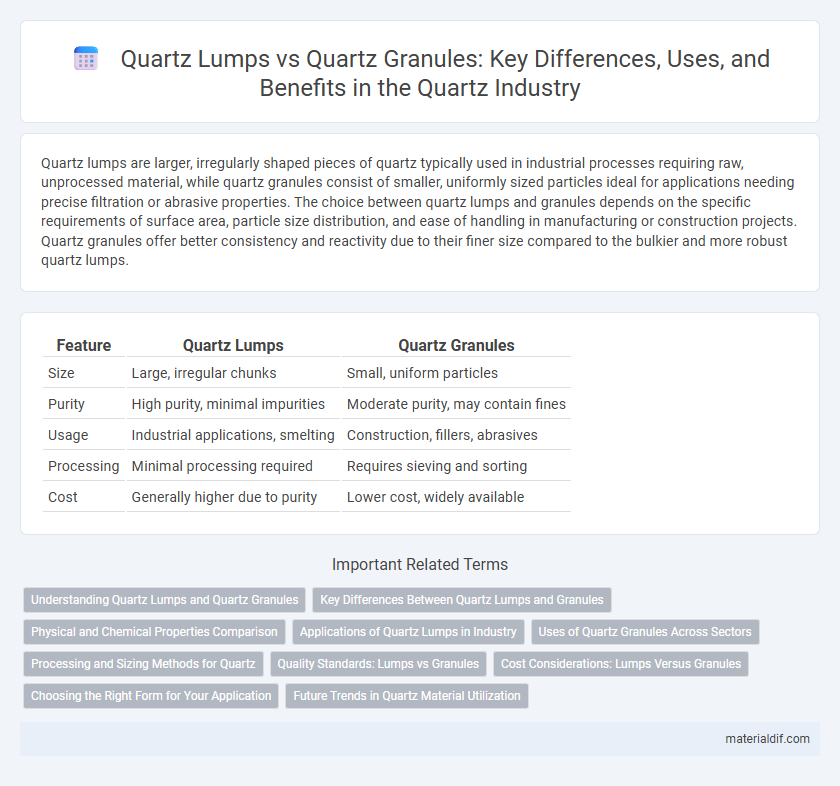
Quartz lumps are larger, irregularly shaped pieces of quartz typically used in industrial processes requiring raw, unprocessed material, while quartz granules consist of smaller, uniformly sized particles ideal for applications needing precise filtration or abrasive properties. The choice between quartz lumps and granules depends on the specific requirements of surface area, particle size distribution, and ease of handling in manufacturing or construction projects. Quartz granules offer better consistency and reactivity due to their finer size compared to the bulkier and more robust quartz lumps.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Quartz Lumps | Quartz Granules |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Large, irregular chunks | Small, uniform particles |
| Purity | High purity, minimal impurities | Moderate purity, may contain fines |
| Usage | Industrial applications, smelting | Construction, fillers, abrasives |
| Processing | Minimal processing required | Requires sieving and sorting |
| Cost | Generally higher due to purity | Lower cost, widely available |
Understanding Quartz Lumps and Quartz Granules
Quartz lumps are larger, irregularly shaped pieces of natural quartz, commonly used in industrial applications such as manufacturing and construction due to their high silica content and durability. Quartz granules consist of smaller, more uniform particles often utilized in abrasive products, filtration systems, and as fillers in resin composites because of their consistent size and enhanced surface area. Understanding the size, shape, and application-specific properties of quartz lumps versus quartz granules is essential for selecting the appropriate form in engineering and commercial processes.
Key Differences Between Quartz Lumps and Granules
Quartz lumps are larger, irregularly shaped pieces typically ranging from 5 to 50 mm, while quartz granules are smaller, more uniform particles usually between 0.5 to 5 mm. The size difference affects their industrial applications, with lumps preferred for use in high-temperature processes and granules favored for precision casting and filtration. Quartz lumps have a lower surface area-to-volume ratio compared to granules, impacting reactivity and processing efficiency.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Quartz lumps exhibit larger, irregular crystal formations with higher mechanical strength and lower surface area compared to quartz granules, which possess smaller, more uniform particles with increased surface area enhancing reactivity. Chemically, both quartz lumps and granules consist primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with high purity levels, but granules may show slight variations in trace mineral content due to their finer size and processing methods. The physical differences impact their applications, where lumps are preferred for heavy-duty industrial uses, while granules suit filtration and abrasive purposes.
Applications of Quartz Lumps in Industry
Quartz lumps are predominantly utilized in the electronics and glass manufacturing industries due to their large, pure crystalline structure, which ensures high thermal stability and minimal impurities. Their robustness makes them ideal for use in furnace linings, silicon wafer production, and quartz crucibles essential in semiconductor fabrication. Compared to quartz granules, lumps offer enhanced durability and heat resistance, facilitating critical industrial processes requiring consistent high-temperature performance.
Uses of Quartz Granules Across Sectors
Quartz granules find extensive application across various industries due to their high purity, uniform size, and heat resistance. In construction, they enhance the strength and durability of concrete and mortars, while in electronics, they serve as essential components in producing oscillators and resonators. The abrasive quality of quartz granules is leveraged in the manufacture of sandpaper and scouring products, making them indispensable in both industrial and consumer markets.
Processing and Sizing Methods for Quartz
Quartz lumps are raw, unprocessed chunks typically ranging from 25mm to over 100mm, requiring primary crushing and coarse screening to break them down into smaller, manageable sizes. Quartz granules, on the other hand, are further processed particles usually sized between 2mm to 25mm, achieved through secondary crushing, milling, and precise screening techniques to ensure uniform granule size. Efficient processing methods incorporate jaw crushers, impact crushers, and vibrating screens to optimize size distribution for industrial applications in glass manufacturing and electronics.
Quality Standards: Lumps vs Granules
Quartz lumps exhibit higher purity levels with fewer impurities compared to quartz granules, adhering to stricter quality standards crucial for industrial applications. The grain size uniformity in quartz lumps ensures consistent chemical composition and enhanced mechanical strength, making them preferable for precision tasks. Conversely, quartz granules, while versatile, often require additional processing to meet equivalent quality thresholds.
Cost Considerations: Lumps Versus Granules
Quartz lumps generally have a higher upfront cost compared to quartz granules due to their larger size and more extensive processing requirements. Quartz granules offer a more cost-effective option for projects requiring finer material, as they are produced in bulk with less intensive processing. Cost considerations also depend on specific applications, with lumps favored for high-purity industrial uses and granules preferred for construction and decorative purposes.
Choosing the Right Form for Your Application
Quartz lumps offer larger, irregularly shaped pieces ideal for applications requiring high durability and strength, such as industrial casting or filtration. Quartz granules provide smaller, uniform particles suitable for precision tasks like abrasive blasting or manufacturing electronics where fine texture and consistency are crucial. Selecting between lumps and granules hinges on the required granularity, surface area, and mechanical properties for optimal performance in specific industrial or scientific processes.
Future Trends in Quartz Material Utilization
Quartz lumps and quartz granules are poised to play significant roles in the evolving market of advanced electronics and green energy applications. Innovations in nanotechnology and enhanced processing techniques are increasing the demand for quartz granules due to their higher surface area and reactivity in semiconductor manufacturing. Sustainable mining practices and recycling of quartz lumps are anticipated to reduce environmental impact while meeting the growing need for high-purity quartz in photovoltaic cells and optical devices.
Quartz Lumps vs Quartz Granules Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com