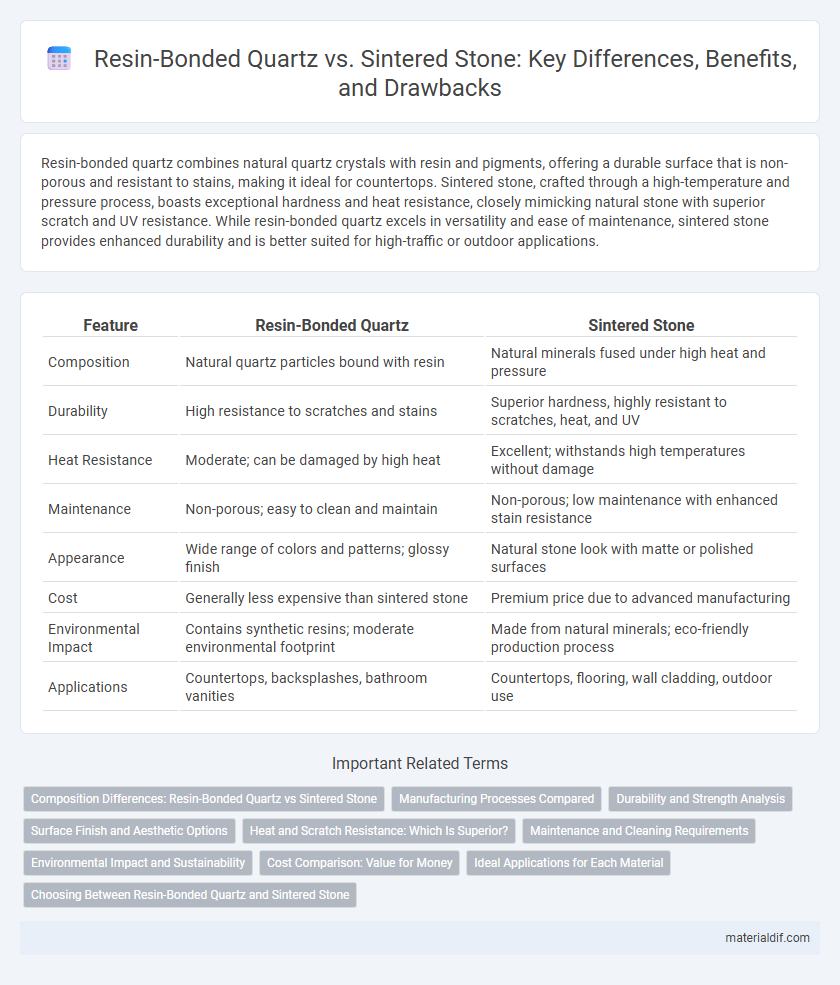
Resin-bonded quartz combines natural quartz crystals with resin and pigments, offering a durable surface that is non-porous and resistant to stains, making it ideal for countertops. Sintered stone, crafted through a high-temperature and pressure process, boasts exceptional hardness and heat resistance, closely mimicking natural stone with superior scratch and UV resistance. While resin-bonded quartz excels in versatility and ease of maintenance, sintered stone provides enhanced durability and is better suited for high-traffic or outdoor applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Resin-Bonded Quartz | Sintered Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural quartz particles bound with resin | Natural minerals fused under high heat and pressure |
| Durability | High resistance to scratches and stains | Superior hardness, highly resistant to scratches, heat, and UV |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate; can be damaged by high heat | Excellent; withstands high temperatures without damage |
| Maintenance | Non-porous; easy to clean and maintain | Non-porous; low maintenance with enhanced stain resistance |
| Appearance | Wide range of colors and patterns; glossy finish | Natural stone look with matte or polished surfaces |
| Cost | Generally less expensive than sintered stone | Premium price due to advanced manufacturing |
| Environmental Impact | Contains synthetic resins; moderate environmental footprint | Made from natural minerals; eco-friendly production process |
| Applications | Countertops, backsplashes, bathroom vanities | Countertops, flooring, wall cladding, outdoor use |
Composition Differences: Resin-Bonded Quartz vs Sintered Stone
Resin-bonded quartz consists of approximately 90% natural quartz aggregates combined with polymer resins and pigments, creating a non-porous, durable surface ideal for countertops. Sintered stone, on the other hand, is formed through a high-temperature and high-pressure process that fuses natural raw materials like feldspar, quartz, and silica, resulting in a highly resistant, 100% natural, and eco-friendly slab. The key composition difference is that resin-bonded quartz incorporates synthetic resins for binding, while sintered stone relies on purely mineral-based fusion without adhesives or binders.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Resin-bonded quartz is produced by combining crushed quartz aggregates with resin and pigments, followed by molding and curing under controlled heat and pressure, resulting in a non-porous, durable surface. Sintered stone undergoes a high-temperature and high-pressure sintering process where natural minerals are compacted and fused without resin, producing a highly dense and scratch-resistant material. Manufacturing differences impact durability, heat resistance, and maintenance, with sintered stone generally offering superior strength and environmental resistance compared to resin-bonded quartz.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Resin-bonded quartz surfaces exhibit high durability due to their polymer resin composition that enhances impact resistance and flexibility, making them less prone to chipping compared to other materials. Sintered stone, created through high heat and pressure, offers superior strength and scratch resistance, surpassing resin-bonded quartz in hardness and thermal stability. While resin-bonded quartz excels in resisting stains and minor impacts, sintered stone provides enhanced toughness, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Options
Resin-bonded quartz offers a polished, glossy surface finish with a wide range of vibrant colors and uniform patterns, enhancing contemporary interior designs. Sintered stone provides a more natural, matte, or honed texture, showcasing intricate veining and organic aesthetics that mimic natural stone. Both materials deliver durable surfaces, but resin-bonded quartz excels in color consistency, while sintered stone offers superior variety in surface textures and visual depth.
Heat and Scratch Resistance: Which Is Superior?
Resin-bonded quartz surfaces offer excellent heat resistance up to approximately 150degC, making them suitable for everyday kitchen use, while sintered stone can withstand much higher temperatures, often exceeding 700degC, without discoloration or damage. Scratch resistance in resin-bonded quartz is moderate due to its resin content, whereas sintered stone exhibits superior scratch resistance attributed to its compact, natural mineral composition and manufacturing process. For applications demanding extreme heat exposure and enhanced durability, sintered stone surpasses resin-bonded quartz in both heat and scratch resistance performance.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Resin-bonded quartz requires regular cleaning with non-abrasive, pH-neutral cleaners to prevent surface damage and maintain its glossy finish, while avoiding excessive heat exposure is crucial to prevent resin deterioration. Sintered stone offers superior stain resistance and durability, allowing for easier cleaning with mild detergents and minimal maintenance, as its dense, non-porous surface resists bacterial growth and chemical damage. Both materials benefit from prompt spill cleanup, but sintered stone's maintenance demands are lower due to its enhanced hardness and resistance to scratching.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Resin-bonded quartz surfaces are made by combining natural quartz crystals with resin binders, leading to lower energy consumption during production compared to sintered stone, which requires high heat and pressure to fuse raw materials. The resin components in resin-bonded quartz can pose recycling challenges and may off-gas volatile organic compounds (VOCs), whereas sintered stone is typically composed entirely of natural minerals, making it more recyclable and inert. Choosing sintered stone promotes sustainability through durability, minimal environmental emissions, and greater potential for end-of-life recycling.
Cost Comparison: Value for Money
Resin-bonded quartz typically offers a lower upfront cost compared to sintered stone, making it a budget-friendly option for many homeowners. While sintered stone demands a higher initial investment, its superior durability and resistance to scratches, heat, and stains often result in lower maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating cost-effectiveness requires balancing the affordable price of resin-bonded quartz against the long-term value and lifespan benefits provided by sintered stone surfaces.
Ideal Applications for Each Material
Resin-bonded quartz offers superior flexibility and is ideal for indoor applications like kitchen countertops and bathroom vanities due to its non-porous surface and resistance to stains. Sintered stone, with its high durability and heat resistance, excels in both indoor and outdoor settings, including flooring, wall cladding, and commercial spaces exposed to heavy wear. Choosing between the two depends on the specific requirements of durability, maintenance, and exposure to elements in the intended environment.
Choosing Between Resin-Bonded Quartz and Sintered Stone
Resin-bonded quartz offers superior flexibility, stain resistance, and a wide range of colors, making it ideal for kitchen countertops and indoor applications. Sintered stone provides exceptional durability, scratch resistance, and heat tolerance, suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. When choosing between resin-bonded quartz and sintered stone, consider factors like application environment, maintenance needs, and budget constraints.
Resin-Bonded Quartz vs Sintered Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com