Polyester film offers excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for packaging and electrical insulation applications. Polycarbonate film provides superior impact resistance, higher temperature tolerance, and enhanced optical clarity, which suits protective coatings and automotive parts. Choosing between polyester and polycarbonate film depends on the specific durability, flexibility, and thermal requirements of the intended use.
Table of Comparison
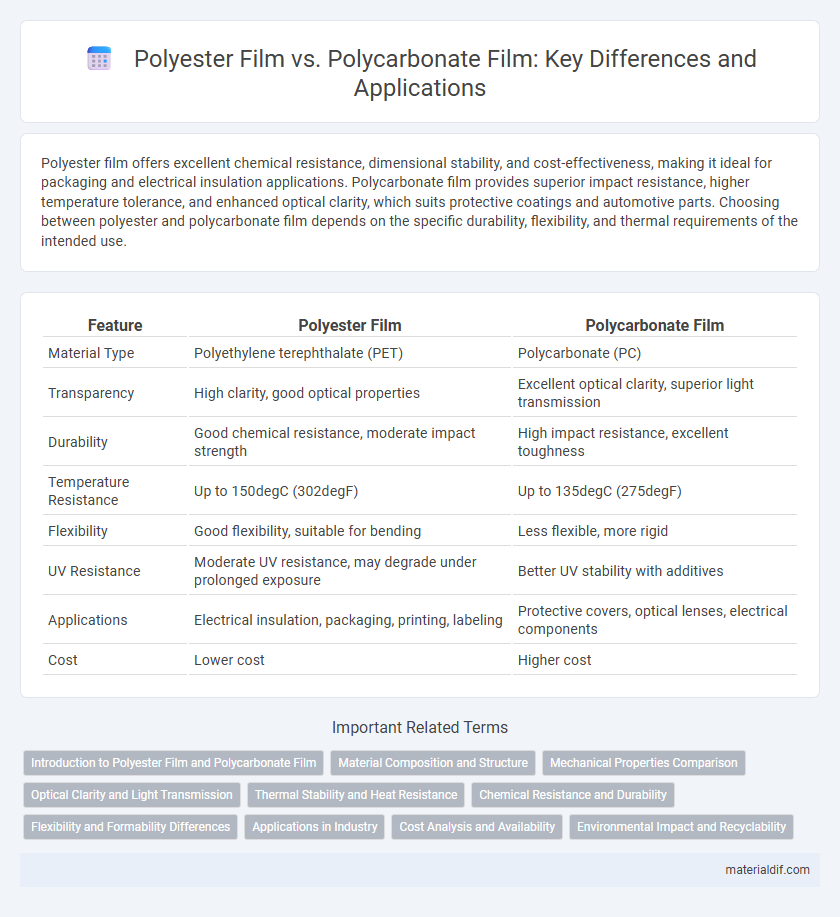
| Feature | Polyester Film | Polycarbonate Film |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
| Transparency | High clarity, good optical properties | Excellent optical clarity, superior light transmission |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, moderate impact strength | High impact resistance, excellent toughness |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC (302degF) | Up to 135degC (275degF) |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, suitable for bending | Less flexible, more rigid |
| UV Resistance | Moderate UV resistance, may degrade under prolonged exposure | Better UV stability with additives |
| Applications | Electrical insulation, packaging, printing, labeling | Protective covers, optical lenses, electrical components |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Polyester Film and Polycarbonate Film
Polyester film, known for its excellent tensile strength, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance, is widely used in electrical insulation, packaging, and imaging applications. Polycarbonate film offers superior impact resistance, optical clarity, and heat resistance, making it ideal for protective coatings, electronic displays, and medical devices. Both films exhibit unique physical and chemical properties, with polyester film excelling in moisture resistance and polycarbonate film providing enhanced toughness and transparency.
Material Composition and Structure
Polyester film is composed primarily of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), featuring a highly crystalline structure that provides excellent tensile strength and chemical resistance. In contrast, polycarbonate film is made from a thermoplastic polymer derived from bisphenol A and phosgene, characterized by an amorphous structure that offers superior impact resistance and optical clarity. The distinct molecular architectures of polyester and polycarbonate films determine their mechanical properties and suitability for various industrial applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyester film exhibits superior tensile strength and dimensional stability compared to polycarbonate film, making it more resistant to stretching and deformation under mechanical stress. Polycarbonate film, however, offers higher impact resistance and greater flexibility, which enhances its performance in applications requiring durability under dynamic loads. Both materials provide excellent mechanical properties, but polyester film is preferred for stable, load-bearing uses while polycarbonate excels in impact-intensive environments.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Polyester film offers excellent optical clarity with high transparency, allowing light transmission rates typically above 90%, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility and minimal distortion. Polycarbonate film also provides good light transmission, generally around 85-90%, but with superior impact resistance and durability compared to polyester. Both films are used in optical and protective applications, but polyester's higher light transmission and clarity make it preferable for display and printing uses where visual quality is critical.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polyester film exhibits superior thermal stability, maintaining its structural integrity at temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for applications requiring consistent performance under heat. Polycarbonate film offers excellent heat resistance but typically deforms at lower temperatures around 130degC, limiting its use in high-temperature environments. The higher glass transition temperature of polyester film ensures better dimensional stability and durability in thermal-intensive applications compared to polycarbonate film.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polyester film exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polycarbonate film, effectively withstanding exposure to acids, alkalis, and solvents without significant degradation. Polyester film also offers greater durability under prolonged UV exposure and maintaining mechanical strength in harsh environments. Polycarbonate film, while impact-resistant, tends to yellow and degrade chemically over time, making polyester film the preferred choice for applications requiring long-term chemical stability and environmental endurance.
Flexibility and Formability Differences
Polyester film exhibits greater flexibility and superior formability compared to polycarbonate film, making it ideal for applications requiring bending and shaping without cracking. Polyester's molecular structure allows it to withstand repeated flexing and stretching, whereas polycarbonate film is more rigid and prone to stress fractures under similar conditions. These differences affect their suitability for packaging, electrical insulation, and flexible display substrates, where durability under deformation is critical.
Applications in Industry
Polyester film is widely used in packaging, electrical insulation, and flexible printed circuits due to its excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and clarity. Polycarbonate film, known for its impact resistance and high heat tolerance, is favored in applications requiring durability such as automotive glazing, optical lenses, and industrial safety shields. Both films serve critical roles in electronics and manufacturing industries, with polyester excelling in lightweight, flexible uses and polycarbonate providing robust protection in demanding environments.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Polyester film offers a cost-effective solution with widespread availability due to its extensive production and lower raw material expenses compared to polycarbonate film. Polycarbonate film, while providing superior impact resistance and optical clarity, comes at a significantly higher price point and limited availability, often restricted to specialized suppliers. Businesses prioritizing budget and mass distribution commonly select polyester film, whereas applications demanding enhanced durability may justify the premium cost of polycarbonate film.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyester film demonstrates superior recyclability compared to polycarbonate film due to its widespread acceptance in municipal recycling programs and lower environmental footprint during production. Polyester's biodegradability and ability to be reprocessed into new film products reduce landfill waste significantly, while polycarbonate film, derived from BPA-containing plastics, poses greater challenges in recycling and potential release of hazardous substances. Energy consumption and carbon emissions during polyester film manufacturing are notably lower, enhancing its advantage in sustainable packaging and industrial applications.
Polyester Film vs Polycarbonate Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com