Food grade wax is specially formulated to be safe for direct contact with edible products, ensuring it meets strict health and safety standards, making it ideal for coating fruits, vegetables, and confections. Technical grade wax, on the other hand, is designed for industrial applications such as in automotive, candle-making, or packaging, where food safety is not a requirement. Choosing the correct wax type is crucial for pet products labeled as food safe to avoid contamination and ensure regulatory compliance.
Table of Comparison
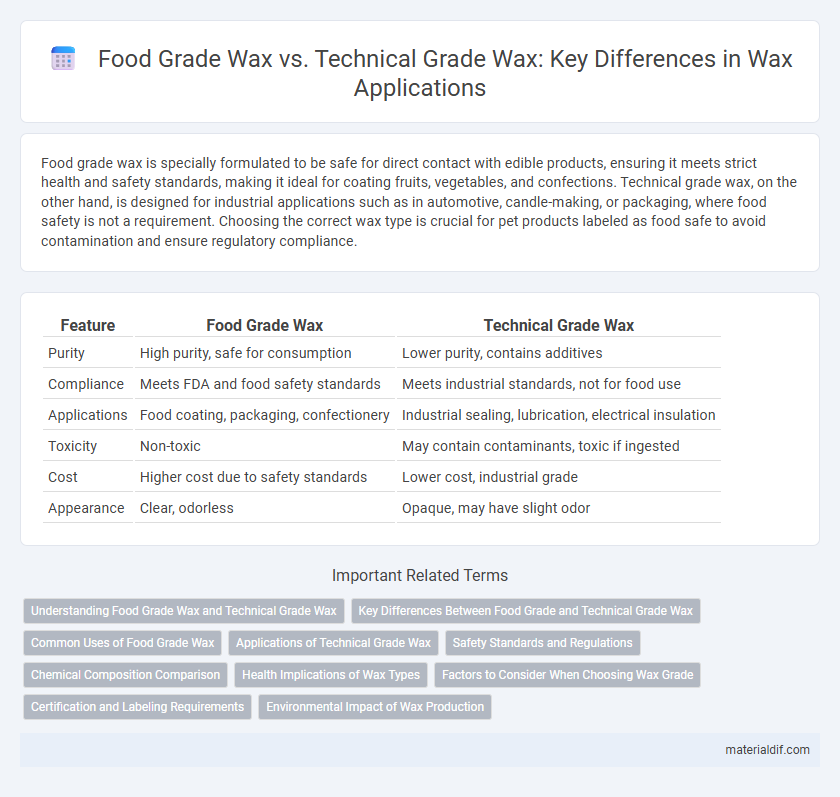
| Feature | Food Grade Wax | Technical Grade Wax |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High purity, safe for consumption | Lower purity, contains additives |
| Compliance | Meets FDA and food safety standards | Meets industrial standards, not for food use |
| Applications | Food coating, packaging, confectionery | Industrial sealing, lubrication, electrical insulation |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic | May contain contaminants, toxic if ingested |
| Cost | Higher cost due to safety standards | Lower cost, industrial grade |
| Appearance | Clear, odorless | Opaque, may have slight odor |
Understanding Food Grade Wax and Technical Grade Wax
Food grade wax is specially formulated to meet strict safety standards for direct contact with food, ensuring it is non-toxic and free from harmful contaminants. Technical grade wax, in contrast, is primarily used for industrial applications where food safety is not a concern, often containing additives unsuitable for consumption. Understanding the distinction between these wax types is essential for manufacturers seeking compliance with food safety regulations and maintaining product integrity.
Key Differences Between Food Grade and Technical Grade Wax
Food grade wax is specifically formulated to meet strict safety and health regulations, making it suitable for direct contact with edible products like fruits, vegetables, and confectionery. Technical grade wax, on the other hand, contains additives and impurities that render it unsafe for food applications and is commonly used in industrial purposes such as coatings, candles, and packaging. The primary distinctions lie in purity levels, regulatory compliance, and intended usage, with food grade wax emphasizing non-toxicity and FDA approval to ensure consumer safety.
Common Uses of Food Grade Wax
Food grade wax is primarily used in the food industry to coat fruits, vegetables, and certain cheeses, enhancing their appearance and extending shelf life by preventing moisture loss and oxidation. This type of wax is safe for consumption and complies with strict FDA regulations, ensuring it does not introduce harmful substances into food products. In contrast, technical grade wax is used in industrial applications such as cosmetics, polishes, and manufacturing processes, where food safety standards are not required.
Applications of Technical Grade Wax
Technical grade wax is commonly used in industrial applications such as coatings, adhesives, and rubber processing due to its cost-effectiveness and robust physical properties. It serves as a release agent in molding processes and as a component in the manufacture of candles and crayons, where food safety standards are not mandatory. Unlike food grade wax, technical grade wax can contain additives that enhance performance but are unsuitable for direct food contact.
Safety Standards and Regulations
Food grade wax complies with strict safety standards and regulations set by authorities such as the FDA and EFSA, ensuring it is free from harmful contaminants and safe for direct contact with food products. Technical grade wax, used primarily in industrial applications, does not meet these rigorous safety criteria and may contain additives unsuitable for food use. Selecting food grade wax is essential to maintain compliance with food safety regulations and protect consumer health.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Food grade wax primarily consists of natural ingredients such as paraffin, beeswax, and carnauba wax, ensuring non-toxicity and suitability for direct food contact. Technical grade wax contains similar hydrocarbons but may include additives or impurities that enhance industrial performance but compromise safety for consumption. The chemical purity and absence of harmful contaminants distinguish food grade wax from technical grade wax in applications involving food preservation and coating.
Health Implications of Wax Types
Food grade wax is specifically formulated to be safe for human consumption, commonly used as a coating on fruits, vegetables, and candies to preserve freshness and prevent contamination. Technical grade wax contains impurities and additives that can pose health risks if ingested, including potential toxicity and allergic reactions. Choosing food grade wax ensures compliance with safety regulations and minimizes adverse health effects associated with wax consumption.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Wax Grade
When selecting wax for applications such as food packaging or coatings, prioritizing food grade wax is essential due to its compliance with health and safety regulations, ensuring non-toxicity and suitability for direct food contact. Technical grade wax, while often more cost-effective and versatile for industrial uses, may contain impurities or additives unsuitable for consumption or sensitive products. Key factors to consider include regulatory standards, purity levels, intended use environment, and potential chemical interactions with food items or packaging materials.
Certification and Labeling Requirements
Food grade wax must comply with strict certification standards such as FDA or EFSA approval, ensuring it is safe for direct food contact and free from harmful contaminants. Technical grade wax lacks these certifications and is typically used in industrial applications, where safety standards for ingestion are not required. Clear labeling is mandatory for food grade wax, highlighting its compliance and suitability for food use, whereas technical grade wax labels emphasize industrial use and safety precautions.
Environmental Impact of Wax Production
Food grade wax is produced using stricter purification processes to ensure non-toxicity and biodegradability, resulting in a lower environmental footprint compared to technical grade wax. Technical grade wax often contains impurities and chemicals that increase pollution and complicate waste management during production and disposal. Selecting food grade wax supports more sustainable practices by minimizing harmful emissions and reducing contamination risks in ecosystems.
Food Grade Wax vs Technical Grade Wax Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com