Gum rosin wax, derived from natural pine tree resin, offers superior tackiness and adhesion properties, making it ideal for applications like adhesives and inks. Synthetic wax, produced through chemical synthesis, provides more consistent melting points and enhanced durability, suited for automotive and industrial uses. Choosing between gum rosin and synthetic wax depends on the desired balance of natural origin and performance stability.
Table of Comparison
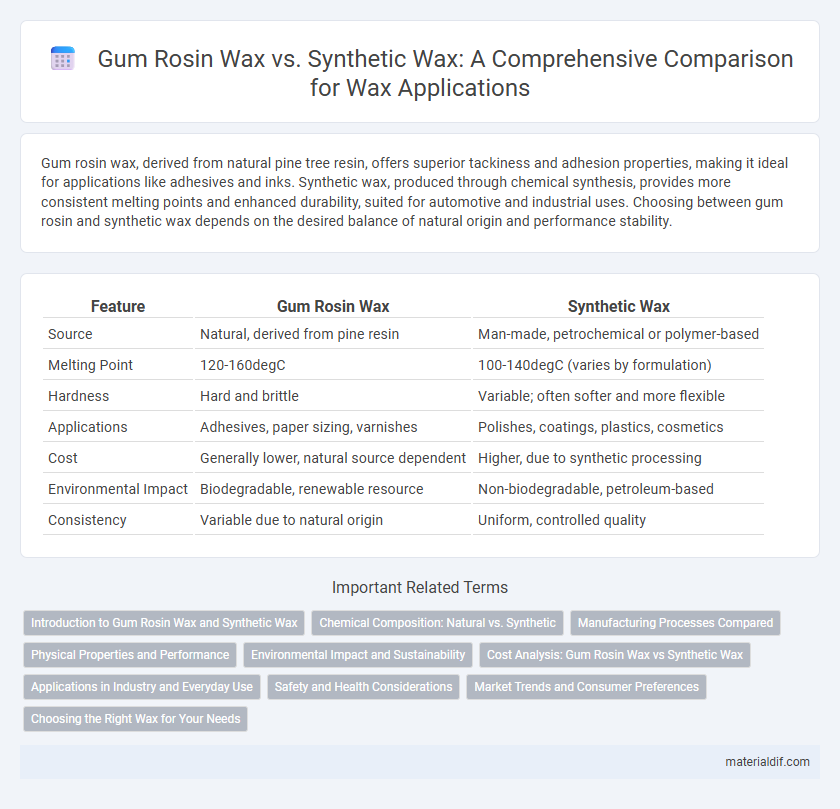
| Feature | Gum Rosin Wax | Synthetic Wax |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, derived from pine resin | Man-made, petrochemical or polymer-based |
| Melting Point | 120-160degC | 100-140degC (varies by formulation) |
| Hardness | Hard and brittle | Variable; often softer and more flexible |
| Applications | Adhesives, paper sizing, varnishes | Polishes, coatings, plastics, cosmetics |
| Cost | Generally lower, natural source dependent | Higher, due to synthetic processing |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resource | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Consistency | Variable due to natural origin | Uniform, controlled quality |
Introduction to Gum Rosin Wax and Synthetic Wax
Gum Rosin Wax, derived from natural pine tree resins, is valued for its excellent adhesive properties and biodegradability in applications like adhesives and coatings. Synthetic Wax, produced through chemical processes such as polymerization or Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, offers uniformity, enhanced durability, and tailored melting points suitable for industrial uses. Both wax types serve distinct purposes, with natural Gum Rosin Wax favored for eco-friendly products and Synthetic Wax preferred for consistent performance and versatility.
Chemical Composition: Natural vs. Synthetic
Gum rosin wax is derived from the natural resin of pine trees, primarily composed of abietic acid and other resin acids, offering biodegradability and eco-friendly properties. Synthetic waxes are chemically engineered hydrocarbons, such as polyethylene or Fischer-Tropsch waxes, designed for consistent molecular weight and melting point control. The fundamental difference lies in gum rosin wax's natural polymeric carboxylic acids versus the purely hydrocarbon structure of synthetic waxes, impacting solubility and application performance.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Gum rosin wax is derived from natural pine resin through distillation and hydrogenation, emphasizing renewable raw materials and eco-friendly extraction methods. Synthetic wax is produced via complex chemical synthesis processes such as Fischer-Tropsch or polymerization, allowing precise control over molecular structure and consistency. The manufacturing of gum rosin wax relies on bio-based inputs, while synthetic wax manufacturing prioritizes industrial-scale chemical engineering for uniformity and tailored properties.
Physical Properties and Performance
Gum Rosin Wax, derived from natural resins, exhibits higher tackiness and excellent adhesion, making it ideal for applications requiring strong bonding and flexibility. Synthetic Wax offers superior hardness, thermal stability, and consistent particle size, resulting in enhanced durability and wear resistance in high-temperature environments. The physical properties of Gum Rosin Wax favor pliability and grip, whereas Synthetic Wax excels in performance under mechanical stress and heat.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gum rosin wax, derived from natural pine resin, offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to synthetic waxes, which are typically petroleum-based and contribute to fossil fuel depletion and pollution. The production of gum rosin wax results in lower carbon emissions and less environmental toxicity, promoting sustainability in industries such as adhesives and cosmetics. Conversely, synthetic waxes often involve energy-intensive manufacturing processes and generate non-biodegradable waste, raising concerns about long-term ecological impact.
Cost Analysis: Gum Rosin Wax vs Synthetic Wax
Gum rosin wax typically incurs higher raw material costs due to its natural extraction from pine resin, making it less cost-effective for large-scale industrial applications compared to synthetic wax. Synthetic wax, produced through chemical processes, offers more consistent pricing and lower production costs, allowing manufacturers to optimize budgets in applications requiring uniformity and reliability. Cost analysis reveals synthetic wax's economic advantage in volume purchases, while gum rosin wax may justify its premium price through superior natural adhesive properties in specialized uses.
Applications in Industry and Everyday Use
Gum rosin wax, derived from natural pine resin, is extensively used in adhesives, inks, and varnishes due to its excellent tackifying properties and biodegradability. Synthetic waxes, produced through petrochemical processes, offer superior consistency, higher melting points, and enhanced chemical resistance, making them ideal for automotive coatings, plastics, and cosmetics. Industries favor gum rosin wax for eco-friendly formulations, while synthetic wax excels in applications requiring durability and uniform performance.
Safety and Health Considerations
Gum rosin wax, derived from natural pine resin, offers better biocompatibility and lower toxicity compared to synthetic waxes, which may contain petroleum-based chemicals with potential health risks. Safety studies highlight that natural waxes tend to have fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reducing respiratory irritation and allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Proper handling of synthetic waxes requires protective measures to mitigate exposure to harmful additives and ensure workplace safety.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Gum rosin wax, derived from natural pine tree resin, is gaining traction in markets emphasizing sustainability and eco-friendly products, appealing to consumers prioritizing organic and biodegradable materials. Synthetic wax, produced through chemical processes, remains dominant in industrial applications due to its consistent quality, lower cost, and versatility in cosmetics, adhesives, and coatings. Market trends indicate a growing consumer preference for natural waxes like gum rosin in personal care and food packaging sectors, driven by increasing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures.
Choosing the Right Wax for Your Needs
Gum rosin wax, derived from natural pine resin, offers excellent adhesion and tackiness, making it ideal for applications in adhesives and sealants requiring strong bonding. Synthetic waxes, produced through chemical processes, provide superior temperature resistance and uniformity, suited for industries needing consistent performance, such as plastics and coatings. Selecting the right wax depends on whether natural properties like biodegradability and adhesion or engineered traits like thermal stability and consistency align better with your product requirements.
Gum Rosin Wax vs Synthetic Wax Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com