UV-cured quartz offers faster curing times and enhanced durability compared to heat-cured quartz, making it ideal for precision applications. The UV curing process ensures superior resistance to high temperatures and chemical exposure, improving performance in demanding environments. Heat-cured quartz, while reliable, generally requires longer processing times and may exhibit slightly lower mechanical strength under extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
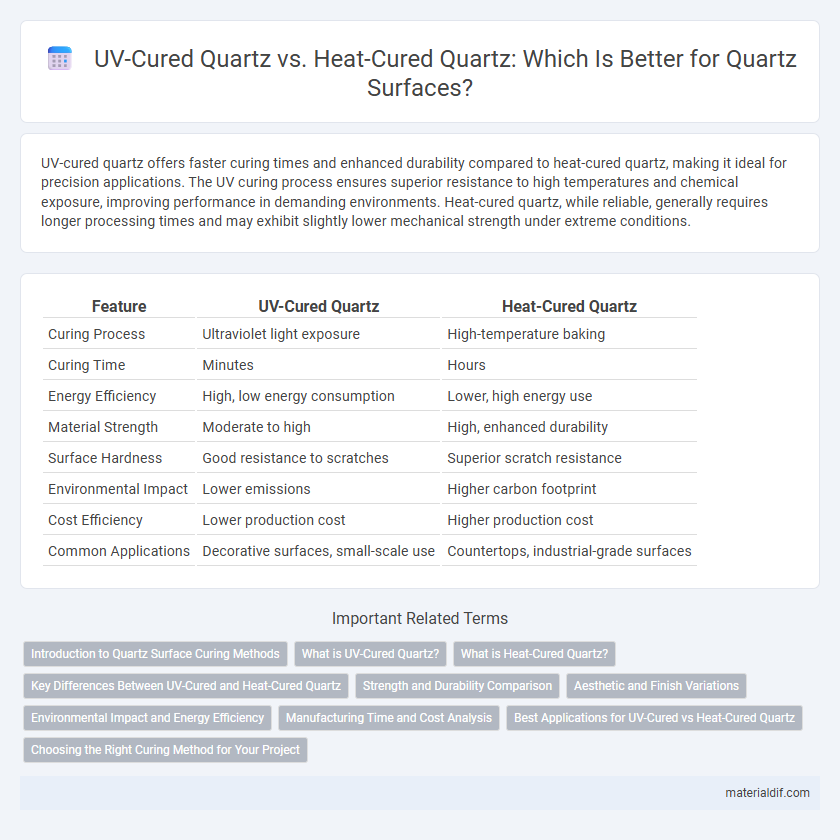
| Feature | UV-Cured Quartz | Heat-Cured Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Process | Ultraviolet light exposure | High-temperature baking |
| Curing Time | Minutes | Hours |
| Energy Efficiency | High, low energy consumption | Lower, high energy use |
| Material Strength | Moderate to high | High, enhanced durability |
| Surface Hardness | Good resistance to scratches | Superior scratch resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions | Higher carbon footprint |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower production cost | Higher production cost |
| Common Applications | Decorative surfaces, small-scale use | Countertops, industrial-grade surfaces |
Introduction to Quartz Surface Curing Methods
UV-cured quartz utilizes ultraviolet light to rapidly harden resin binders, enhancing surface durability and chemical resistance while minimizing energy consumption compared to traditional methods. Heat-cured quartz relies on high temperatures to polymerize resin, creating a robust and long-lasting surface with improved mechanical strength. Both curing methods impact the quartz's structural integrity and aesthetic quality, influencing the final performance and application suitability of quartz surfaces.
What is UV-Cured Quartz?
UV-cured quartz is engineered using ultraviolet light to rapidly harden a resin binder that fuses natural quartz particles, resulting in a durable and non-porous surface ideal for countertops. This curing process enhances scratch and stain resistance while allowing for faster production compared to heat-cured quartz, which requires high-temperature ovens to solidify the resin. UV-cured quartz surfaces provide consistent color and pattern, optimal for modern kitchen and bathroom applications.
What is Heat-Cured Quartz?
Heat-cured quartz is a type of engineered quartz surface created by exposing a mixture of crushed quartz and resin to controlled high temperatures, which enhances the bonding strength and durability of the material. This curing process improves heat resistance, chemical stability, and overall mechanical performance, making heat-cured quartz ideal for countertops and industrial applications. Compared to UV-cured quartz, heat-cured quartz typically exhibits superior hardness and resilience under extreme conditions.
Key Differences Between UV-Cured and Heat-Cured Quartz
UV-cured quartz undergoes polymerization through ultraviolet light exposure, resulting in faster curing times and higher surface hardness. Heat-cured quartz relies on thermal energy to initiate polymerization, offering enhanced thermal stability and improved mechanical properties. The key differences lie in curing speed, resulting durability, and resistance to environmental factors, with UV-cured quartz excelling in rapid processing and heat-cured quartz providing superior long-term robustness.
Strength and Durability Comparison
UV-cured quartz exhibits superior strength and enhanced durability compared to heat-cured quartz due to its advanced polymerization process, which results in a denser and more resilient surface. This curing method improves resistance to scratches, stains, and thermal stress, making UV-cured quartz ideal for high-traffic areas. Heat-cured quartz, while still durable, typically has a slightly lower hardness rating and may show increased susceptibility to micro-cracking under heavy use or extreme temperature changes.
Aesthetic and Finish Variations
UV-cured quartz offers a high-gloss, durable finish with enhanced color vibrancy and clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring precise aesthetic appeal. Heat-cured quartz, on the other hand, provides a more natural, matte texture with subtle variations in tone, lending a handcrafted look to surfaces. Both curing methods influence the quartz's surface hardness and resistance to wear, but UV curing typically results in a smoother, more uniform finish compared to the textured, organic feel achieved through heat curing.
Environmental Impact and Energy Efficiency
UV-cured quartz significantly reduces environmental impact by using lower energy consumption during the curing process compared to heat-cured quartz, which requires prolonged high-temperature exposure. The UV curing method decreases carbon emissions and conserves energy, making it a more sustainable choice in quartz production. Furthermore, UV-cured quartz minimizes waste through faster curing times and less thermal degradation, enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Manufacturing Time and Cost Analysis
UV-cured quartz offers significantly shorter manufacturing times compared to heat-cured quartz, reducing production cycles from several hours to mere minutes due to rapid polymerization under UV light. Cost analysis reveals that UV curing lowers energy consumption and labor expenses, resulting in overall cost savings despite higher initial equipment investment. Heat-cured quartz involves prolonged thermal exposure, increasing operational costs and elongating manufacturing lead times.
Best Applications for UV-Cured vs Heat-Cured Quartz
UV-cured quartz offers superior precision and faster production cycles, making it ideal for intricate microelectronics and optical devices requiring fine detail and minimal thermal stress. Heat-cured quartz excels in applications demanding high mechanical strength and thermal stability, such as aerospace components and industrial tooling. Selecting between UV-cured and heat-cured quartz depends on the balance between manufacturing speed, dimensional accuracy, and end-use environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Curing Method for Your Project
UV-cured quartz offers faster curing times and enhanced surface durability, making it ideal for projects requiring quick turnaround and abrasion resistance. Heat-cured quartz provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, preferred in applications exposed to high temperatures or harsh environments. Selecting the right curing method depends on project-specific factors such as exposure conditions, desired mechanical properties, and production timelines.
UV-Cured Quartz vs Heat-Cured Quartz Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com