Wool is prized for its durability, moisture-wicking properties, and natural elasticity, making it ideal for cold weather garments. Alpaca fibers, though softer and hypoallergenic, lack the same elasticity and are more susceptible to pilling over time. Comparing insulation, alpaca tends to provide warmer, lightweight layers, while wool offers greater resilience and moisture management, perfect for active wear.
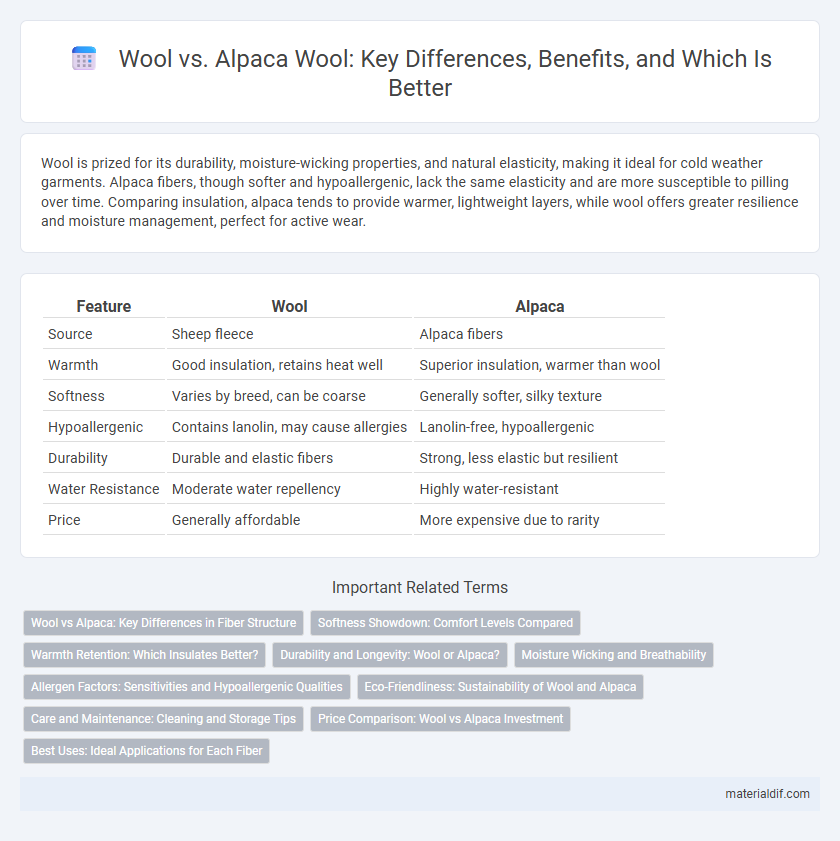
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wool | Alpaca |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Sheep fleece | Alpaca fibers |
| Warmth | Good insulation, retains heat well | Superior insulation, warmer than wool |
| Softness | Varies by breed, can be coarse | Generally softer, silky texture |
| Hypoallergenic | Contains lanolin, may cause allergies | Lanolin-free, hypoallergenic |
| Durability | Durable and elastic fibers | Strong, less elastic but resilient |
| Water Resistance | Moderate water repellency | Highly water-resistant |
| Price | Generally affordable | More expensive due to rarity |
Wool vs Alpaca: Key Differences in Fiber Structure
Wool fibers are characterized by their scaly surface and crimped structure, which provides elasticity and warmth, while alpaca fibers are smoother with fewer scales, resulting in a silkier texture and less itchiness. Wool tends to be more resilient and moisture-wicking, making it suitable for activewear, whereas alpaca fiber offers superior insulation and is hypoallergenic due to the absence of lanolin. The diameter of alpaca fibers generally ranges from 18 to 25 microns, finer than many wool fibers, contributing to its softness and lightweight properties.
Softness Showdown: Comfort Levels Compared
Wool and alpaca fibers differ significantly in softness, with alpaca known for its ultra-fine, silky texture that offers superior comfort against the skin. Wool, particularly fine merino varieties, provides excellent warmth and breathability but can sometimes feel slightly coarse to sensitive skin. The natural hypoallergenic properties of alpaca make it a preferred choice for those seeking maximum softness and irritation-free wear in luxury textiles.
Warmth Retention: Which Insulates Better?
Wool provides excellent warmth retention due to its natural crimp, which traps air and creates effective insulation against cold temperatures. Alpaca fibers are hollow, offering superior thermal insulation by trapping more heat while remaining lightweight and breathable. While wool excels in moisture-wicking, alpaca often outperforms in warmth-to-weight ratio, making it a preferred choice for extreme cold conditions.
Durability and Longevity: Wool or Alpaca?
Wool is renowned for its exceptional durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-traffic garments and long-term use. Alpaca fibers, although softer and lighter, have a slightly lower durability due to their finer fiber structure but offer impressive longevity when properly cared for. Choosing between wool and alpaca depends on the balance between durability needs and desired softness in textile applications.
Moisture Wicking and Breathability
Wool excels in moisture-wicking due to its natural ability to absorb up to 30% of its weight in moisture without feeling wet, keeping skin dry during physical activities. Alpaca fibers offer superior thermal insulation but have less breathability and moisture-wicking capability compared to wool, making them less effective in high-humidity or sweat-intensive conditions. Wool's open fiber structure promotes better airflow and quicker drying, enhancing comfort and temperature regulation in various climates.
Allergen Factors: Sensitivities and Hypoallergenic Qualities
Wool often triggers allergic reactions due to lanolin content and its coarse fibers, which can irritate sensitive skin, whereas alpaca fiber is naturally hypoallergenic, lacking lanolin and possessing smoother, finer strands that reduce irritation risks. People with wool allergies typically tolerate alpaca products better, benefiting from its softness and breathability. Medical studies highlight alpaca's suitability for those with sensitive skin conditions, making it a preferred choice for hypoallergenic textiles.
Eco-Friendliness: Sustainability of Wool and Alpaca
Wool and alpaca fibers both offer sustainable textile options, with wool being biodegradable and renewable through sheep shearing, while alpaca production has a low environmental footprint due to the animals' efficient grazing and minimal water requirements. Alpacas produce less methane compared to sheep, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions in wool versus alpaca comparisons. Both fibers support eco-friendly fashion, but alpaca's durability and hypoallergenic properties combined with sustainable farming practices elevate its status in environmentally conscious markets.
Care and Maintenance: Cleaning and Storage Tips
Wool fibers require gentle cleaning with mild detergent and cold water, avoiding high heat to prevent shrinking, while alpaca fibers need even more delicate handling to maintain softness and avoid felting. Proper storage for both materials involves keeping them in breathable containers away from direct sunlight and moisture to prevent mold and moth damage. Using cedar blocks or lavender sachets can naturally deter pests and preserve the quality of wool and alpaca garments over time.
Price Comparison: Wool vs Alpaca Investment
Wool typically costs less than alpaca fiber due to its widespread availability and established supply chains, making it a more budget-friendly investment for textile production. Alpaca fleece commands higher prices because of its limited supply, softness, and hypoallergenic properties, attracting premium markets and justifying the increased cost. Investing in alpaca offers greater potential for luxury product differentiation, whereas wool provides cost efficiency for mass-market applications.
Best Uses: Ideal Applications for Each Fiber
Wool excels in insulation and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for outdoor clothing, blankets, and performance wear designed for cold and wet conditions. Alpaca fibers are prized for their softness, hypoallergenic qualities, and lightweight warmth, which suits luxury garments, scarves, and accessories worn close to the skin. Each fiber's unique thermal regulation and texture determine its best applications, with wool favored for durability and alpaca preferred for comfort and fine textiles.
Wool vs Alpaca Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com