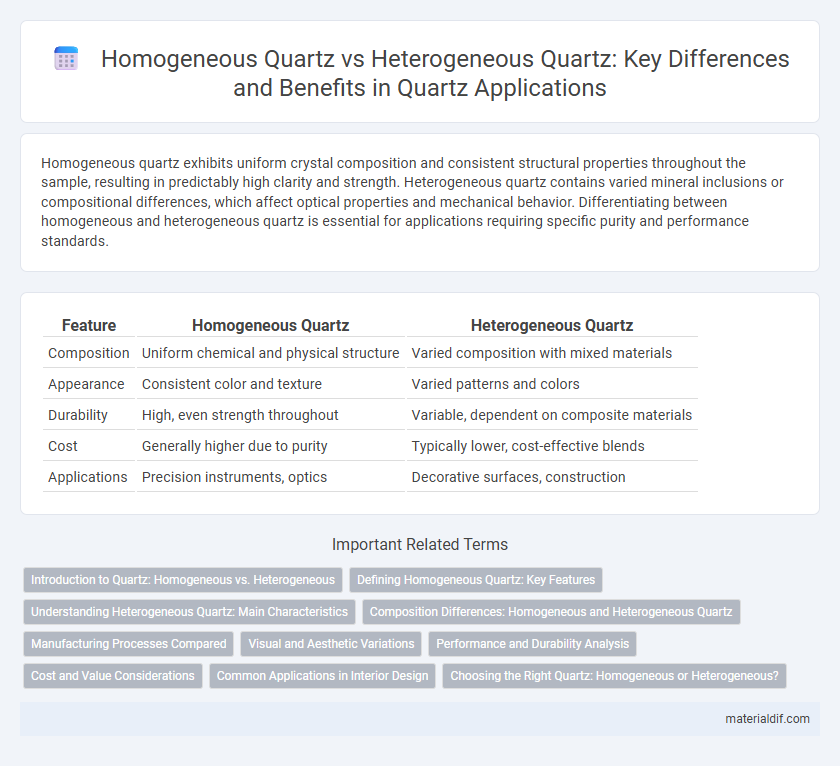
Homogeneous quartz exhibits uniform crystal composition and consistent structural properties throughout the sample, resulting in predictably high clarity and strength. Heterogeneous quartz contains varied mineral inclusions or compositional differences, which affect optical properties and mechanical behavior. Differentiating between homogeneous and heterogeneous quartz is essential for applications requiring specific purity and performance standards.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Homogeneous Quartz | Heterogeneous Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Uniform chemical and physical structure | Varied composition with mixed materials |
| Appearance | Consistent color and texture | Varied patterns and colors |
| Durability | High, even strength throughout | Variable, dependent on composite materials |
| Cost | Generally higher due to purity | Typically lower, cost-effective blends |
| Applications | Precision instruments, optics | Decorative surfaces, construction |
Introduction to Quartz: Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous
Homogeneous quartz consists of uniformly structured silicon dioxide crystals with consistent chemical composition and optical properties throughout the material. In contrast, heterogeneous quartz contains variations in crystal size, impurities, or inclusions, resulting in diverse physical and chemical characteristics within the same sample. Understanding these differences is crucial for applications in optics, electronics, and geology where material uniformity impacts performance and reliability.
Defining Homogeneous Quartz: Key Features
Homogeneous quartz is characterized by uniform composition and consistent physical properties throughout the crystal, making it ideal for electronic and optical applications. Key features include a single dominant crystallographic orientation, absence of visible inclusions or color zoning, and stable chemical purity which ensures reliable performance in high-precision devices. This uniformity contrasts with heterogeneous quartz, where varying mineral inclusions or compositional gradients can affect functionality and durability.
Understanding Heterogeneous Quartz: Main Characteristics
Heterogeneous quartz is characterized by variations in its crystal structure, chemical composition, and physical properties, resulting from impurities or mixed phases within the quartz matrix. Unlike homogeneous quartz, which exhibits uniformity and consistency, heterogeneous quartz often displays diverse coloration, inclusions, and irregular growth patterns that affect its optical and mechanical behavior. These distinguishing features make heterogeneous quartz valuable in geological studies and industrial applications where material variability is crucial.
Composition Differences: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Quartz
Homogeneous quartz consists of a uniform chemical composition primarily made up of silicon dioxide (SiO2), resulting in consistent physical and optical properties throughout the crystal. Heterogeneous quartz contains variations in composition due to inclusions, impurities, or the presence of multiple mineral phases, causing localized differences in color, clarity, and structural characteristics. These compositional differences influence the quartz's applications in electronics, optics, and jewelry by affecting durability and electronic conductivity.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Homogeneous quartz manufacturing involves controlled growth techniques such as hydrothermal synthesis, yielding uniform crystalline structures with consistent purity and mechanical properties ideal for precision applications. Heterogeneous quartz production typically includes natural quartz mining followed by crushing and size classification, resulting in variations in crystal composition and quality due to inherent geological impurities. The controlled environment and process parameters in homogeneous quartz manufacturing provide enhanced reliability over the variable nature of heterogeneous quartz sourced from natural deposits.
Visual and Aesthetic Variations
Homogeneous quartz features a consistent color and pattern throughout the slab, offering a uniform and sleek appearance ideal for minimalist designs. Heterogeneous quartz displays varied tones, veining, and textures created by combining different minerals, resulting in more dynamic and natural stone-like aesthetics. These visual and aesthetic variations allow designers to choose quartz surfaces that either complement modern environments with subtlety or enhance traditional spaces with rich, intricate patterns.
Performance and Durability Analysis
Homogeneous quartz exhibits consistent composition throughout, resulting in superior performance and enhanced durability due to uniform thermal and mechanical properties. Heterogeneous quartz, with its varied mineral content and inconsistent structure, may experience uneven wear and reduced resistance to fractures under stress. Performance analysis reveals homogeneous quartz materials maintain stability under fluctuating temperatures and physical impact, making them ideal for high-precision applications, while heterogeneous quartz is more prone to degradation over time.
Cost and Value Considerations
Homogeneous quartz offers consistent color and pattern throughout the slab, often resulting in higher manufacturing costs but increased durability and aesthetic value, making it ideal for premium applications. Heterogeneous quartz, characterized by variations in pattern and color, tends to be less expensive due to simpler production processes, appealing to budget-conscious projects without compromising basic functionality. Cost considerations for homogeneous versus heterogeneous quartz largely depend on the intended use, with homogeneous quartz providing greater long-term value in high-traffic or luxury environments.
Common Applications in Interior Design
Homogeneous quartz surfaces, with their consistent color and pattern, are commonly used for kitchen countertops and bathroom vanities, providing a sleek and uniform look that enhances modern interior designs. Heterogeneous quartz, featuring varied textures and intricate patterns, is ideal for decorative wall cladding and custom furniture, adding depth and visual interest to living spaces. Both types of quartz offer durability and low maintenance, making them popular choices for high-traffic areas in residential and commercial interiors.
Choosing the Right Quartz: Homogeneous or Heterogeneous?
Choosing the right quartz involves understanding the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous quartz structures. Homogeneous quartz features a uniform composition and consistent physical properties, ideal for applications requiring predictable performance and clarity. Heterogeneous quartz contains varied mineral inclusions or structural inconsistencies, making it suitable for decorative purposes or uses where unique optical effects are desired.
Homogeneous Quartz vs Heterogeneous Quartz Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com