Sand plaster offers a finer finish and better workability compared to cement plaster, making it ideal for interior walls and surfaces requiring smooth textures. Cement plaster, known for its higher strength and durability, is preferred for exterior walls and areas exposed to harsh weather conditions. Choosing between sand plaster and cement plaster depends on the specific requirements of surface finish, strength, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
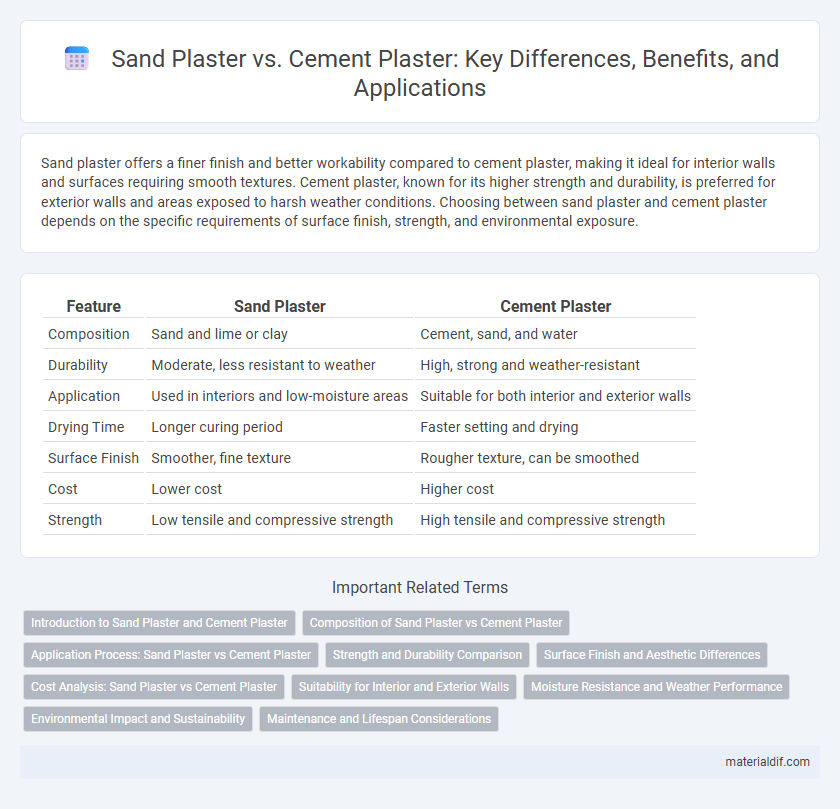
| Feature | Sand Plaster | Cement Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sand and lime or clay | Cement, sand, and water |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to weather | High, strong and weather-resistant |
| Application | Used in interiors and low-moisture areas | Suitable for both interior and exterior walls |
| Drying Time | Longer curing period | Faster setting and drying |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, fine texture | Rougher texture, can be smoothed |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Strength | Low tensile and compressive strength | High tensile and compressive strength |
Introduction to Sand Plaster and Cement Plaster
Sand plaster is a traditional building material consisting primarily of sand, water, and lime or cement, used to provide a smooth, durable finish on walls and ceilings. Cement plaster, on the other hand, is a mixture of cement, sand, and water specifically designed for bonding to surfaces, offering higher strength and water resistance compared to sand plaster. Both types play crucial roles in construction, with sand plaster favored for its workability and aesthetic finish, while cement plaster is preferred for structural durability and weather protection.
Composition of Sand Plaster vs Cement Plaster
Sand plaster primarily consists of a mixture of sand, lime, and water, creating a smooth and breathable finish ideal for interior walls. Cement plaster is composed of cement, fine sand, and water, offering a stronger, more durable surface suited for exterior applications and high-moisture areas. The higher cement content in cement plaster provides enhanced bonding and water resistance compared to the lime-based composition of sand plaster.
Application Process: Sand Plaster vs Cement Plaster
Sand plaster involves mixing sand with lime or cement and water, applied in thin layers to walls for a smooth finish, requiring careful layering and curing to prevent cracks. Cement plaster combines cement, sand, and water, applied in thicker coats with faster setting times, making it suitable for exterior surfaces demanding higher durability. The application process for sand plaster is more labor-intensive and time-consuming, while cement plaster offers quicker application and stronger bonding on diverse substrates.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Sand plaster exhibits moderate strength and durability suitable for interior walls and non-load-bearing surfaces, relying on fine sand particles for smooth finishes. Cement plaster, composed of cement, sand, and water, offers superior strength and enhanced durability ideal for exterior surfaces exposed to weather and heavy wear. The high compressive strength and water resistance of cement plaster make it the preferred choice for long-lasting protective coatings.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Differences
Sand plaster offers a smoother and more uniform surface finish, enhancing aesthetic appeal with its fine texture ideal for interior walls. Cement plaster provides a more robust and durable surface, often resulting in a rougher texture suited for exterior applications requiring weather resistance. The choice between sand and cement plaster significantly influences the final appearance and tactile quality of walls, impacting design outcomes and maintenance needs.
Cost Analysis: Sand Plaster vs Cement Plaster
Sand plaster is generally more cost-effective than cement plaster due to the lower price of sand compared to cement and fewer additives required in its preparation. Cement plaster, while more expensive upfront, offers enhanced durability and water resistance, potentially reducing repair and maintenance costs over time. Evaluating the overall expenditure involves balancing the initial material costs with long-term benefits and site conditions.
Suitability for Interior and Exterior Walls
Sand plaster offers excellent breathability and moisture regulation, making it highly suitable for interior walls where humidity control is important. Cement plaster provides superior durability and weather resistance, ideal for exterior walls exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Selecting sand plaster for interiors and cement plaster for exteriors optimizes wall longevity and indoor air quality.
Moisture Resistance and Weather Performance
Sand plaster offers moderate moisture resistance suitable for interior walls but may deteriorate with prolonged exposure to humidity. Cement plaster provides superior moisture resistance and weather performance, making it ideal for exterior surfaces exposed to rain and harsh environmental conditions. Its dense composition prevents water penetration and enhances durability against weather fluctuations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sand plaster has a lower environmental impact compared to cement plaster due to its natural composition and minimal processing requirements, which reduce carbon emissions significantly. Cement plaster production involves high energy consumption and releases substantial CO2, making it less sustainable over time. Using sand plaster promotes eco-friendly construction with enhanced biodegradability and reduced resource depletion.
Maintenance and Lifespan Considerations
Sand plaster generally requires more frequent maintenance due to its susceptibility to weathering and cracking, with a typical lifespan of 5 to 10 years. Cement plaster offers superior durability and reduced maintenance needs, often lasting 15 to 20 years or more when properly applied. Choosing between sand and cement plaster depends on balancing initial application costs against long-term upkeep and structural protection requirements.
Sand plaster vs Cement plaster Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com