Shoddy wool is made from recycled fibers that are often tangled and weaker, resulting in a coarser texture and lower durability compared to carded wool. Carded wool undergoes a process that aligns fibers, producing a smoother, stronger, and more uniform material ideal for high-quality textiles. Choosing carded wool enhances the softness and longevity of woolen products, making it a preferred choice for premium pet bedding and clothing.
Table of Comparison
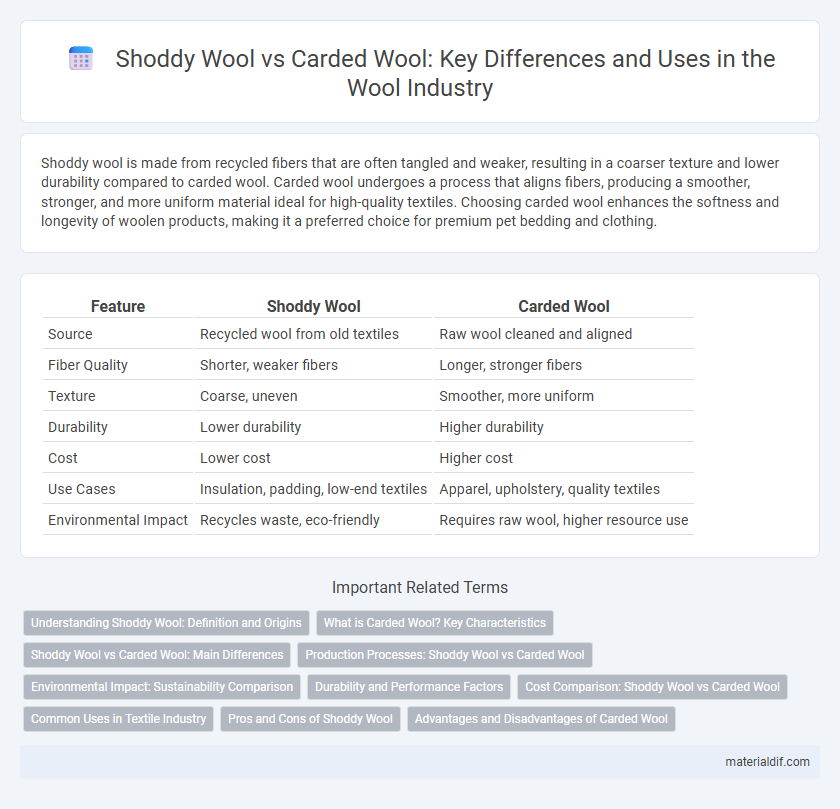
| Feature | Shoddy Wool | Carded Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recycled wool from old textiles | Raw wool cleaned and aligned |
| Fiber Quality | Shorter, weaker fibers | Longer, stronger fibers |
| Texture | Coarse, uneven | Smoother, more uniform |
| Durability | Lower durability | Higher durability |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Use Cases | Insulation, padding, low-end textiles | Apparel, upholstery, quality textiles |
| Environmental Impact | Recycles waste, eco-friendly | Requires raw wool, higher resource use |
Understanding Shoddy Wool: Definition and Origins
Shoddy wool is reclaimed fiber produced by shredding and reprocessing old wool garments and fabric waste, offering a sustainable alternative to virgin wool. Originating from the textile recycling industry, shoddy wool blends shorter fibers and impurities, resulting in a lower-quality but cost-effective material. Unlike carded wool, which is made from fresh wool fibers aligned through the carding process for consistency and strength, shoddy wool's reclaimed nature affects its durability and texture.
What is Carded Wool? Key Characteristics
Carded wool is processed by brushing raw wool fibers to remove dirt and short fibers, aligning them into a loose web. This method increases fiber uniformity and creates a soft, airy texture ideal for spinning fine yarns. Unlike shoddy wool, which is recycled from old textiles, carded wool is fresh fiber, resulting in higher quality, stronger fabric production.
Shoddy Wool vs Carded Wool: Main Differences
Shoddy wool is recycled from used woolen products, often containing shorter fibers and impurities, resulting in a coarser texture compared to carded wool. Carded wool undergoes a cleaning and disentangling process that aligns fibers, producing a smoother, more uniform material ideal for high-quality textiles. The main differences lie in fiber length, texture, and purity, with shoddy wool being more economical and carded wool preferred for durability and finish.
Production Processes: Shoddy Wool vs Carded Wool
Shoddy wool is produced by recycling old wool garments through shredding and re-spinning, resulting in fibers that are shorter and less uniform. Carded wool, however, undergoes a carding process where fibers are cleaned, disentangled, and aligned, creating a smoother and more consistent texture ideal for higher quality textiles. The production of carded wool involves careful mechanical treatment to maintain fiber length and strength, contrasting with the more fragmented structure found in shoddy wool.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Comparison
Shoddy wool, made from recycled fibers, significantly reduces waste and decreases the demand for new raw wool, minimizing environmental impact through lowered resource consumption and carbon emissions. Carded wool, produced from raw fleece, requires more water, energy, and chemical use during processing, resulting in a higher ecological footprint compared to shoddy wool. Choosing shoddy wool supports circular economy principles and offers a more sustainable alternative by repurposing existing materials and reducing environmental strain.
Durability and Performance Factors
Shoddy wool, made from recycled fibers, generally exhibits lower durability due to shorter fiber lengths and weaker fiber bonds, resulting in reduced tensile strength and faster wear. Carded wool consists of longer, aligned fibers, enhancing its resilience, elasticity, and overall performance for long-term use. The difference in fiber quality significantly impacts fabric longevity, with carded wool preferred for garments requiring sustained durability and shape retention.
Cost Comparison: Shoddy Wool vs Carded Wool
Shoddy wool is significantly cheaper than carded wool due to its source from recycled fibers, reducing raw material costs. Carded wool undergoes a more intensive cleaning and aligning process, increasing production expenses and retail price. Choosing shoddy wool offers cost savings but may compromise fiber quality and durability compared to carded wool.
Common Uses in Textile Industry
Shoddy wool, made from recycled fibers, is commonly used in insulation, upholstery, and low-cost blankets due to its affordability and lower quality. Carded wool, processed to align fibers, is preferred for producing durable fabrics, sweaters, and high-quality yarns in the textile industry. The choice between shoddy and carded wool depends on the desired strength, texture, and end-use application of the wool products.
Pros and Cons of Shoddy Wool
Shoddy wool, made from recycled or shredded wool fibers, offers significant cost savings compared to carded wool but often sacrifices durability and fiber length resulting in lower strength and quality. It is ideal for applications such as insulation or stuffing where softness is less critical, yet it performs poorly in textiles requiring resilience or fine finishes. While shoddy wool supports sustainability by reusing waste materials, its inconsistent fiber properties limit its use in high-end garment production.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Carded Wool
Carded wool offers advantages such as a more uniform fiber alignment and improved fabric strength compared to shoddy wool, resulting in higher-quality textiles suitable for garments and upholstery. The carding process removes impurities and short fibers, enhancing the wool's appearance and durability, but it is less environmentally friendly due to higher energy consumption and processing costs. Despite these disadvantages, carded wool provides superior insulation and softness, making it preferable for premium wool products over the recycled fuzz found in shoddy wool.
Shoddy wool vs Carded wool Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com