Quartz is a natural mineral composed primarily of silicon dioxide, known for its hardness and durability, making it ideal for various applications. Engineered stone, often branded as quartz countertops, combines crushed natural quartz with resins and pigments to create a highly uniform and customizable surface. Unlike natural quartz, engineered stone offers enhanced stain resistance, a wider range of colors and patterns, and greater consistency in appearance.
Table of Comparison
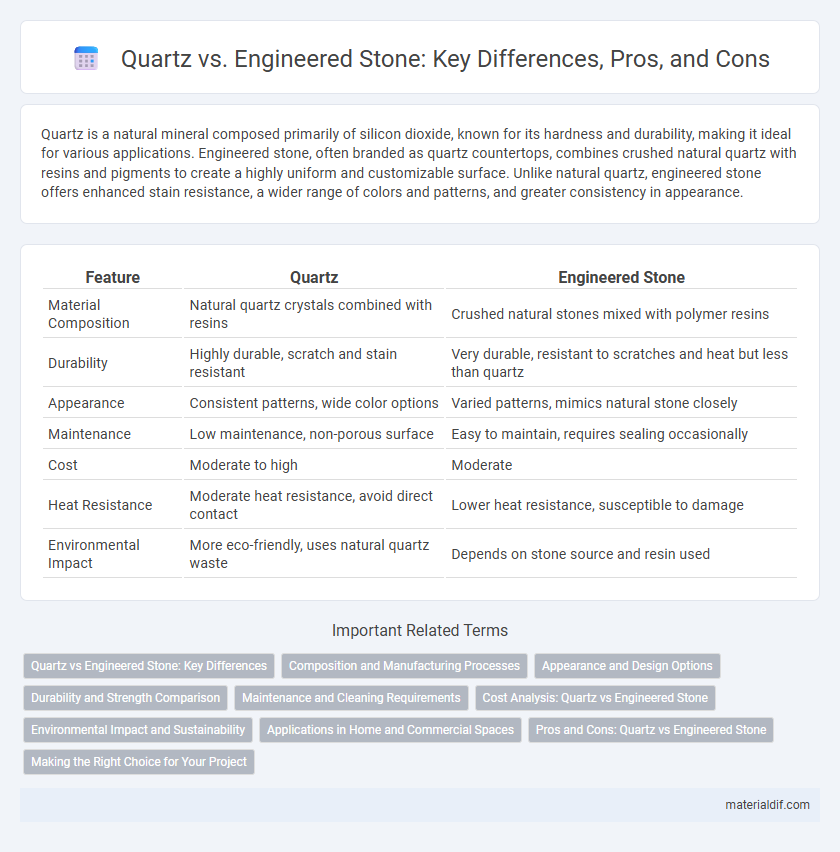
| Feature | Quartz | Engineered Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural quartz crystals combined with resins | Crushed natural stones mixed with polymer resins |
| Durability | Highly durable, scratch and stain resistant | Very durable, resistant to scratches and heat but less than quartz |
| Appearance | Consistent patterns, wide color options | Varied patterns, mimics natural stone closely |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, non-porous surface | Easy to maintain, requires sealing occasionally |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance, avoid direct contact | Lower heat resistance, susceptible to damage |
| Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly, uses natural quartz waste | Depends on stone source and resin used |
Quartz vs Engineered Stone: Key Differences
Quartz is a natural mineral primarily composed of silicon dioxide, valued for its hardness and durability in countertops and surfaces. Engineered stone, often branded as quartz countertops, combines crushed natural quartz with resin and pigments to create a non-porous, stain-resistant material. Key differences include the natural origin of quartz versus the composite manufacturing process of engineered stone, affecting aesthetic variety, maintenance requirements, and cost efficiency in kitchen and bathroom applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Quartz consists primarily of natural quartz crystals combined with resin binders and pigments, creating a durable and visually consistent surface. Engineered stone incorporates crushed natural stones mixed with polymers through a vibration and compression process, resulting in enhanced strength and non-porous properties. Both materials undergo advanced manufacturing techniques, but engineered stone offers greater design flexibility due to the controlled composition and fabrication.
Appearance and Design Options
Quartz offers a wide range of vibrant colors and patterns due to the combination of natural quartz crystals and resin, providing a more uniform and consistent appearance compared to engineered stone. Engineered stone, while also versatile, often mimics natural stone with unique veining and texture variations, creating a more authentic look. Both materials provide customizable design options, but quartz's enhanced color stability and low maintenance make it a preferred choice for modern interiors.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Quartz surfaces offer exceptional durability due to their composition of approximately 90% natural quartz crystals bound with resin, resulting in high resistance to scratches, chips, and cracks. Engineered stone varieties, while also durable, often vary in strength depending on resin content and binding processes, making them generally less resilient than pure quartz composites. The superior hardness of quartz, typically rated 7 on the Mohs scale, ensures long-lasting performance in high-traffic applications where toughness is critical.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Quartz surfaces demand minimal maintenance due to their non-porous nature, preventing stains and bacterial growth. Engineered stone, composed of crushed natural stone and resins, also resists stains but may require periodic sealing depending on the resin-to-stone ratio. Both materials benefit from gentle cleaners, avoiding harsh chemicals or abrasive pads to preserve their polished finish and ensure longevity.
Cost Analysis: Quartz vs Engineered Stone
Quartz countertops typically cost between $50 and $150 per square foot, reflecting the high-quality natural quartz content and advanced manufacturing processes. Engineered stone prices vary widely but generally fall within the $40 to $100 per square foot range, offering a more budget-friendly alternative with similar durability and aesthetic appeal. Cost differences arise from material sourcing, production techniques, and brand premiums, influencing long-term value and project budgeting decisions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Quartz countertops, primarily composed of natural quartz combined with resins and pigments, exhibit a lower environmental impact compared to engineered stone that often relies heavily on synthetic materials and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. The sustainability of quartz is enhanced by its durability and recyclability, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing waste. Engineered stone, while customizable and versatile, tends to have a higher carbon footprint due to its production methods and less renewable raw material usage.
Applications in Home and Commercial Spaces
Quartz offers exceptional durability and resistance to stains and scratches, making it ideal for kitchen countertops and bathroom vanities in both residential and commercial settings. Engineered stone, composed of crushed quartz mixed with resins, provides consistent color and pattern options suitable for wall cladding, flooring, and reception desks in office buildings and retail spaces. Both materials deliver low-maintenance surfaces that withstand heavy use, with quartz favored for its natural appearance and engineered stone prized for design versatility in high-traffic environments.
Pros and Cons: Quartz vs Engineered Stone
Quartz offers superior durability, stain resistance, and low maintenance compared to engineered stone, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Engineered stone provides greater design flexibility and a wider range of colors and patterns but tends to be less heat resistant and more prone to scratches. Cost-wise, quartz is generally more expensive, while engineered stone can offer budget-friendly options without significantly compromising quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Quartz offers natural durability and unique patterns formed through natural processes, making it an excellent choice for projects emphasizing authenticity. Engineered stone provides consistent appearance, enhanced stain resistance, and greater design flexibility due to its composite nature of crushed stone and resin. Assess project needs such as budget, aesthetic preference, and maintenance to determine the optimal balance between natural beauty and engineered performance.
Quartz vs Engineered Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com