Wenge wood is known for its deep, dark brown to black coloration with striking grain patterns, making it a bold choice for furniture and flooring. Walnut features a rich, warm brown tone with a smooth, fine grain that ages beautifully and offers versatile design options. Both woods are durable and dense, but wenge tends to be harder and more resistant to wear, while walnut is easier to work with and finish.
Table of Comparison
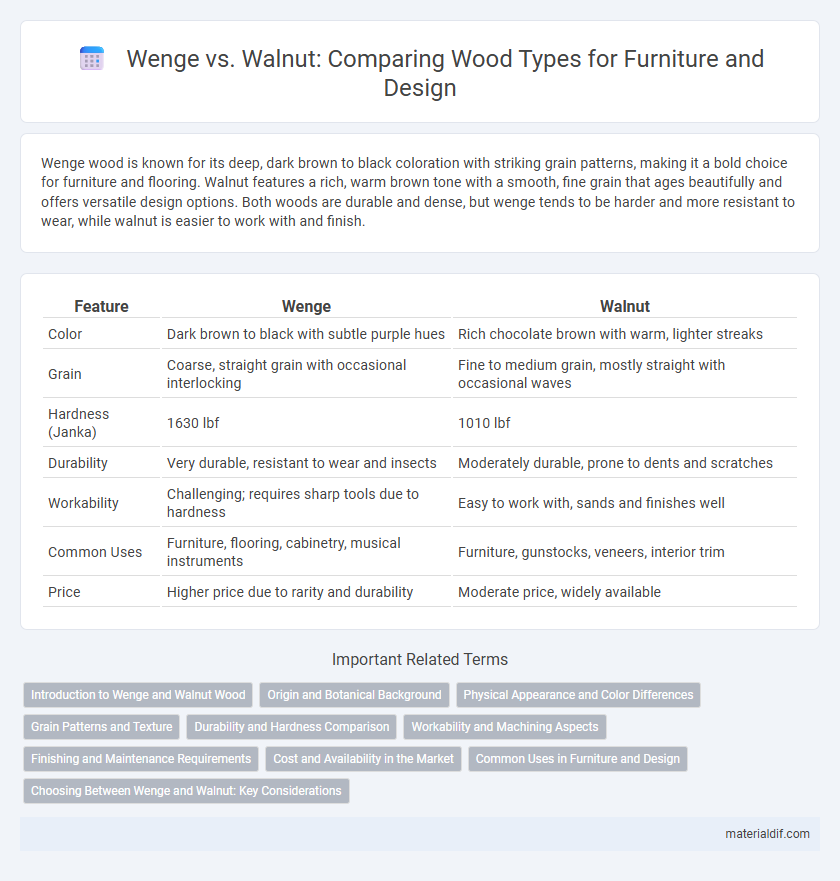
| Feature | Wenge | Walnut |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Dark brown to black with subtle purple hues | Rich chocolate brown with warm, lighter streaks |
| Grain | Coarse, straight grain with occasional interlocking | Fine to medium grain, mostly straight with occasional waves |
| Hardness (Janka) | 1630 lbf | 1010 lbf |
| Durability | Very durable, resistant to wear and insects | Moderately durable, prone to dents and scratches |
| Workability | Challenging; requires sharp tools due to hardness | Easy to work with, sands and finishes well |
| Common Uses | Furniture, flooring, cabinetry, musical instruments | Furniture, gunstocks, veneers, interior trim |
| Price | Higher price due to rarity and durability | Moderate price, widely available |
Introduction to Wenge and Walnut Wood
Wenge wood, sourced primarily from the African Millettia laurentii tree, is renowned for its deep, dark brown color with subtle black streaks and strong, dense grain that offers exceptional durability and resistance to wear. Walnut wood, particularly from the American Black Walnut (Juglans nigra), features a rich, warm chocolate-brown hue with fine, straight grain patterns, prized for its workability and elegant finish in furniture and cabinetry. Both woods are valued for luxury woodworking, but Wenge's hardness and exotic appearance contrast with Walnut's smooth texture and classic aesthetic.
Origin and Botanical Background
Wenge (Millettia laurentii) is a tropical hardwood native to Central Africa, specifically the Congo region, prized for its deep, dark brown color with distinctive black streaks. Walnut (Juglans regia), originating from Eastern North America and parts of Europe and Asia, is a deciduous tree known for its rich, warm brown heartwood and fine, straight grain. Both woods belong to different botanical families; Wenge is part of the Fabaceae family while Walnut belongs to the Juglandaceae family, reflecting their diverse ecological adaptations and growth environments.
Physical Appearance and Color Differences
Wenge wood features a dark brown to black color with fine, close grain patterns creating a dramatic and exotic look, while Walnut typically presents rich, chocolate brown hues with streaks of lighter and darker tones, offering a warm and luxurious appearance. The surface of Wenge exhibits a rougher texture with pronounced veins, whereas Walnut has a smoother, more uniform texture. Color variations in Wenge tend to be more contrasting and bold compared to the subtle, elegant gradients found in Walnut.
Grain Patterns and Texture
Wenge wood features a distinctive, deep brown to black coloration with very coarse, pronounced grain patterns that create a bold, dramatic texture, often exhibiting linear streaks and contrasting hues. Walnut wood, typically rich chocolate brown with occasional purplish tints, displays a smoother, more refined texture with fine, straight to wavy grain patterns that offer a classic, elegant appearance. The tactile experience of Wenge is rougher due to its open pores, while Walnut provides a softer, more polished feel suitable for high-end furniture and cabinetry.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Wenge wood is known for its exceptional durability and hardness, ranking around 1,930 on the Janka hardness scale, making it highly resistant to wear and impact. Walnut, while also durable, measures lower on the Janka scale at approximately 1,010, indicating it is softer and more susceptible to dents and scratches compared to Wenge. Both woods are valued for different applications, with Wenge favored in high-traffic areas requiring superior strength and Walnut preferred for decorative purposes due to its softer texture.
Workability and Machining Aspects
Wenge wood is dense and hard, making it more challenging to machine but offering excellent durability for detailed work, while walnut is softer and easier to work with hand tools and machines, providing smoother finishes and less tool wear. The high oil content in walnut enhances its workability and reduces the risk of splintering, unlike wenge which can dull tools quickly due to its coarse grain and silica content. For intricate joinery or fine detailing, walnut is preferred for ease of shaping, whereas wenge excels in applications requiring robust, wear-resistant components despite its tougher machining characteristics.
Finishing and Maintenance Requirements
Wenge wood demands a more protective finish due to its coarse texture and high oil content, often requiring oils or polyurethane for longevity. Walnut offers a smoother grain that accepts stains and finishes uniformly, but it needs regular polishing to maintain its rich color and prevent dullness. Both woods benefit from dusting and avoiding excessive moisture, though walnut generally requires more frequent maintenance to preserve its appearance.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Wenge wood, sourced primarily from Central Africa, tends to be more expensive due to its rarity and slower growth rate, resulting in limited availability in global markets. Walnut, especially American black walnut, is more widely available and moderately priced, benefiting from established timber farms and sustainable harvesting practices. Cost differences reflect market demand and supply challenges, with walnut often preferred for cost-effective projects while wenge suits luxury applications.
Common Uses in Furniture and Design
Wenge is commonly used for flooring, cabinetry, and modern furniture due to its dark, dense grain that offers high durability and a striking aesthetic. Walnut is favored in fine furniture, veneers, and decorative pieces because of its rich, warm tones and smooth texture that enhance traditional and contemporary designs. Both woods provide distinctive visual appeal, but Wenge is typically chosen for bold, rustic styles while Walnut suits elegant, classic interiors.
Choosing Between Wenge and Walnut: Key Considerations
Wenge offers a dark, exotic appearance with deep brown tones and black streaks, making it ideal for modern, bold designs, while walnut features a rich, warm brown color with a straight grain that complements traditional and contemporary settings. Wenge is denser and harder, providing superior durability and resistance to wear compared to walnut, which is softer and easier to work with during woodworking. Choosing between wenge and walnut depends on the desired aesthetic, durability requirements, and the project's complexity, with wenge suited for high-traffic areas and walnut favored for fine furniture and detailed carvings.
Wenge vs Walnut Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com