Polyester monofilament consists of single, continuous filaments, offering high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for fishing lines and industrial applications. In contrast, polyester multifilament is composed of numerous fine filaments twisted together, providing greater flexibility, softness, and enhanced drape for textiles and apparel. Choosing between polyester monofilament and multifilament depends on the specific requirements for strength, texture, and end-use performance.
Table of Comparison
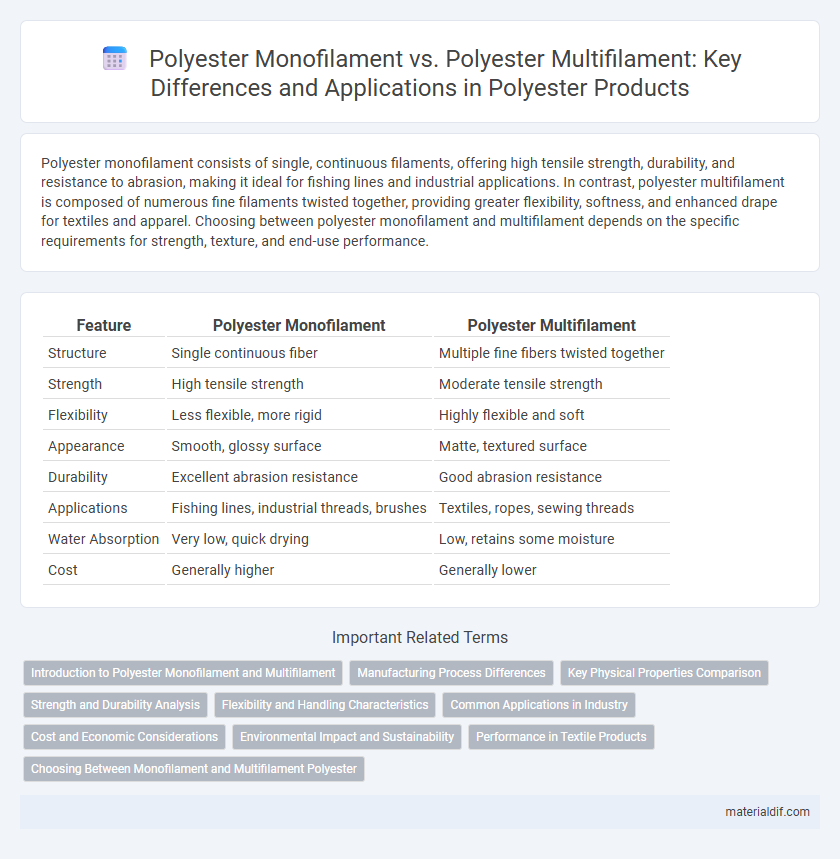
| Feature | Polyester Monofilament | Polyester Multifilament |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single continuous fiber | Multiple fine fibers twisted together |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, more rigid | Highly flexible and soft |
| Appearance | Smooth, glossy surface | Matte, textured surface |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance | Good abrasion resistance |
| Applications | Fishing lines, industrial threads, brushes | Textiles, ropes, sewing threads |
| Water Absorption | Very low, quick drying | Low, retains some moisture |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Introduction to Polyester Monofilament and Multifilament
Polyester monofilament consists of a single continuous fiber, offering high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications and fishing lines. Polyester multifilament is composed of multiple fine filaments twisted together, providing flexibility, softness, and enhanced drape suitable for textiles and upholstery. Both forms utilize polyethylene terephthalate (PET) but differ in filament structure, influencing mechanical properties and end-use performance.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Polyester monofilament is manufactured through a single continuous filament extrusion process, where molten polyester polymer is forced through a single spinneret hole, resulting in a single, thicker filament. Polyester multifilament involves extruding multiple filaments simultaneously through a spinneret with numerous holes, producing fine individual strands that are bundled together. The multifilament process requires additional steps like drawing, texturizing, and twisting to enhance strength and flexibility, whereas monofilament typically undergoes minimal post-processing.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Polyester monofilament features higher tensile strength and lower elongation compared to polyester multifilament, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and rigidity. Multifilament polyester offers greater flexibility, softness, and improved abrasion resistance due to its fine, multiple fiber strands. Both types exhibit excellent chemical resistance and UV stability, but the choice depends on the specific mechanical performance and texture needs of the end-use product.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Polyester monofilament exhibits superior tensile strength due to its single continuous filament structure, making it highly resistant to breaking under stress. In contrast, polyester multifilament, composed of multiple fine fibers twisted together, offers enhanced flexibility and abrasion resistance but lower overall strength compared to monofilaments. Durability analysis shows monofilament excels in applications requiring high load-bearing capacity, while multifilament provides better performance in dynamic, flexible environments.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Polyester monofilament features a single, continuous filament that offers high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, but tends to be less flexible and more rigid in handling compared to polyester multifilament. Polyester multifilament consists of multiple fine filaments twisted together, providing superior flexibility, softness, and ease of manipulation, which enhances comfort and dexterity in textile applications. The choice between monofilament and multifilament polyester significantly impacts the fabric's drape, stretchability, and tactile characteristics in industrial and apparel uses.
Common Applications in Industry
Polyester monofilament is widely used in industries requiring high strength and abrasion resistance, such as fishing lines, conveyor belts, and industrial sewing threads. Polyester multifilament finds common applications in textiles, upholstery, and automotive seat belts due to its flexibility, softness, and durability. Both types are essential in manufacturing processes where specific mechanical properties tailor the product's performance and longevity.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Polyester monofilament typically commands a higher price due to its production complexity and durability, making it suitable for applications requiring strength and abrasion resistance. Polyester multifilament is generally more cost-effective, offering flexibility and softness, which reduces material expenses in bulk manufacturing. Economic considerations favor multifilament for budget-sensitive projects, while monofilament is chosen for long-term performance despite higher initial costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyester monofilament typically has a lower environmental footprint than multifilament due to its simpler manufacturing process and reduced energy consumption. Multifilament polyester often requires more raw materials and emits higher greenhouse gases during production, impacting sustainability negatively. Recycling initiatives for both types are growing but monofilament shows greater potential for efficient reuse and reduced landfill waste.
Performance in Textile Products
Polyester monofilament fibers offer superior durability and stiffness, making them ideal for applications requiring high tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, such as industrial fabrics and heavy-duty textiles. Polyester multifilament fibers provide enhanced flexibility, softness, and moisture-wicking properties, improving comfort and breathability in apparel and soft textiles. Performance in textile products depends on the specific fiber structure, with monofilament excelling in strength-focused applications and multifilament favored for comfort and versatility.
Choosing Between Monofilament and Multifilament Polyester
Choosing between polyester monofilament and multifilament depends on the specific application requirements such as strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance. Polyester monofilament offers higher durability and stiffness, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial uses, while multifilament polyester provides greater softness and flexibility, suited for textiles and apparel. Evaluating factors like tensile strength, moisture resistance, and intended fabric texture ensures optimal performance in the chosen polyester filament type.
Polyester Monofilament vs Polyester Multifilament Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com