Porcelain insulators offer superior mechanical strength and excellent resistance to environmental factors compared to glass insulators, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Glass insulators, while providing better visibility for detecting defects and easier recyclability, are more prone to breakage under mechanical stress. Both materials have distinct advantages, but porcelain's durability ensures longer service life in harsh conditions.
Table of Comparison
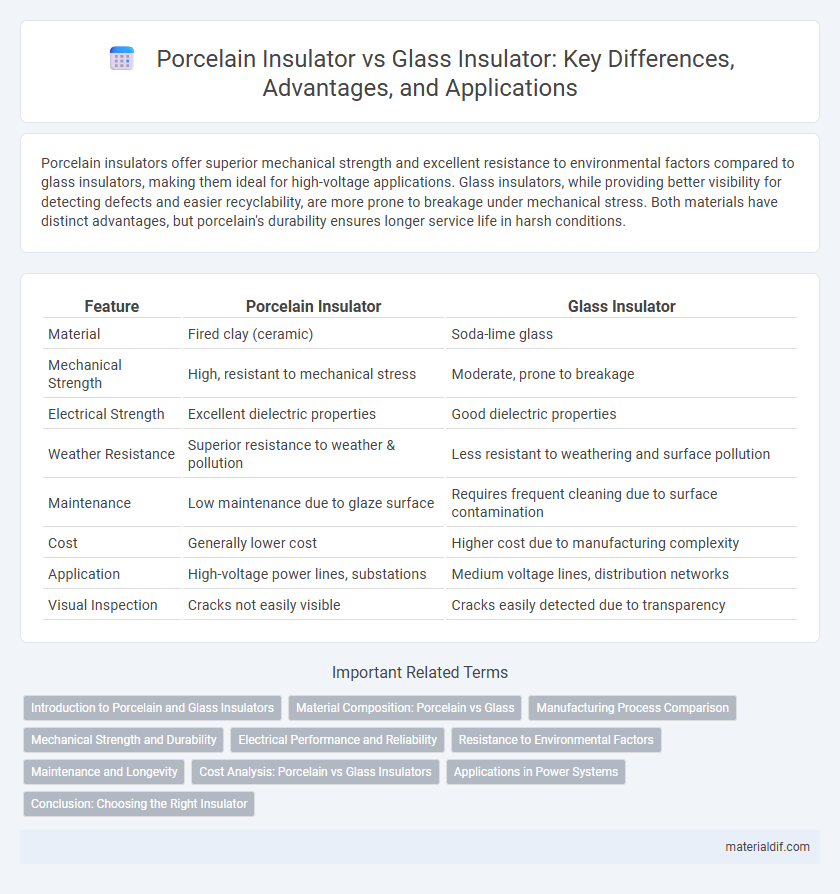
| Feature | Porcelain Insulator | Glass Insulator |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Fired clay (ceramic) | Soda-lime glass |
| Mechanical Strength | High, resistant to mechanical stress | Moderate, prone to breakage |
| Electrical Strength | Excellent dielectric properties | Good dielectric properties |
| Weather Resistance | Superior resistance to weather & pollution | Less resistant to weathering and surface pollution |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to glaze surface | Requires frequent cleaning due to surface contamination |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity |
| Application | High-voltage power lines, substations | Medium voltage lines, distribution networks |
| Visual Inspection | Cracks not easily visible | Cracks easily detected due to transparency |
Introduction to Porcelain and Glass Insulators
Porcelain insulators, made from high-strength ceramic materials, exhibit excellent electrical resistance and mechanical durability, making them ideal for high-voltage power transmission. Glass insulators, composed of tempered glass, offer superior visibility and high tensile strength but are more prone to impact damage compared to porcelain. Both types are critical in electrical engineering for preventing current leakage and maintaining system reliability in power distribution networks.
Material Composition: Porcelain vs Glass
Porcelain insulators are composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, which provide excellent mechanical strength and resistance to weathering. Glass insulators, made from tempered soda-lime silica glass, offer superior transparency and resistance to chemical corrosion but are more brittle under mechanical stress. The high dielectric strength and durability of porcelain make it ideal for heavy-load applications, while glass excels in environments requiring visual inspection of insulator integrity.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Porcelain insulators are manufactured by firing a mixture of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz at temperatures exceeding 1300degC, resulting in a dense, durable ceramic material with excellent electrical properties. Glass insulators are produced by melting raw materials such as silica sand, soda ash, and limestone at around 1500degC, followed by controlled cooling to create a transparent or translucent glass structure with high dielectric strength. The porcelain process emphasizes sintering and vitrification for mechanical strength, while glass manufacturing relies on precise melting and annealing to ensure structural integrity and insulation performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to glass insulators, making them more resistant to physical impacts and heavy loads in high-voltage applications. Their high compressive strength and excellent toughness contribute to enhanced durability, allowing porcelain insulators to withstand harsh weather conditions and mechanical stresses over extended periods. In contrast, glass insulators, while offering good electrical insulation, tend to be more brittle and vulnerable to shattering under impact, reducing their long-term reliability in demanding environments.
Electrical Performance and Reliability
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior electrical performance compared to glass insulators due to their higher dielectric strength and better resistance to surface contamination, ensuring consistent insulation under various environmental conditions. Porcelain's inherent mechanical robustness and resistance to thermal shock contribute to enhanced reliability and longevity in high-voltage applications. While glass insulators offer excellent visibility for damage detection, porcelain's overall electrical insulation and durability make it the preferred choice for critical infrastructure.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Porcelain insulators exhibit superior resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and pollution, making them highly durable in harsh outdoor conditions. Glass insulators, while aesthetically clear and resistant to chemical corrosion, tend to be more brittle and susceptible to damage from mechanical impacts and extreme temperature variations. Porcelain's non-porous surface and robust material composition provide enhanced performance in resisting weathering and contamination buildup compared to glass insulators.
Maintenance and Longevity
Porcelain insulators provide superior durability and require less frequent maintenance compared to glass insulators due to their resistance to weathering and mechanical stress. They exhibit higher mechanical strength, reducing the risk of cracks and contamination buildup, which extends their operational lifespan. Glass insulators, while offering excellent electrical insulation, are more prone to damage and surface deterioration, leading to increased maintenance efforts over time.
Cost Analysis: Porcelain vs Glass Insulators
Porcelain insulators typically cost more than glass insulators due to higher manufacturing expenses and material durability, offering longer service life and better resistance to environmental stress. Glass insulators, while cheaper initially, may require more frequent replacements and maintenance, impacting long-term expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, porcelain insulators provide better value in high-stress or corrosive environments despite the higher upfront investment.
Applications in Power Systems
Porcelain insulators offer superior mechanical strength and weather resistance, making them ideal for high-voltage transmission lines and heavy-load power systems. Glass insulators provide excellent electrical insulation and visibility for defect detection, often used in lower voltage distribution networks and areas prone to contamination. Both materials serve critical roles in power systems, selected based on environmental conditions and operational requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulator
Porcelain insulators provide superior mechanical strength and excellent resistance to weathering, making them ideal for high-voltage and heavy-load applications, while glass insulators offer greater visibility for surface defects and high dielectric strength, which improves operational safety. The choice between porcelain and glass insulators depends on specific project requirements such as environmental conditions, mechanical stress, and cost considerations. Selecting the right insulator ensures optimal performance, reliability, and longevity in electrical power systems.
Porcelain Insulator vs Glass Insulator Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com