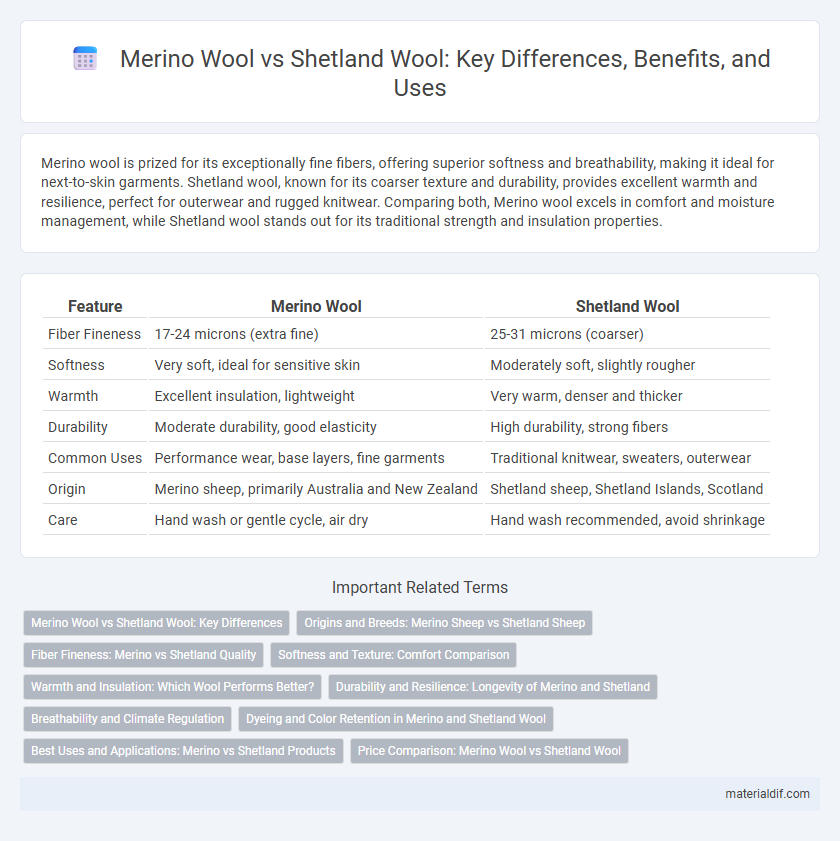
Merino wool is prized for its exceptionally fine fibers, offering superior softness and breathability, making it ideal for next-to-skin garments. Shetland wool, known for its coarser texture and durability, provides excellent warmth and resilience, perfect for outerwear and rugged knitwear. Comparing both, Merino wool excels in comfort and moisture management, while Shetland wool stands out for its traditional strength and insulation properties.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Merino Wool | Shetland Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Fineness | 17-24 microns (extra fine) | 25-31 microns (coarser) |
| Softness | Very soft, ideal for sensitive skin | Moderately soft, slightly rougher |
| Warmth | Excellent insulation, lightweight | Very warm, denser and thicker |
| Durability | Moderate durability, good elasticity | High durability, strong fibers |
| Common Uses | Performance wear, base layers, fine garments | Traditional knitwear, sweaters, outerwear |
| Origin | Merino sheep, primarily Australia and New Zealand | Shetland sheep, Shetland Islands, Scotland |
| Care | Hand wash or gentle cycle, air dry | Hand wash recommended, avoid shrinkage |
Merino Wool vs Shetland Wool: Key Differences
Merino wool is renowned for its exceptional softness, fine fibers measuring 17-24 microns, and superior moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for next-to-skin garments. Shetland wool, coarser with fibers around 30-35 microns, offers greater durability and insulation, often used in traditional knitwear and outerwear. The key differences lie in fiber fineness, softness, and use cases, with Merino suited for comfort and Shetland for rugged warmth.
Origins and Breeds: Merino Sheep vs Shetland Sheep
Merino wool originates from Merino sheep, primarily found in Spain and Australia, known for their fine, soft fibers that make high-quality, lightweight garments. Shetland wool comes from Shetland sheep native to the Shetland Islands of Scotland, prized for their coarser, warmer fibers used in durable knitwear like traditional Fair Isle patterns. The distinct breeding environments influence fiber texture, with Merino producing finer, smoother wool and Shetland yielding hardy, insulating wool ideal for harsh climates.
Fiber Fineness: Merino vs Shetland Quality
Merino wool is renowned for its exceptional fiber fineness, typically ranging from 15 to 24 microns, making it incredibly soft and suitable for next-to-skin garments. In comparison, Shetland wool fibers measure coarser, generally between 28 to 38 microns, which contributes to its durability and warmth but results in a rougher texture. The finer fiber diameter of Merino wool enhances breathability and moisture-wicking properties, while Shetland wool excels in resilience and insulation for outerwear.
Softness and Texture: Comfort Comparison
Merino wool is highly prized for its exceptional softness and fine fiber diameter, typically ranging from 18 to 24 microns, which makes it incredibly comfortable and gentle against the skin. In contrast, Shetland wool is coarser, with fiber diameters often above 30 microns, providing a more rugged texture that is durable but less soft. As a result, Merino wool is preferred for garments requiring a softer touch and greater comfort, while Shetland wool excels in warmth and durability with a distinctive, textured feel.
Warmth and Insulation: Which Wool Performs Better?
Merino wool excels in warmth and insulation due to its fine fibers that trap heat efficiently while remaining breathable, making it ideal for active wear in cold conditions. Shetland wool, with its coarser and thicker fibers, provides superior insulation and wind resistance, offering robust warmth for more static cold environments. When comparing thermal performance, Merino wool is preferred for moisture-wicking warmth, whereas Shetland wool delivers heavier insulation suitable for rugged outdoor use.
Durability and Resilience: Longevity of Merino and Shetland
Merino wool is renowned for its fine fibers, offering superior softness while maintaining excellent durability, making it ideal for garments requiring long-lasting comfort. Shetland wool features coarser and denser fibers, providing exceptional resilience and robustness suited for heavy-duty wear and outdoor activities. The longevity of Merino wool is enhanced by its natural elasticity that resists wear and tear, whereas Shetland wool's strength and thicker structure contribute to its extended lifespan in rugged conditions.
Breathability and Climate Regulation
Merino wool offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for regulating body temperature in a wide range of climates. Shetland wool, while durable and insulating, is denser and less effective in moisture management, which can lead to reduced breathability. The fine fibers of Merino wool enhance airflow and comfort, providing better climate regulation compared to the coarser Shetland wool.
Dyeing and Color Retention in Merino and Shetland Wool
Merino wool exhibits superior dye absorption due to its fine, smooth fibers, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting color retention ideal for high-quality garments. In contrast, Shetland wool's coarser and more textured fibers absorb dyes less evenly, leading to a more rustic, muted appearance but with durable color that withstands outdoor wear. Both wools maintain color integrity over time, but Merino's finer fiber structure enhances dye uptake and brilliance, while Shetland's natural resilience ensures color durability in rugged conditions.
Best Uses and Applications: Merino vs Shetland Products
Merino wool excels in high-performance activewear and fine knitwear due to its softness, moisture-wicking properties, and temperature regulation, making it ideal for base layers and outdoor apparel. Shetland wool, known for its durability and coarser texture, suits rugged outerwear, traditional knitwear, and heavy-duty blankets designed for warmth and longevity. Choosing between Merino and Shetland wool depends on whether the application prioritizes comfort and breathability or durability and insulation.
Price Comparison: Merino Wool vs Shetland Wool
Merino wool commands a higher price than Shetland wool due to its finer fibers and superior softness, making it a premium choice for luxury garments. Shetland wool is more affordable and valued for its durability and warmth, often favored in traditional outerwear and knitwear. Price variations also reflect differences in production scale, with Merino sourced from large-scale farms primarily in Australia and New Zealand, while Shetland wool originates from smaller, heritage-focused farms in Scotland.
Merino wool vs Shetland wool Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com