, and end-use.
Worsted vs Woolen: Key Differences
Worsted and woolen fabrics differ primarily in fiber preparation and texture, with worsted yarn spun from long, combed fibers for a smooth, fine finish, while woolen yarn uses shorter, carded fibers creating a softer, bulkier texture. Worsted wool offers greater durability, strength, and a sleek appearance ideal for tailored garments, whereas woolen wool provides enhanced warmth and a fuzzy, insulating quality suited for cozy sweaters and blankets. The manufacturing process impacts breathability and weight, making worsted fabrics lighter and more breathable compared to the heavier, denser woolen fabrics.
The Woolen Process Explained
The woolen process involves carding wool fibers to create a soft, airy fabric with a fuzzy texture suitable for insulation and warmth. Unlike worsted wool, which uses combed fibers aligned parallel for a smooth, dense finish, woolen wool retains shorter, more randomly arranged fibers, enhancing loft and breathability. This process yields a fabric ideal for cozy garments and blankets that emphasize comfort over sharp tailoring.
The Worsted Method: How It Differs
The worsted method involves combing wool fibers to align them parallel before spinning, resulting in a smooth, fine yarn with high tensile strength, distinct from the woolen method where fibers are carded but remain more randomly arranged. This technique produces fabrics with a sleek finish, superior durability, and less bulk, making worsted wool ideal for tailored garments like suits and trousers. The key difference lies in fiber preparation--worsted's combing removes shorter fibers, enhancing softness and luster, whereas woolen fibers retain a fuzzy texture for warmth and insulation.
Texture and Appearance Comparison
Worsted wool features tightly spun fibers, producing a smooth, fine texture with a sleek appearance ideal for tailored garments. Woolen fabric, created from loosely spun fibers, offers a soft, fuzzy texture and a fuller, bulkier look, providing warmth and a casual style. The contrast in fiber processing results in worsted wool having a crisp, polished finish, while woolen material appears more textured and insulating.
Performance and Durability Factors
Worsted wool, made from long, tightly spun fibers, offers superior durability and a smoother finish, enhancing its resistance to wear and tear compared to woolen wool, which uses shorter, fuzzier fibers resulting in a softer but less durable fabric. Woolen wool excels in insulation and warmth due to its lofty, air-trapping fiber structure, but it is more prone to pilling and abrasion. Performance differences impact garment longevity and suitability, with worsted ideal for tailored, high-wear clothing, while woolen suits casual, insulating apparel.
Common Uses of Worsted Wool
Worsted wool, known for its smooth texture and durability, is commonly used in tailored garments such as suits, trousers, and formal wear due to its ability to hold sharp creases and resist wrinkles. This type of wool undergoes a unique spinning process that aligns fibers tightly, making it ideal for high-quality, long-lasting apparel. Its fine, dense fabric also finds frequent use in upholstery and heavy-duty textiles where strength and a polished appearance are essential.
Popular Applications of Woolen Fabric
Woolen fabric, known for its soft, airy texture and excellent insulation, is popularly used in sweaters, scarves, and blankets due to its warmth and comfort. Its loosely spun fibers trap air effectively, making it ideal for cozy winter garments and home textiles. Woolen fabric is also favored in casual outerwear and upholstery, providing durability alongside softness.
Choosing Between Worsted and Woolen
Choosing between worsted and woolen fabrics depends on the desired texture and durability; worsted wool is tightly spun and smooth, ideal for formal suits and garments requiring a sleek appearance, while woolen fabric is loosely spun and softer, offering warmth and a fuzzy texture suitable for casual wear and insulating layers. Worsted fibers create a stronger, more resilient fabric with higher durability and a refined finish, whereas woolen fibers trap more air, enhancing insulation properties and comfort in cold weather. Selecting the right type involves weighing the need for structure and durability against softness and warmth based on the specific use case.
Care Tips for Woolen and Worsted Garments
Woolen garments, made from carded wool fibers, require gentle hand washing in cold water or dry cleaning to maintain their loft and softness, avoiding high heat that can cause shrinking. Worsted fabrics, composed of tightly spun and combed wool fibers, benefit from careful machine washing on a wool or delicate cycle with mild detergent and air drying to preserve their smooth texture and durability. Proper storage in a cool, dry place with moth repellents helps extend the lifespan of both woolen and worsted wool items.
Worsted vs Woolen Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com