Polyester filament offers continuous, smooth fibers ideal for high-strength applications, while polyester staple consists of shorter, cut fibers enhancing softness and flexibility. Filament polyester is commonly used in weaving and knitting for durable fabrics, whereas staple polyester is preferred in spinning processes for creating fluffy, breathable textiles. Understanding the differences between polyester filament and staple helps manufacturers select materials suited for specific fabric performance and texture.
Table of Comparison
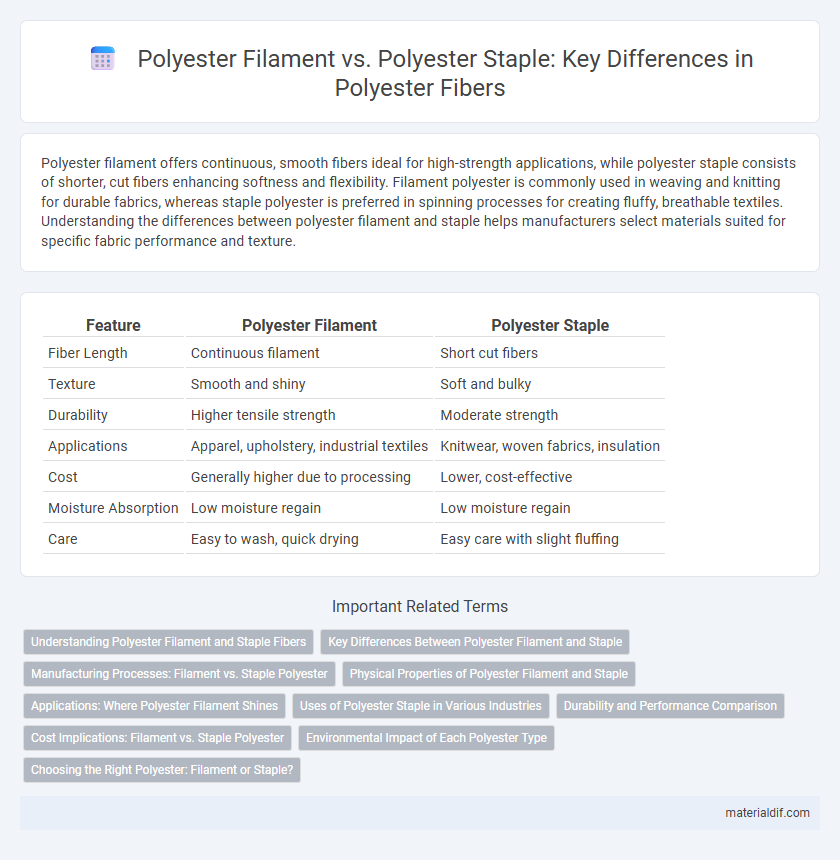
| Feature | Polyester Filament | Polyester Staple |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Length | Continuous filament | Short cut fibers |
| Texture | Smooth and shiny | Soft and bulky |
| Durability | Higher tensile strength | Moderate strength |
| Applications | Apparel, upholstery, industrial textiles | Knitwear, woven fabrics, insulation |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Lower, cost-effective |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture regain | Low moisture regain |
| Care | Easy to wash, quick drying | Easy care with slight fluffing |
Understanding Polyester Filament and Staple Fibers
Polyester filament fibers consist of continuous, long strands that provide strength, smooth texture, and sheen, making them ideal for high-performance textiles like activewear and upholstery. In contrast, polyester staple fibers are short, cut lengths that mimic natural fibers, offering breathability and softness suited for blended fabrics and insulation. Understanding the fiber form influences fabric properties such as durability, appearance, and end-use applications in the textile industry.
Key Differences Between Polyester Filament and Staple
Polyester filament consists of continuous, long fibers that provide superior strength, smoothness, and durability, making it ideal for high-quality textiles and industrial applications. In contrast, polyester staple fibers are short, cut fibers that offer greater flexibility and softness, commonly used in blended fabrics and upholstery for enhanced comfort. The key differences lie in fiber length, texture, and end-use suitability, with filament fibers favoring performance and staple fibers optimizing versatility.
Manufacturing Processes: Filament vs. Staple Polyester
Polyester filament fibers are produced through a continuous spinning process where molten polymer is extruded through spinnerets to form long, continuous strands, resulting in smooth, uniform filaments ideal for high-strength textiles. In contrast, polyester staple fibers involve cutting the continuous filaments into short lengths, followed by carding and spinning processes that produce yarns with a fibrous texture suitable for blending or down alternative products. The manufacturing distinction between continuous filament production and staple fiber cutting directly influences the final yarn properties and textile applications.
Physical Properties of Polyester Filament and Staple
Polyester filament fibers exhibit high tensile strength, excellent durability, and smooth, consistent diameter, resulting in superior abrasion resistance and a lustrous appearance. In comparison, polyester staple fibers are shorter, with a coarser texture and lower tensile strength, offering better insulation and bulkiness but reduced smoothness. The filament's uniformity enhances fabric resilience and drape, while staple fibers contribute to softness and increased air permeability in textile applications.
Applications: Where Polyester Filament Shines
Polyester filament excels in applications requiring high tensile strength and smooth texture, such as in textiles for activewear, industrial fabrics, and upholstery. Its continuous fiber structure enhances durability and wrinkle resistance, making it ideal for automotive seat belts, ropes, and tire reinforcements. The consistent filament quality also supports advanced weaving techniques, crucial for high-performance sportswear and technical textiles.
Uses of Polyester Staple in Various Industries
Polyester staple fibers find extensive use in the textile industry for producing durable, breathable fabrics in apparel, upholstery, and home furnishings. They are also integral to the nonwoven sector, where they enhance filtration efficiency, insulation materials, and geotextiles. Additionally, polyester staple's versatility supports applications in automotive interiors and industrial sewing threads, making it a critical component across diverse manufacturing domains.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Polyester filament fibers exhibit superior tensile strength and durability compared to polyester staple fibers, making them ideal for high-performance applications such as industrial textiles and upholstery. The continuous filament structure in polyester filament provides enhanced resistance to abrasion, stretching, and pilling, resulting in longer-lasting fabric performance. Polyester staple fibers, composed of shorter fiber lengths, offer greater breathability and softness but generally compromise on durability and tensile resilience.
Cost Implications: Filament vs. Staple Polyester
Polyester filament fibers generally incur higher production costs due to their continuous filament structure and advanced extrusion processes, leading to greater durability and smoother texture ideal for high-end textiles. Polyester staple fibers, produced by cutting filament fibers into shorter lengths, offer more cost-effective solutions with lower manufacturing expenses, making them suitable for bulkier fabrics like fleece and upholstery. The choice between filament and staple polyester significantly influences material pricing, with filament types commanding premium prices while staple fibers optimize budget efficiency without compromising essential polyester qualities.
Environmental Impact of Each Polyester Type
Polyester filament, made from continuous long fibers, generally results in less waste during manufacturing compared to polyester staple, which involves shorter fibers requiring more processing and generating higher emissions. Polyester filament's production typically consumes less water and energy, while polyester staple, often used in spun yarns, can contribute to microplastic pollution due to fiber shedding during washing. Choosing polyester filament over staple can reduce overall environmental impact by minimizing resource consumption and lowering carbon footprint across the textile supply chain.
Choosing the Right Polyester: Filament or Staple?
Polyester filament fibers offer smooth, continuous strands ideal for producing strong, durable fabrics with a sleek finish, making them perfect for high-performance sportswear and upholstery. Polyester staple fibers, composed of shorter lengths, provide a softer texture and better insulation, commonly used in fleece, knitwear, and cozy home textiles. Selecting between polyester filament and staple depends on the desired fabric characteristics, with filament favoring strength and sheen, while staple emphasizes warmth and comfort.
Polyester Filament vs Polyester Staple Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com