Quartz stone offers superior durability and low maintenance compared to granite stone, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and busy kitchens. Unlike granite, quartz is non-porous, which enhances its resistance to stains, bacteria, and moisture damage. While granite provides a unique, natural appearance with varied patterns, quartz delivers consistent color and design, allowing for more customization in modern interior applications.
Table of Comparison
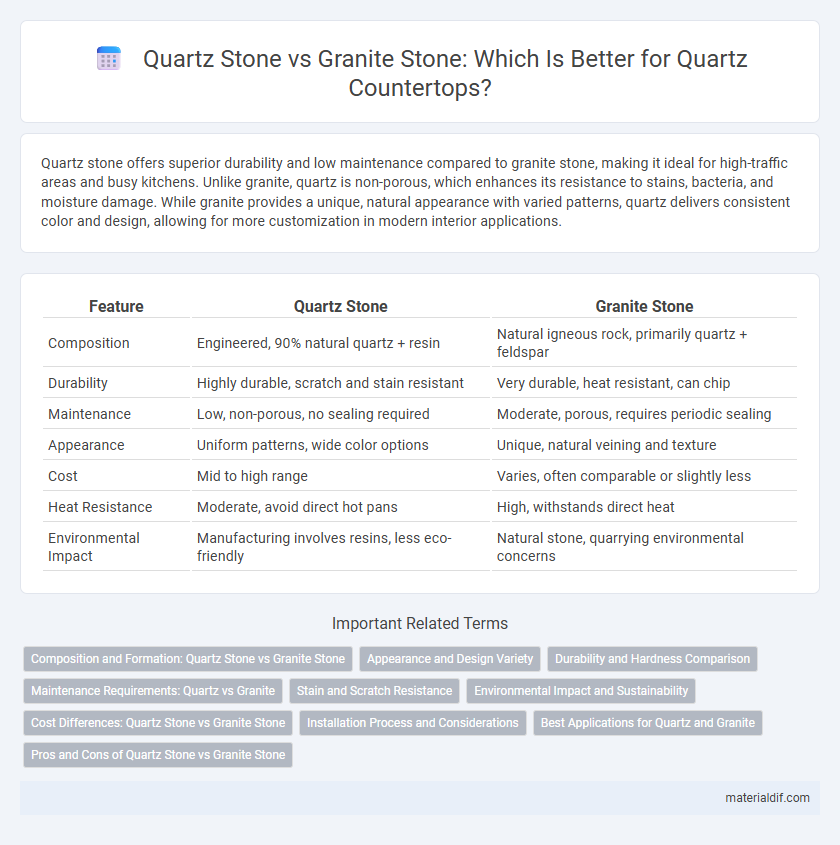
| Feature | Quartz Stone | Granite Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Engineered, 90% natural quartz + resin | Natural igneous rock, primarily quartz + feldspar |
| Durability | Highly durable, scratch and stain resistant | Very durable, heat resistant, can chip |
| Maintenance | Low, non-porous, no sealing required | Moderate, porous, requires periodic sealing |
| Appearance | Uniform patterns, wide color options | Unique, natural veining and texture |
| Cost | Mid to high range | Varies, often comparable or slightly less |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, avoid direct hot pans | High, withstands direct heat |
| Environmental Impact | Manufacturing involves resins, less eco-friendly | Natural stone, quarrying environmental concerns |
Composition and Formation: Quartz Stone vs Granite Stone
Quartz stone is engineered by combining natural quartz crystals with resins and pigments, creating a non-porous, durable surface with consistent patterns and colors. Granite stone forms naturally through the slow crystallization of magma beneath the Earth's surface, resulting in a coarse-grained texture composed mainly of quartz, feldspar, and mica. The difference in formation impacts their physical properties, with granite offering natural variation and quartz providing uniformity and enhanced resistance to stains.
Appearance and Design Variety
Quartz stone offers a consistent and uniform appearance with a wide range of colors and patterns, including options that mimic natural stone or feature bold, modern designs. Granite stone exhibits unique, natural veining and speckling, providing distinctive patterns that vary from slab to slab, emphasizing organic beauty. Quartz's engineered composition allows for greater design versatility, while granite's natural formation results in one-of-a-kind aesthetics prized in traditional and rustic decor.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Quartz stone exhibits superior durability compared to granite stone due to its engineered composition, making it highly resistant to scratches, stains, and impact. Granite, a natural igneous rock, provides excellent hardness and heat resistance but is more porous, requiring regular sealing to prevent damage. The Mohs hardness scale rates quartz around 7, while granite ranges from 6 to 7, positioning quartz as slightly more resilient under daily wear conditions.
Maintenance Requirements: Quartz vs Granite
Quartz stone requires low maintenance due to its non-porous surface, which resists staining and eliminates the need for sealing. Granite stone, being porous, demands regular sealing to maintain its resistance to stains and bacteria. Cleaning quartz only needs mild soap and water, whereas granite requires specialized cleaners to preserve its natural finish.
Stain and Scratch Resistance
Quartz stone exhibits superior stain resistance compared to granite due to its non-porous surface, which prevents liquids from penetrating and causing discoloration. Scratch resistance in quartz is enhanced by its engineered composition, blending natural quartz crystals with resins that create a durable, hard surface. Granite, while naturally hard, tends to be more porous and can be susceptible to staining and surface scratches if not properly sealed and maintained.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Quartz stone production typically has a lower environmental impact compared to granite due to its engineered nature, which utilizes abundant natural quartz and recycled materials. Granite quarrying involves extensive extraction processes that contribute to habitat disruption and higher energy consumption. Quartz surfaces offer enhanced sustainability through reduced waste and longer lifespan, making them a greener choice for eco-conscious consumers.
Cost Differences: Quartz Stone vs Granite Stone
Quartz stone typically costs between $50 and $150 per square foot, influenced by factors such as brand, color, and pattern complexity. Granite stone prices range from $40 to $200 per square foot, depending on rarity, origin, and finish quality. Quartz tends to offer more consistent pricing due to its engineered nature, while granite's natural variations can lead to higher fluctuations in cost.
Installation Process and Considerations
Quartz stone installation requires precise handling due to its engineered composition, demanding professional expertise to avoid damage during cutting and fitting. Granite stone, being natural and heavier, often necessitates reinforced support structures and skilled labor to accommodate its irregularities and weight. Both materials require careful templating and sealing considerations, but quartz typically allows for more uniform seams and less post-installation maintenance.
Best Applications for Quartz and Granite
Quartz stone excels in kitchen countertops and bathroom vanities due to its non-porous surface, resisting stains and requiring low maintenance. Granite stone is ideal for outdoor applications and high-heat areas like fireplace surrounds, thanks to its natural durability and heat resistance. Both stones offer unique aesthetic appeal, with quartz providing uniform patterns and granite showcasing natural veining.
Pros and Cons of Quartz Stone vs Granite Stone
Quartz stone offers superior non-porosity and low maintenance, making it highly resistant to stains and bacteria compared to granite. Granite provides natural variability and heat resistance, but it requires periodic sealing to prevent moisture absorption and potential damage. Quartz's engineered consistency allows for a broader range of colors and patterns, while granite's natural fissures may lead to chipping or cracking under heavy impact.
Quartz Stone vs Granite Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com