Hot pour wax requires melting to a specific temperature before application, allowing for deeper penetration and longer-lasting results. Cold pour wax is ready-to-use at room temperature, offering convenience but providing less effective adhesion and a shorter wear time. Choosing between them depends on the desired application ease and durability of the finish.
Table of Comparison
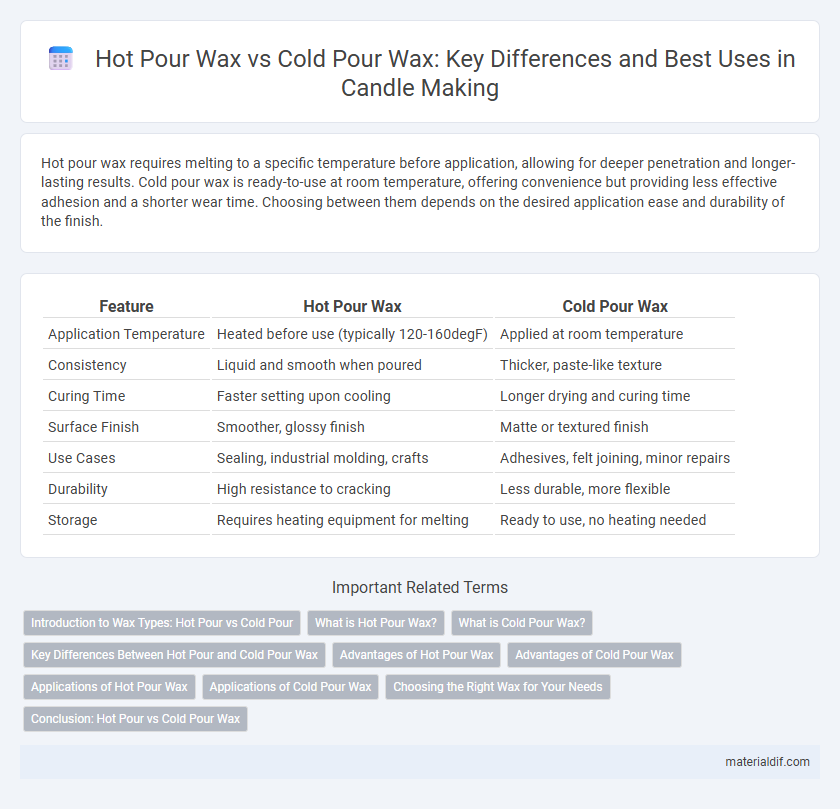
| Feature | Hot Pour Wax | Cold Pour Wax |
|---|---|---|
| Application Temperature | Heated before use (typically 120-160degF) | Applied at room temperature |
| Consistency | Liquid and smooth when poured | Thicker, paste-like texture |
| Curing Time | Faster setting upon cooling | Longer drying and curing time |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, glossy finish | Matte or textured finish |
| Use Cases | Sealing, industrial molding, crafts | Adhesives, felt joining, minor repairs |
| Durability | High resistance to cracking | Less durable, more flexible |
| Storage | Requires heating equipment for melting | Ready to use, no heating needed |
Introduction to Wax Types: Hot Pour vs Cold Pour
Hot pour wax melts at higher temperatures and is commonly used for industrial applications such as coatings, adhesives, and candle making, offering a smooth, durable finish. Cold pour wax, also known as room-temperature wax, sets without heating and is ideal for quick, easy applications like sealing and crafting, providing convenience and energy efficiency. Understanding the melting points and usage scenarios of hot pour versus cold pour wax helps optimize performance and suitability for specific projects.
What is Hot Pour Wax?
Hot Pour Wax is a type of wax melted and applied in a liquid state at high temperatures, typically between 125degF to 160degF, allowing for deep penetration into porous surfaces or molding materials. It is commonly used in industrial applications such as sealing, coating, and candle making due to its ability to create thick, durable layers. The heat-activated properties of Hot Pour Wax enable strong adhesion and faster setting times compared to Cold Pour Wax, which is applied at room temperature.
What is Cold Pour Wax?
Cold pour wax is a type of wax formulation that hardens at room temperature without the need for external heating, making it ideal for easy application and quick setting. It typically contains low-melting point waxes, oils, and additives designed to cure rapidly upon cooling. Cold pour wax is commonly used for encapsulation, coatings, and sealing applications where heat-sensitive materials require protection without exposure to high temperatures.
Key Differences Between Hot Pour and Cold Pour Wax
Hot pour wax melts at higher temperatures, requiring direct heating before application, which allows for a smoother, more even finish ideal for deep crevices and intricate molds. Cold pour wax, on the other hand, sets at room temperature without additional heat, making it faster and easier to use but less suitable for detailed or high-precision projects. The primary distinction lies in their melting points and application methods, impacting drying times, texture, and the final quality of the wax surface.
Advantages of Hot Pour Wax
Hot pour wax offers superior adhesion and flexibility, ensuring a more durable and long-lasting seal compared to cold pour wax. Its high-temperature application enables faster curing times and better penetration into surfaces, reducing gaps and enhancing structural integrity. This type of wax is ideal for industrial uses where strong, weather-resistant bonds are critical.
Advantages of Cold Pour Wax
Cold pour wax offers several advantages including ease of application without the need for heating, making it safer and more convenient for at-home use. It maintains a stable consistency, reducing the risk of burns and allowing precise control during the waxing process. This wax type is ideal for sensitive skin, as it adheres gently without excessive heat, minimizing irritation and discomfort.
Applications of Hot Pour Wax
Hot pour wax is widely used in applications requiring robust adhesion and precise molding, such as in packaging seals, candle making, and industrial coatings. Its ability to remain molten at high temperatures allows for effective filling of intricate molds and strong bonding to various surfaces. This property makes hot pour wax ideal for creating durable seals and detailed decorative items.
Applications of Cold Pour Wax
Cold pour wax is ideal for applications requiring detailed molds, such as small figurines, cosmetics, and sealing due to its easy handling at room temperature. It offers superior control without the need for heating equipment, making it perfect for crafts and cosmetic products like lip balms and lotion bars. Cold pour wax also reduces the risk of burns and material degradation, ensuring safer and more consistent results in delicate projects.
Choosing the Right Wax for Your Needs
Hot pour wax offers deeper penetration and stronger adhesion, ideal for items requiring durable, long-lasting seals or coatings. Cold pour wax provides convenience and ease of use, suitable for quick applications and delicate surfaces where heat could cause damage. Selecting the right wax depends on the material, purpose, and the level of durability needed in the final product.
Conclusion: Hot Pour vs Cold Pour Wax
Hot pour wax offers superior adhesion and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty sealing and industrial applications. Cold pour wax provides convenience and safety, suitable for light sealing tasks and quick, low-temperature use. Choosing between hot pour and cold pour wax depends on the specific requirements of the task, balancing performance with ease of application.
Hot Pour Wax vs Cold Pour Wax Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com