Wool-insulated garments provide superior breathability and natural moisture-wicking properties, keeping you warm and dry even in damp conditions. Synthetic-insulated clothing often excels in lightweight warmth and quick drying but can retain odors and lose insulating power when wet. Choosing wool insulation ensures eco-friendliness and long-lasting temperature regulation, while synthetic options offer affordability and performance in highly active scenarios.
Table of Comparison
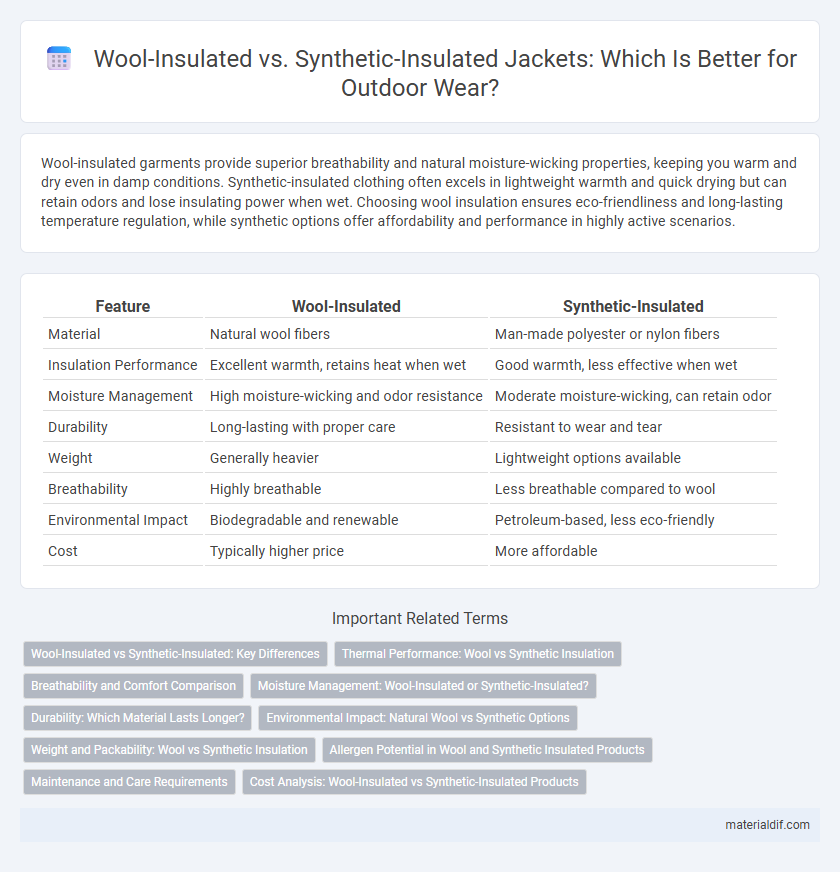
| Feature | Wool-Insulated | Synthetic-Insulated |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural wool fibers | Man-made polyester or nylon fibers |
| Insulation Performance | Excellent warmth, retains heat when wet | Good warmth, less effective when wet |
| Moisture Management | High moisture-wicking and odor resistance | Moderate moisture-wicking, can retain odor |
| Durability | Long-lasting with proper care | Resistant to wear and tear |
| Weight | Generally heavier | Lightweight options available |
| Breathability | Highly breathable | Less breathable compared to wool |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and renewable | Petroleum-based, less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Typically higher price | More affordable |
Wool-Insulated vs Synthetic-Insulated: Key Differences
Wool-insulated garments provide superior natural moisture-wicking and temperature regulation compared to synthetic-insulated alternatives, making them ideal for fluctuating weather conditions. Wool fibers are biodegradable and possess antimicrobial properties, reducing odor and environmental impact, whereas synthetic insulation often relies on petroleum-based materials and may retain odors. The resilience and compressibility of synthetic insulation typically offer lighter weight and faster drying times, but wool excels in breathability and sustainable sourcing.
Thermal Performance: Wool vs Synthetic Insulation
Wool insulation offers superior moisture-wicking properties and maintains thermal performance even when damp, making it highly effective for temperature regulation in varied conditions. Synthetic insulation typically provides quicker drying times and consistent warmth but may lose insulating efficiency when wet. Both materials excel in different environments, with wool favoring breathability and natural temperature control, while synthetic fibers often emphasize lightweight and water-resistant thermal retention.
Breathability and Comfort Comparison
Wool-insulated garments excel in breathability due to natural moisture-wicking properties, allowing sweat to evaporate and maintaining a comfortable body temperature. Synthetic insulation often traps heat and moisture, potentially causing discomfort during extended wear or high-intensity activities. The inherent elasticity and softness of wool fibers provide superior comfort by adapting to body movements and reducing skin irritation compared to most synthetic alternatives.
Moisture Management: Wool-Insulated or Synthetic-Insulated?
Wool-insulated garments excel in moisture management due to wool's natural ability to absorb up to 30% of its weight in moisture without feeling wet, which helps regulate body temperature and keeps skin dry. Synthetic-insulated materials often trap moisture, leading to reduced insulation performance and discomfort during extended wear in wet conditions. Wool's breathability and hygroscopic properties make it superior for maintaining dryness and comfort in moisture-rich environments.
Durability: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Wool-insulated materials exhibit superior durability due to their natural resilience, resistance to compression, and ability to maintain insulating properties despite repeated use and moisture exposure. Synthetic-insulated materials often degrade faster because fibers can break down, clump, or lose loft over time, especially when exposed to harsh conditions and frequent washing. Research shows wool insulation can maintain warmth and structural integrity for years longer than typical synthetic alternatives, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting performance.
Environmental Impact: Natural Wool vs Synthetic Options
Wool insulation offers a significantly lower environmental footprint due to its natural biodegradability and renewable sourcing from sheep, unlike synthetic insulation made from petrochemicals that contribute to plastic pollution and carbon emissions. Wool's production cycle is energy-efficient, sequesters carbon during sheep grazing, and avoids microplastic release during washing, which synthetic fibers often release into waterways. Choosing wool insulation supports sustainable farming practices and reduces landfill waste, making it a more eco-friendly alternative compared to synthetic materials derived from fossil fuels.
Weight and Packability: Wool vs Synthetic Insulation
Wool insulation offers moderate weight but excels in breathability and moisture management compared to synthetic insulation, which tends to be lighter and more compressible for superior packability. Synthetic fibers, such as PrimaLoft or polyester blends, are specifically engineered to provide high warmth-to-weight ratios and easily compress into small sizes, making them ideal for activities demanding minimal bulk. Wool's natural bulkiness may reduce packability but provides consistent thermal regulation, making it a reliable choice in damp or variable conditions.
Allergen Potential in Wool and Synthetic Insulated Products
Wool-insulated products tend to have a lower allergen potential compared to synthetic-insulated alternatives due to their natural antimicrobial and moisture-wicking properties that reduce bacterial growth and associated allergens. Synthetic insulation materials, often made from polyester fibers, can trap sweat and create an environment conducive to dust mites and mold, increasing allergen risks. Individuals with sensitive skin or allergies may benefit from wool-insulated products, which offer hypoallergenic benefits by naturally resisting common irritants and allergens.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Wool-insulated garments require gentle washing with mild detergents and air drying to maintain their natural fibers and insulation properties, avoiding heat that can cause shrinkage. In contrast, synthetic-insulated clothing typically allows for machine washing and quick drying, but repeated high-heat exposure can degrade the insulation's loft and performance. Proper care of wool insulation extends durability and moisture-wicking benefits, while synthetic insulation benefits from regular cleaning to prevent clumping and maintain breathability.
Cost Analysis: Wool-Insulated vs Synthetic-Insulated Products
Wool-insulated products generally have a higher upfront cost due to the natural fiber's sourcing and processing expenses, while synthetic-insulated items tend to be more affordable and mass-produced. Over time, wool insulation offers better durability and moisture-wicking properties, potentially reducing replacement frequency and long-term costs compared to synthetic alternatives. Consumers should weigh initial price differences against lifespan and performance benefits when evaluating wool-insulated versus synthetic-insulated options.
Wool-insulated vs Synthetic-insulated Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com