Transparent quartz showcases a clear, glass-like appearance that allows light to pass through, enhancing its visual appeal and making it popular for decorative and metaphysical uses. Opaque quartz, in contrast, lacks transparency due to inclusions or mineral impurities, presenting a solid, matte finish that offers a more grounded and earthy aesthetic. Both types serve distinct purposes in jewelry and healing practices, with transparent quartz symbolizing clarity and energy flow, while opaque quartz is valued for protection and stability.
Table of Comparison
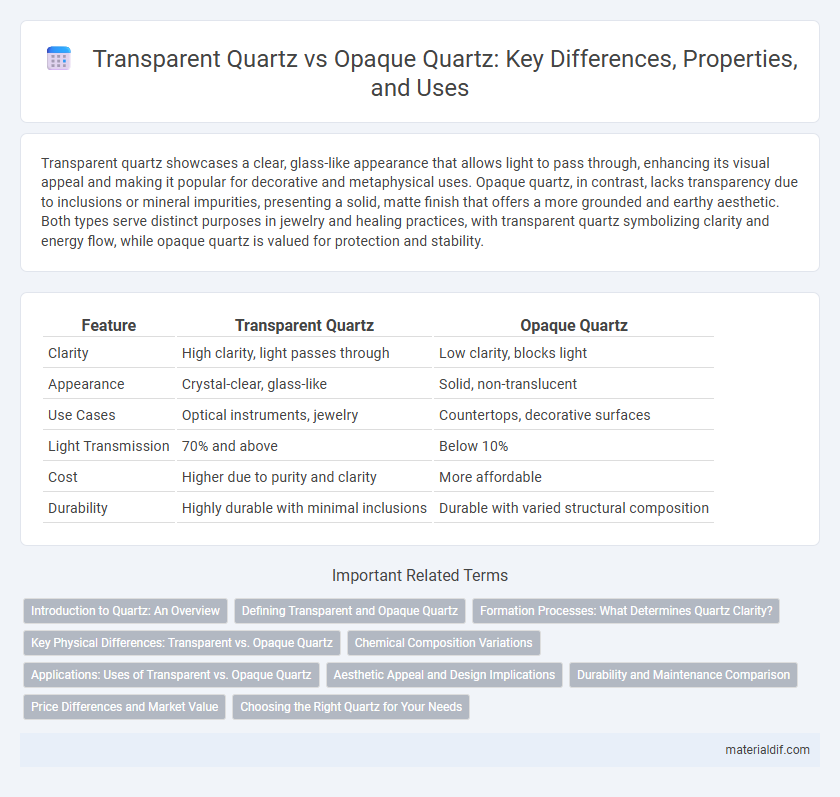
| Feature | Transparent Quartz | Opaque Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Clarity | High clarity, light passes through | Low clarity, blocks light |
| Appearance | Crystal-clear, glass-like | Solid, non-translucent |
| Use Cases | Optical instruments, jewelry | Countertops, decorative surfaces |
| Light Transmission | 70% and above | Below 10% |
| Cost | Higher due to purity and clarity | More affordable |
| Durability | Highly durable with minimal inclusions | Durable with varied structural composition |
Introduction to Quartz: An Overview
Quartz, a versatile mineral composed of silicon dioxide, exists primarily in two forms: transparent and opaque. Transparent quartz, known for its clarity and luminous appearance, is highly valued in electronics and optical applications due to its ability to transmit light and withstand high temperatures. Opaque quartz, characterized by its solid, non-transmissive surface, is commonly used in construction and decorative stonework for its durability and aesthetic diversity.
Defining Transparent and Opaque Quartz
Transparent quartz is characterized by its clear, glass-like appearance, allowing light to pass through with minimal distortion, which makes it ideal for optical applications and jewelry. Opaque quartz, however, lacks translucency due to the presence of inclusions or mineral impurities, resulting in a solid appearance that blocks light entirely. These fundamental differences in clarity and light transmission define their distinct uses in various industrial and decorative contexts.
Formation Processes: What Determines Quartz Clarity?
Quartz clarity is primarily determined by the presence or absence of microscopic inclusions and structural impurities during the crystal's formation. Transparent quartz forms in environments with minimal mineral impurities and stable growth conditions, allowing light to pass through without significant scattering. In contrast, opaque quartz contains trapped minerals, gas bubbles, or tiny fractures caused by rapid crystallization or environmental disturbances, inhibiting transparency.
Key Physical Differences: Transparent vs. Opaque Quartz
Transparent quartz exhibits clarity and light transmission due to fewer inclusions and internal fractures, allowing it to refract light and appear glass-like. Opaque quartz, in contrast, contains numerous inclusions or structural impurities that scatter light, resulting in a solid, non-translucent appearance. These key physical differences impact their use in jewelry, decorative objects, and optical applications.
Chemical Composition Variations
Transparent quartz and opaque quartz differ primarily in their chemical composition variations, with transparent quartz consisting mainly of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) that allows light to pass through without significant scattering. Opaque quartz contains impurities such as iron, aluminum, or microscopic inclusions that disrupt the crystal lattice, causing light to be absorbed or reflected, resulting in its non-transparent appearance. These variations in trace elements and structural defects directly influence the optical properties and industrial applications of each quartz type.
Applications: Uses of Transparent vs. Opaque Quartz
Transparent quartz is widely used in optical instruments, watches, and electronics due to its clarity and ability to transmit light with minimal distortion. Opaque quartz, with its varied colors and textures, is favored in construction, decorative countertops, and jewelry where aesthetic appeal and durability are essential. Both types serve critical roles in industrial and design applications, leveraging their distinct physical and visual properties.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Implications
Transparent quartz enhances interior spaces with its luminous clarity and light-reflecting properties, creating a sense of openness and elegance. Opaque quartz offers a more solid, uniform appearance with rich color depths and varied patterns, adding a bold, sophisticated touch to surfaces. Designers often select transparent quartz for modern, minimalist aesthetics, while opaque quartz suits traditional or rustic themes, influencing lighting, color coordination, and spatial perception.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Transparent quartz exhibits higher durability due to its dense crystalline structure that resists scratches and impacts more effectively than opaque quartz. Maintenance for transparent quartz is minimal, requiring only regular cleaning with mild soap and water to preserve its clarity and prevent surface buildup. In contrast, opaque quartz may show wear more quickly and can accumulate dirt in its textured surface, demanding more frequent and careful upkeep to maintain its appearance.
Price Differences and Market Value
Transparent quartz, often referred to as clear quartz, commands higher market value due to its optical clarity, making it highly sought after for jewelry and decorative applications. Opaque quartz varieties, such as milky or rose quartz, generally have lower prices because their lack of transparency limits their use in premium designs. The price difference between transparent and opaque quartz can vary significantly, with transparent types fetching up to three times the price of common opaque stones in both retail and wholesale markets.
Choosing the Right Quartz for Your Needs
Transparent quartz offers superior clarity and light transmission, making it ideal for decorative applications, optical instruments, and jewelry where visual appeal and purity are crucial. Opaque quartz provides enhanced durability and resistance to scratches and stains, suitable for countertops, flooring, and industrial uses where strength and maintenance are priorities. Selecting the right quartz depends on balancing aesthetic requirements with functional demands, ensuring the material aligns with specific design and performance goals.
Transparent Quartz vs Opaque Quartz Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com