Polyester filament fibers, known for their continuous length, offer superior strength, smoothness, and durability compared to polyester staple fibers, which are shorter and have a more textured feel. Staple fibers are often blended to create softer, more breathable fabrics, while filament fibers are preferred for producing high-performance textiles with enhanced luster and resistance to wear. Choosing between polyester filament and staple fiber depends on the desired fabric properties, such as durability, texture, and end-use applications.
Table of Comparison
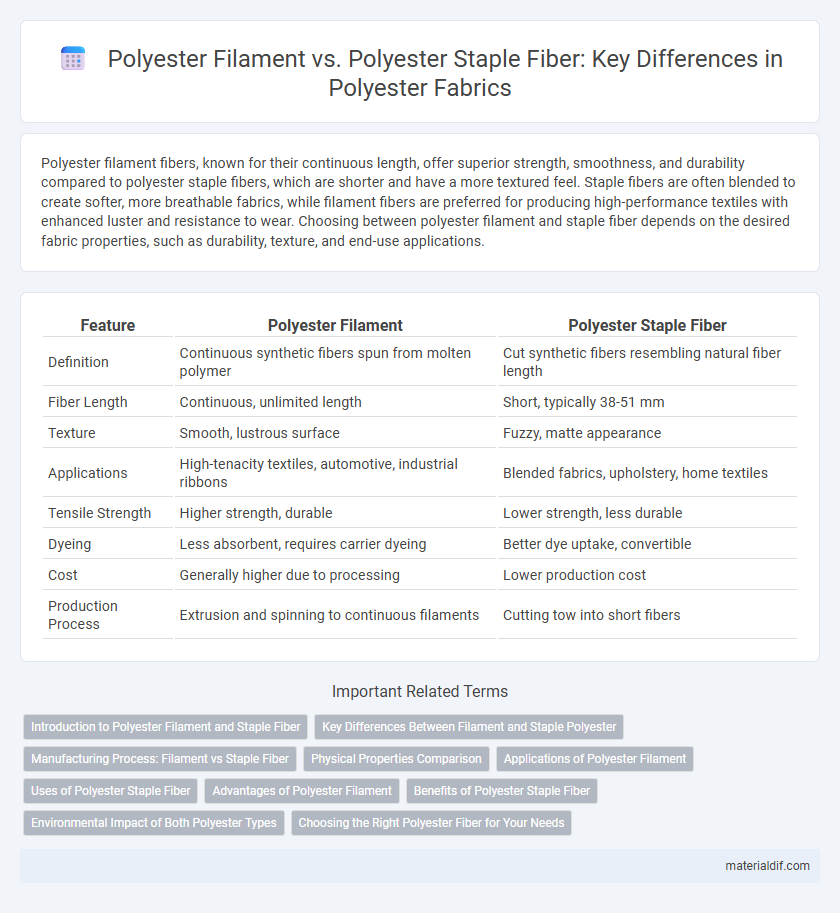
| Feature | Polyester Filament | Polyester Staple Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous synthetic fibers spun from molten polymer | Cut synthetic fibers resembling natural fiber length |
| Fiber Length | Continuous, unlimited length | Short, typically 38-51 mm |
| Texture | Smooth, lustrous surface | Fuzzy, matte appearance |
| Applications | High-tenacity textiles, automotive, industrial ribbons | Blended fabrics, upholstery, home textiles |
| Tensile Strength | Higher strength, durable | Lower strength, less durable |
| Dyeing | Less absorbent, requires carrier dyeing | Better dye uptake, convertible |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Lower production cost |
| Production Process | Extrusion and spinning to continuous filaments | Cutting tow into short fibers |
Introduction to Polyester Filament and Staple Fiber
Polyester filament consists of continuous, long fibers that provide high tensile strength and smooth texture, commonly used in textiles requiring durability and sheen. Polyester staple fiber is made from short, cut fibers that resemble natural fibers, offering versatility in blending with cotton or wool for enhanced softness and fluffiness. Both variants derive from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), differing primarily in fiber length and end-use applications within the textile industry.
Key Differences Between Filament and Staple Polyester
Polyester filament consists of continuous long fibers offering superior strength, smoothness, and uniformity, making it ideal for high-performance textiles and industrial applications. Polyester staple fibers are short, cut lengths that provide a softer texture and better breathability, commonly used in apparel and upholstery for enhanced comfort. The key difference lies in fiber length and application, where filament excels in durability and staple prioritizes flexibility and softness.
Manufacturing Process: Filament vs Staple Fiber
Polyester filament is produced through a continuous spinning process where molten polymer is extruded through spinnerets to create long, smooth fibers, ensuring high tensile strength and uniformity. In contrast, polyester staple fiber manufacturing involves cutting the continuous filament into short lengths, followed by crimping to enhance texture and bulk, mimicking natural fiber properties. The filament process offers superior luster and durability, while staple fiber allows for greater versatility in textile applications such as blending with natural fibers.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyester filament fibers exhibit higher tensile strength and elongation compared to polyester staple fibers, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility. Staple fibers have a higher fuzziness and are shorter in length, contributing to a softer hand feel but lower abrasion resistance. The smooth, continuous filament structure enhances luster and reduces pilling in filament polyester, whereas staple fiber's cut length enhances breathability and moisture wicking in textile products.
Applications of Polyester Filament
Polyester filament is widely used in high-strength industrial applications, including tire cords, conveyor belts, and safety belts, due to its continuous fiber structure and superior tensile strength. The textile industry favors polyester filament for producing smooth, wrinkle-resistant fabrics suitable for sportswear, upholstery, and home furnishings. Its high durability and chemical resistance make polyester filament ideal for outdoor gear and technical textiles where longevity and performance are critical.
Uses of Polyester Staple Fiber
Polyester staple fiber is widely used in textile applications such as upholstery, bedding, and nonwoven fabrics due to its excellent durability, wrinkle resistance, and ease of dyeing. It is commonly blended with natural fibers like cotton to enhance fabric strength and maintain comfort in apparel production. Additionally, polyester staple fiber plays a crucial role in industrial uses, including filtration, insulation, and mattress stuffing, benefiting from its resilience and moisture-wicking properties.
Advantages of Polyester Filament
Polyester filament fibers offer superior strength and durability compared to polyester staple fibers, making them ideal for high-performance textiles and industrial applications. The continuous filament structure provides a smoother surface, reducing pilling and enhancing fabric appearance over time. Polyester filament's excellent resistance to abrasion, moisture, and chemicals contributes to longer-lasting, low-maintenance garments and technical products.
Benefits of Polyester Staple Fiber
Polyester staple fiber offers enhanced versatility and softness compared to polyester filament, making it ideal for applications such as upholstery, non-woven fabrics, and blended textiles. Its shorter fiber length enables better fabric texture and improved moisture-wicking properties, contributing to greater comfort in apparel. Moreover, polyester staple fiber facilitates easier fabric spinning and dyeing processes, delivering cost-effective production and vibrant color retention.
Environmental Impact of Both Polyester Types
Polyester filament production consumes less energy and generates fewer microplastics compared to polyester staple fiber due to its continuous fiber structure, which reduces washing-related fiber shedding. However, both types are derived from petrochemicals, contributing to non-renewable resource depletion and persistent environmental pollution. Recycling technologies are advancing to mitigate waste and carbon footprint associated with both polyester filament and staple fiber.
Choosing the Right Polyester Fiber for Your Needs
Polyester filament offers continuous, smooth fibers ideal for high-strength applications such as industrial textiles and automotive components, while polyester staple fiber, composed of shorter fibers spun together, provides versatility and softness suited for apparel and home furnishings. Selecting the right polyester fiber depends on end-use requirements like durability, texture, and cost-efficiency; filament fibers excel in strength and luster, whereas staple fibers deliver comfort and ease of dyeing. Consider factors such as fabric performance, processing method, and desired aesthetics to optimize the choice between polyester filament and staple fiber.
Polyester Filament vs Polyester Staple Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com