Wool shrinkage occurs when the fibers contract due to exposure to heat, moisture, or agitation, causing the garment to become smaller and denser. In contrast, wool stretch involves the fibers elongating temporarily under tension without permanent deformation, allowing the fabric to regain its original shape after the strain is removed. Understanding the difference between wool shrinkage and stretch is essential for proper garment care and maintaining durability.
Table of Comparison
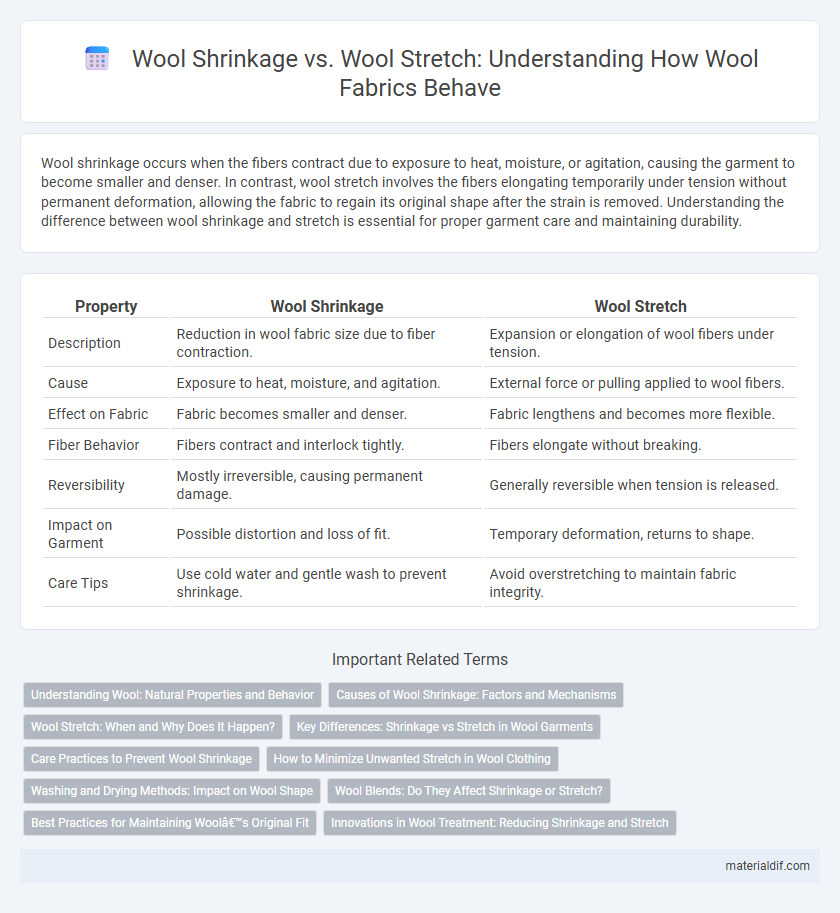
| Property | Wool Shrinkage | Wool Stretch |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Reduction in wool fabric size due to fiber contraction. | Expansion or elongation of wool fibers under tension. |
| Cause | Exposure to heat, moisture, and agitation. | External force or pulling applied to wool fibers. |
| Effect on Fabric | Fabric becomes smaller and denser. | Fabric lengthens and becomes more flexible. |
| Fiber Behavior | Fibers contract and interlock tightly. | Fibers elongate without breaking. |
| Reversibility | Mostly irreversible, causing permanent damage. | Generally reversible when tension is released. |
| Impact on Garment | Possible distortion and loss of fit. | Temporary deformation, returns to shape. |
| Care Tips | Use cold water and gentle wash to prevent shrinkage. | Avoid overstretching to maintain fabric integrity. |
Understanding Wool: Natural Properties and Behavior
Wool exhibits unique natural properties characterized by its ability to both shrink and stretch due to the structure of its protein fibers. Shrinkage occurs primarily when wool fibers are exposed to heat, moisture, and agitation, causing the scales on the fibers to interlock tightly in a process known as felting. Conversely, wool has inherent elasticity that allows it to stretch up to 30% without losing shape, a key factor in its durability and comfort in garments.
Causes of Wool Shrinkage: Factors and Mechanisms
Wool shrinkage primarily results from the fiber's unique scaly outer layer, which interlocks when exposed to moisture, heat, and agitation during washing, causing the fabric to contract. Factors such as fiber length, wool type (e.g., Merino vs. coarse wool), and washing conditions critically influence the extent of shrinkage. Wool stretch occurs when fibers realign under tension, but it is generally reversible, whereas shrinkage involves permanent structural changes due to fiber felting and tightening of the wool scales.
Wool Stretch: When and Why Does It Happen?
Wool stretch occurs primarily due to the natural elasticity of wool fibers, which allows them to elongate under tension and return to their original shape when the tension is released. This phenomenon is common during wear or improper drying methods, where moisture and heat soften the fibers, causing them to relax and stretch beyond their normal length. Understanding wool stretch is essential for garment care, as avoiding excessive stretching helps maintain the fabric's shape, durability, and texture over time.
Key Differences: Shrinkage vs Stretch in Wool Garments
Wool shrinkage occurs when wool fibers contract due to exposure to heat, moisture, and agitation, causing garments to become smaller and denser. In contrast, wool stretch results from the natural elasticity of wool fibers, allowing garments to expand slightly under tension without losing shape. Understanding these key differences helps in proper wool garment care by preventing unwanted size changes and maintaining fabric integrity.
Care Practices to Prevent Wool Shrinkage
Proper care practices to prevent wool shrinkage include washing wool garments in cold water with mild detergent designed for delicate fibers to maintain their original size and shape. Avoiding high heat during drying by air drying flat on a clean towel helps prevent the wool fibers from contracting and shrinking. Additionally, gentle handling and avoiding agitation in washing machines minimize fiber stress, preserving the wool's natural elasticity and preventing both shrinkage and unwanted stretch.
How to Minimize Unwanted Stretch in Wool Clothing
Wool shrinkage occurs when fibers contract due to heat, moisture, or agitation, while wool stretch results from the fibers' natural elasticity being pulled beyond their limit. Minimizing unwanted stretch in wool clothing involves proper laundering techniques such as washing in cold water, using gentle cycles, and laying garments flat to dry. Avoid hanging wet wool items and excessive stretching during wear to help maintain their original shape and fit.
Washing and Drying Methods: Impact on Wool Shape
Washing wool in cold water and using gentle detergent minimizes shrinkage by preserving the fiber structure, while hot water causes the scales on wool fibers to interlock, leading to felting and shrinkage. Air drying flat is essential to maintain the wool's original shape, as tumble drying or hanging can stretch and distort the garment. Proper laundering techniques ensure wool retains its size and elasticity, preventing irreversible damage to wool products.
Wool Blends: Do They Affect Shrinkage or Stretch?
Wool blends significantly influence shrinkage and stretch characteristics, with synthetic fibers like polyester reducing shrinkage by enhancing fabric stability. Blends containing elastane improve stretchability, making garments more flexible and resistant to deformation. Optimal wool blend ratios balance natural wool's warmth and softness with durability and shape retention, minimizing unwanted shrinkage while allowing controlled stretch.
Best Practices for Maintaining Wool’s Original Fit
Wool shrinkage occurs due to the fiber scales locking together when exposed to heat and moisture, while wool stretch results from fiber elongation under tension. To maintain wool's original fit, wash items in cold water, use gentle detergents, and avoid excessive agitation or heat during drying by air-drying flat. Storing wool garments properly on padded hangers or folded prevents distortion and preserves shape over time.
Innovations in Wool Treatment: Reducing Shrinkage and Stretch
Innovations in wool treatment have significantly reduced shrinkage and stretch by incorporating enzyme-based processes and advanced fiber coatings that stabilize the wool's natural scales. Nanotechnology and plasma treatments enhance fiber resilience, maintaining the garment's shape and size after multiple washes. These breakthroughs improve fabric durability while preserving wool's softness and breathability, redefining performance standards in wool apparel.
Wool Shrinkage vs Wool Stretch Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com