Spun polyester consists of short fibers twisted together, creating a soft and breathable fabric ideal for comfort and warmth in clothing and upholstery. Filament polyester is made from long continuous fibers, offering a smooth, strong, and durable material commonly used in outdoor gear and industrial applications. Spun polyester provides better moisture absorption, while filament polyester excels in abrasion resistance and maintaining shape.
Table of Comparison
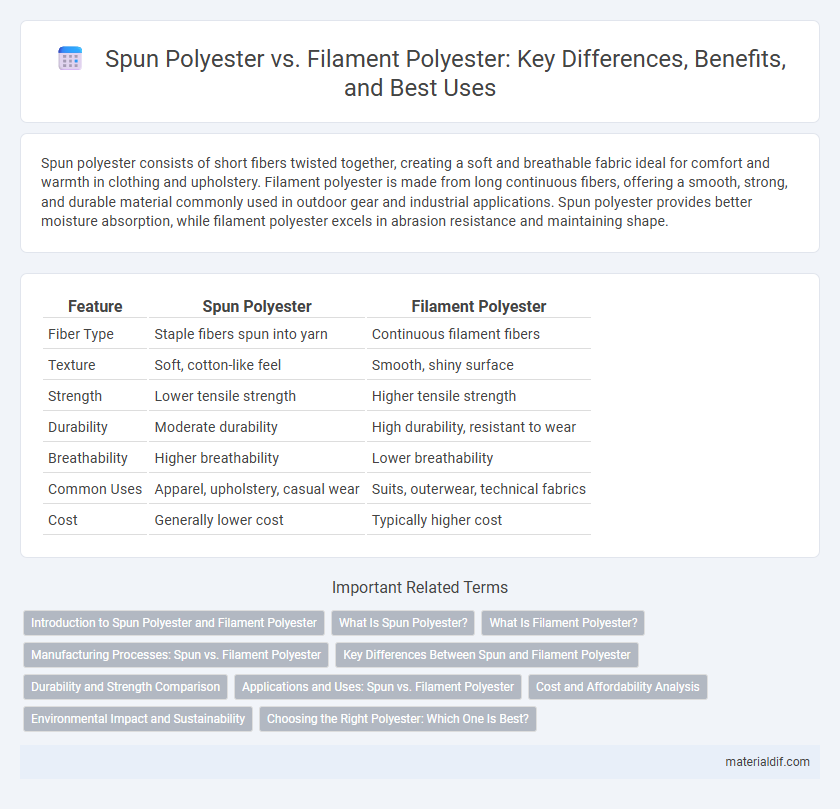
| Feature | Spun Polyester | Filament Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Staple fibers spun into yarn | Continuous filament fibers |
| Texture | Soft, cotton-like feel | Smooth, shiny surface |
| Strength | Lower tensile strength | Higher tensile strength |
| Durability | Moderate durability | High durability, resistant to wear |
| Breathability | Higher breathability | Lower breathability |
| Common Uses | Apparel, upholstery, casual wear | Suits, outerwear, technical fabrics |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
Introduction to Spun Polyester and Filament Polyester
Spun polyester is made by spinning short polyester fibers together to create a yarn that closely resembles natural cotton in texture and softness. Filament polyester, on the other hand, consists of long continuous fibers that offer higher strength, durability, and a smooth, lustrous finish. Both types serve different applications, with spun polyester used in apparel and home textiles, while filament polyester is preferred for industrial and performance fabrics.
What Is Spun Polyester?
Spun polyester is a type of polyester fiber created by spinning short polyester staple fibers into yarn, resembling natural cotton in texture and appearance. It provides enhanced breathability and softness, making it ideal for apparel and home textiles where comfort is key. Unlike filament polyester, spun polyester offers improved moisture absorption and a matte finish due to its staple fiber construction.
What Is Filament Polyester?
Filament polyester consists of continuous strands of synthetic fibers that provide a smooth, lustrous appearance and superior strength compared to spun polyester. It is commonly used in applications requiring durability and a sleek finish, such as upholstery, outdoor gear, and high-performance textiles. The continuous filament structure enhances moisture-wicking properties and reduces pilling, making it ideal for long-lasting, high-quality fabric products.
Manufacturing Processes: Spun vs. Filament Polyester
Spun polyester is produced by first melting polyester chips and then extruding them through spinnerets to create short fibers, which are subsequently spun into yarns, resembling natural fibers like cotton. Filament polyester manufacturing involves extruding continuous filaments directly from molten polyester, resulting in smooth, strong fibers ideal for high-performance fabrics. The key difference lies in fiber length and texture, with spun polyester offering a fuzzier, softer feel and filament polyester providing durability and sheen.
Key Differences Between Spun and Filament Polyester
Spun polyester is produced by short staple fibers spun together, resembling the feel and texture of cotton, making it breathable and soft, ideal for apparel and home textiles. Filament polyester consists of continuous long fibers that provide a smooth, lustrous finish with higher strength and durability, commonly used in industrial fabrics and elegant apparel. Key differences lie in fiber length, texture, breathability, and application suitability, with spun polyester favored for comfort and filament polyester for strength and sheen.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Spun polyester fibers, produced by twisting staple fibers, offer moderate strength and are more prone to abrasion compared to filament polyester, which consists of continuous long fibers providing superior tensile strength and durability. Filament polyester exhibits enhanced resistance to stretching and tearing, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications where fabric longevity is critical. The structural integrity of filament fibers contributes to greater performance in high-stress environments, outperforming spun polyester in wear resistance and overall durability.
Applications and Uses: Spun vs. Filament Polyester
Spun polyester fibers, known for their soft texture and breathability, are widely used in apparel, home textiles, and upholstery where comfort and moisture absorption are prioritized. Filament polyester, characterized by smooth, continuous fibers, is preferred in industrial applications, technical textiles, and high-performance fabrics due to its strength, durability, and resistance to stretching. The choice between spun and filament polyester depends on specific application requirements, with spun fibers suited for softness and filament fibers for robustness and longevity.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Spun polyester fibers, created by cutting continuous filament fibers into staple lengths, generally incur lower production costs due to simpler manufacturing processes and suitability for blending with other fibers, making them more affordable for mass-market applications. Filament polyester, composed of long, continuous fibers, offers higher durability and smoothness but involves higher raw material and processing expenses, leading to increased costs. The affordability of spun polyester positions it as a cost-effective option for budget-conscious consumers, while filament polyester is preferred in premium textile products where quality justifies the price.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spun polyester, made from staple fibers, often requires more energy and water during processing, leading to a higher environmental footprint compared to filament polyester, which uses continuous fibers and allows for more efficient manufacturing. Filament polyester typically offers better durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacement and contributing to sustainability. Recycling capabilities are more advanced for filament polyester, enhancing circularity and minimizing waste in textile production.
Choosing the Right Polyester: Which One Is Best?
Spun polyester, made from short fibers twisted together, offers a softer feel and better moisture absorption, making it ideal for apparel and home textiles. Filament polyester consists of continuous fibers that provide higher strength, durability, and a smooth finish, preferred for industrial applications and high-performance fabrics. Selecting the right polyester depends on the intended use, where comfort favors spun polyester and longevity or technical performance calls for filament polyester.
Spun polyester vs Filament polyester Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com