Laminated wood consists of multiple layers of solid wood glued together to enhance strength and stability, making it ideal for structural applications such as beams and furniture components. Veneered wood features a thin layer of high-quality wood glued onto a core material like plywood or MDF, providing an attractive appearance at a lower cost while maintaining lighter weight. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right material for durability, aesthetics, and budget in woodworking projects.
Table of Comparison
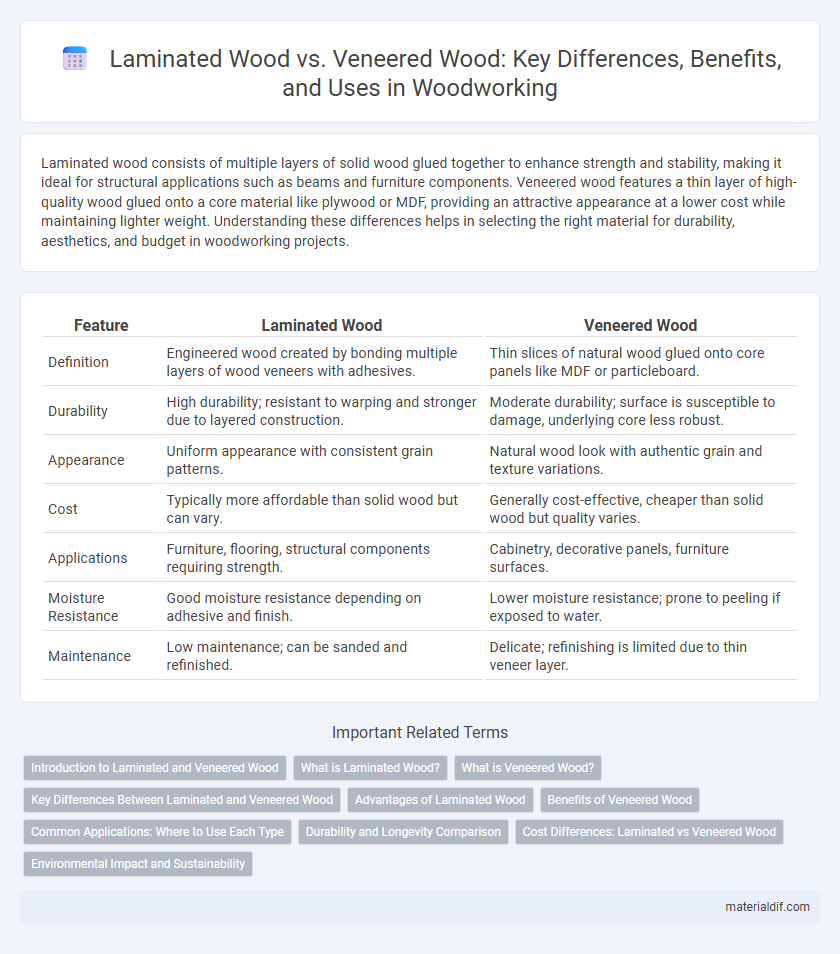
| Feature | Laminated Wood | Veneered Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engineered wood created by bonding multiple layers of wood veneers with adhesives. | Thin slices of natural wood glued onto core panels like MDF or particleboard. |
| Durability | High durability; resistant to warping and stronger due to layered construction. | Moderate durability; surface is susceptible to damage, underlying core less robust. |
| Appearance | Uniform appearance with consistent grain patterns. | Natural wood look with authentic grain and texture variations. |
| Cost | Typically more affordable than solid wood but can vary. | Generally cost-effective, cheaper than solid wood but quality varies. |
| Applications | Furniture, flooring, structural components requiring strength. | Cabinetry, decorative panels, furniture surfaces. |
| Moisture Resistance | Good moisture resistance depending on adhesive and finish. | Lower moisture resistance; prone to peeling if exposed to water. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; can be sanded and refinished. | Delicate; refinishing is limited due to thin veneer layer. |
Introduction to Laminated and Veneered Wood
Laminated wood consists of multiple layers of wood glued together, creating a strong and stable material commonly used in structural applications and furniture manufacturing. Veneered wood features a thin layer of high-quality wood adhered to a core of less expensive material, offering the appearance of solid wood while reducing costs. Both materials optimize wood usage by enhancing strength and aesthetics, making them popular choices in construction and design.
What is Laminated Wood?
Laminated wood consists of multiple layers of wood veneers or thin boards bonded together with strong adhesives, resulting in a sturdy and dimensionally stable material. It offers enhanced strength and resistance to warping compared to solid wood, making it ideal for structural applications and furniture manufacturing. The lamination process allows for precise customization in thickness and size, providing versatility for various design requirements.
What is Veneered Wood?
Veneered wood consists of a thin layer of high-quality wood adhered to a core of less expensive materials, such as plywood or particleboard, enhancing the appearance without the cost of solid wood. Its primary purpose is to provide aesthetic appeal while improving durability and reducing material waste. Commonly used in furniture and cabinetry, veneered wood offers a cost-effective alternative with the visual characteristics of premium hardwoods.
Key Differences Between Laminated and Veneered Wood
Laminated wood consists of multiple layers of wood glued together to enhance strength and stability, whereas veneered wood features a thin layer of high-quality wood applied over a less expensive core material for aesthetic appeal. Laminated wood offers superior structural integrity and resistance to warping, making it ideal for furniture and flooring, while veneered wood primarily serves decorative purposes with limited durability. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate material based on performance requirements and budget constraints in woodworking projects.
Advantages of Laminated Wood
Laminated wood offers superior strength and stability compared to veneered wood, as it is constructed by bonding multiple layers of solid wood under pressure. This layered composition enhances resistance to warping, making laminated wood ideal for structural applications and heavy-duty furniture. Its consistent thickness and improved durability provide a reliable and long-lasting material choice in construction and woodworking projects.
Benefits of Veneered Wood
Veneered wood offers the benefit of providing the appearance of expensive or rare wood species at a fraction of the cost, making it a budget-friendly choice for high-end aesthetics. It is lightweight and dimensionally stable, reducing the likelihood of warping compared to solid or laminated wood, which enhances its durability in various applications. The thin layer of natural wood veneer also allows for efficient use of timber resources, supporting sustainable practices without compromising on design quality.
Common Applications: Where to Use Each Type
Laminated wood is commonly used in structural applications such as flooring, furniture framing, and beams due to its enhanced strength and durability. Veneered wood is often applied in decorative surfaces like cabinetry, paneling, and high-end furniture where aesthetics and wood grain appearance are prioritized. Selecting laminated wood suits projects requiring robustness, while veneered wood is ideal for visually appealing finishes.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Laminated wood consists of multiple layers of wood glued together, providing enhanced structural strength and resistance to warping, making it significantly more durable over time compared to veneered wood. Veneered wood features a thin layer of high-quality wood glued onto a core material, which may be prone to peeling, chipping, and damage under heavy use. For applications requiring long-term durability and stability, laminated wood is the superior choice due to its resistance to moisture and mechanical stress.
Cost Differences: Laminated vs Veneered Wood
Laminated wood typically offers a lower cost compared to veneered wood due to its construction using layers of solid wood or wood composites bonded with adhesives. Veneered wood involves a thin layer of high-quality hardwood glued to a less expensive core, resulting in higher manufacturing costs driven by the precision required for slicing and adhering thin veneers. Budget-conscious projects often favor laminated wood for its affordability, while veneered wood is chosen for premium aesthetics despite its increased expense.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Laminated wood, made from layers of solid wood glued together, offers enhanced durability and reduces waste by utilizing smaller wood pieces, contributing to better resource efficiency and lower deforestation rates. Veneered wood consists of a thin layer of high-quality wood adhered to a core of less expensive or recycled materials, which conserves valuable hardwood resources and minimizes the environmental footprint. Both materials support sustainable forestry if sourced responsibly, but laminated wood typically has a longer lifespan, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacement and further decreasing environmental impact.
Laminated wood vs Veneered wood Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com