Beeswax and carnauba wax both serve as natural, sustainable options for pet care products but differ significantly in their properties and uses. Beeswax, derived from honeybee hives, offers excellent moisturizing and protective benefits, making it ideal for soothing dry skin and creating a breathable barrier on pets. Carnauba wax, sourced from the leaves of the carnauba palm, is harder and more water-resistant, often used to create durable, glossy finishes on pet accessories or in formulations requiring long-lasting protection.
Table of Comparison
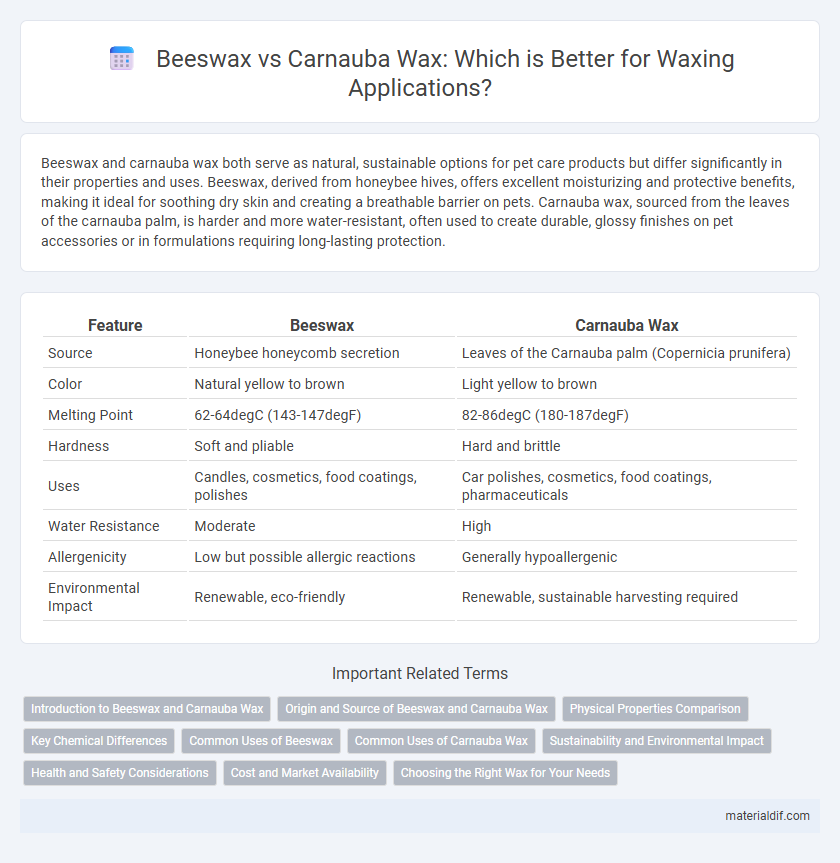
| Feature | Beeswax | Carnauba Wax |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Honeybee honeycomb secretion | Leaves of the Carnauba palm (Copernicia prunifera) |
| Color | Natural yellow to brown | Light yellow to brown |
| Melting Point | 62-64degC (143-147degF) | 82-86degC (180-187degF) |
| Hardness | Soft and pliable | Hard and brittle |
| Uses | Candles, cosmetics, food coatings, polishes | Car polishes, cosmetics, food coatings, pharmaceuticals |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Allergenicity | Low but possible allergic reactions | Generally hypoallergenic |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, eco-friendly | Renewable, sustainable harvesting required |
Introduction to Beeswax and Carnauba Wax
Beeswax, a natural substance produced by honeybees, is prized for its malleability, moisture resistance, and rich, warm color, making it ideal for cosmetics, candles, and food-grade applications. Carnauba wax, derived from the leaves of the Brazilian carnauba palm, is harder and more brittle than beeswax, valued for its high melting point and glossy finish used in automotive polishes, food coatings, and pharmaceuticals. Both waxes serve distinct industrial roles due to their unique chemical compositions, with beeswax primarily composed of esters and fatty acids, and carnauba wax containing aliphatic esters, acids, and hydrocarbons.
Origin and Source of Beeswax and Carnauba Wax
Beeswax originates from the honeycomb secreted by worker honeybees, predominantly from the Apis mellifera species, and is harvested directly from beehives. Carnauba wax is derived from the leaves of the Copernicia prunifera palm tree, native to northeastern Brazil, where its natural coatings are scraped off and processed. Both waxes serve diverse cosmetic and industrial purposes, with beeswax offering natural antimicrobial properties and carnauba wax providing a harder, more lustrous finish.
Physical Properties Comparison
Beeswax is a natural wax produced by honeybees, characterized by a melting point between 62-64degC and a soft, pliable texture, making it ideal for cosmetics and candles. Carnauba wax, derived from the leaves of the carnauba palm, boasts a higher melting point around 82-86degC and a harder, glossy finish, often used in automotive polish and food coatings. Both waxes exhibit excellent water resistance, but Carnauba's superior hardness and higher melting point enhance durability in high-temperature applications.
Key Chemical Differences
Beeswax primarily consists of esters of fatty acids and long-chain alcohols, with notable components like palmitic acid, whereas Carnauba wax is rich in esters of long-chain fatty acids and diols, including significant amounts of cinnamic acid esters. The melting point of Carnauba wax (82-86degC) is higher than that of Beeswax (62-65degC), reflecting its denser molecular structure and greater hardness. These chemical differences influence their respective applications, with Beeswax favored for natural products and Carnauba wax used in industrial coatings for its superior durability and gloss.
Common Uses of Beeswax
Beeswax is widely used in cosmetics, candle making, food preservation, and pharmaceuticals due to its natural emulsifying properties and hypoallergenic nature. It serves as a key ingredient in lip balms, moisturizers, and hair-care products, providing moisture retention and skin protection. Unlike carnauba wax, which is primarily valued for its hardness and high melting point in automotive and furniture polishes, beeswax is preferred for applications requiring gentle, non-toxic, and breathable wax.
Common Uses of Carnauba Wax
Carnauba wax is widely used in automotive waxes, shoe polishes, and food coatings due to its high melting point and glossy finish. It serves as a key ingredient in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals for its water-resistant and hypoallergenic properties. This natural plant-based wax offers superior hardness and durability compared to beeswax, making it ideal for protective and decorative applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Beeswax, a natural byproduct of honeybee activity, offers exceptional biodegradability and supports biodiversity but faces sustainability challenges due to declining bee populations and habitat loss. Carnauba wax, harvested from the leaves of the Brazilian Carnauba palm, provides a renewable and eco-friendly alternative with minimal environmental disruption when sourced responsibly. Both waxes contribute to sustainable practices, yet the environmental impact hinges on ethical sourcing and ecosystem preservation efforts.
Health and Safety Considerations
Beeswax, a natural product produced by honeybees, is non-toxic, hypoallergenic, and safe for use in food, cosmetics, and medical applications, offering antimicrobial properties that help reduce the risk of infections. Carnauba wax, derived from the leaves of the Brazilian palm tree, is generally considered safe but may cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals and should be used with caution in food products due to potential impurities. Both waxes require proper sourcing and handling to ensure purity and avoid contamination, which is critical for maintaining health and safety standards in consumer products.
Cost and Market Availability
Beeswax generally commands a higher price due to its natural origin and limited supply compared to carnauba wax, which is more abundant and cost-effective as it is derived from the leaves of the carnauba palm. Market availability of carnauba wax is widespread, supported by large-scale harvesting in Brazil, whereas beeswax supply fluctuates seasonally with honeybee populations, affecting its market stability and price. Industries often select carnauba wax for cost-efficiency and consistent availability, while beeswax is preferred for premium natural products despite its higher and less predictable cost.
Choosing the Right Wax for Your Needs
Beeswax offers natural antibacterial properties and a pleasant scent, making it ideal for skincare and cosmetics, while Carnauba wax provides a harder, more heat-resistant finish suited for automotive and furniture polishing. Considering the application's durability and texture requirements helps determine the best choice; beeswax excels in moisturizing uses, whereas carnauba wax excels in protective coatings. For eco-friendly and allergen-sensitive options, pure beeswax is preferred, whereas carnauba wax is favored for its high melting point and glossy sheen.
Beeswax vs Carnauba wax Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com