Interior plaster is typically formulated to provide a smooth, decorative finish that enhances indoor walls and ceilings, offering moisture resistance and ease of painting. Exterior plaster is designed with added durability and weather resistance to protect against rain, wind, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring long-lasting performance on building exteriors. Both types of plaster require proper surface preparation and application techniques to achieve optimal adhesion and finish quality.
Table of Comparison
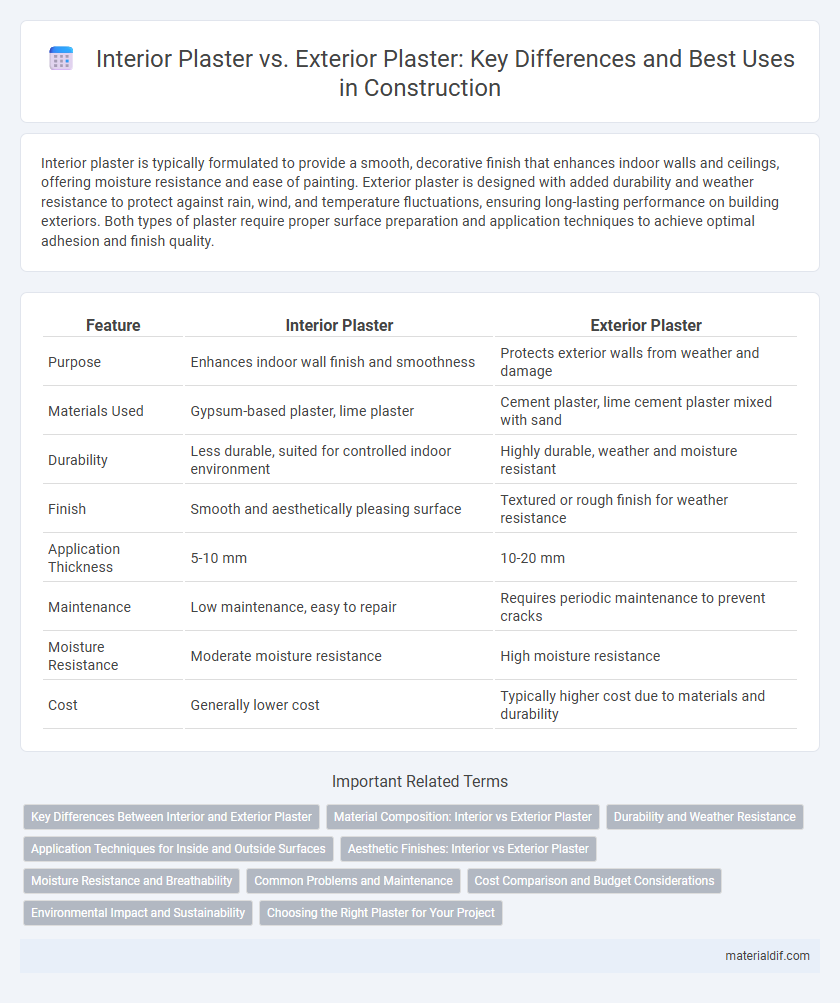
| Feature | Interior Plaster | Exterior Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances indoor wall finish and smoothness | Protects exterior walls from weather and damage |
| Materials Used | Gypsum-based plaster, lime plaster | Cement plaster, lime cement plaster mixed with sand |
| Durability | Less durable, suited for controlled indoor environment | Highly durable, weather and moisture resistant |
| Finish | Smooth and aesthetically pleasing surface | Textured or rough finish for weather resistance |
| Application Thickness | 5-10 mm | 10-20 mm |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to repair | Requires periodic maintenance to prevent cracks |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate moisture resistance | High moisture resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost due to materials and durability |
Key Differences Between Interior and Exterior Plaster
Interior plaster is formulated to offer a smooth, decorative finish that enhances indoor aesthetics while providing flexibility against minor cracking due to temperature and humidity variations. Exterior plaster contains more robust ingredients like lime or cement to resist weather elements such as rain, wind, and UV exposure, ensuring durability and water resistance. The key differences lie in composition, moisture resistance, and application techniques tailored to indoor climate control versus outdoor environmental protection.
Material Composition: Interior vs Exterior Plaster
Interior plaster typically consists of gypsum or lime-based materials designed for smooth finishes and indoor air quality. Exterior plaster is formulated with cement, sand, and additives to withstand weather exposure and provide moisture resistance. The distinct compositions ensure durability and performance suited to their respective environments.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Interior plaster is designed for durability in controlled environments, offering smooth finishes and resistance to everyday wear and tear without exposure to harsh weather. Exterior plaster incorporates additives like cement and lime to enhance weather resistance, making it highly durable against rain, wind, and temperature fluctuations. The composition and application techniques of exterior plaster ensure long-lasting protection for building facades, while interior plaster prioritizes aesthetic appeal and minor impact resilience.
Application Techniques for Inside and Outside Surfaces
Interior plaster application involves thin, smooth layers to create a refined finish on walls and ceilings, using techniques such as troweling and floating for even surfaces. Exterior plaster requires thicker, more durable coats with additives like lime or cement to withstand weather conditions, applied using rougher strokes and sometimes reinforced with mesh for crack resistance. Proper surface preparation, including cleaning and priming, is crucial for both interior and exterior plaster to ensure strong adhesion and long-lasting results.
Aesthetic Finishes: Interior vs Exterior Plaster
Interior plaster offers smooth, refined finishes tailored for walls and ceilings, enhancing indoor aesthetics with a variety of textures and colors. Exterior plaster is formulated to withstand weather conditions, providing durable, textured finishes that protect and beautify building facades. Both types prioritize aesthetic appeal but differ in composition and application to suit indoor elegance versus outdoor resilience.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
Interior plaster typically features higher breathability to regulate indoor humidity and prevent mold growth, whereas exterior plaster prioritizes moisture resistance to withstand rain, snow, and environmental exposure. Exterior plaster is often formulated with additives like acrylics or cement-based materials to create a durable, water-repellent surface. Breathable interior plaster allows vapor diffusion, protecting indoor air quality and maintaining structural integrity.
Common Problems and Maintenance
Interior plaster often faces issues like cracking, damp stains, and surface deterioration due to humidity and temperature fluctuations, requiring regular inspection and prompt repairs to maintain smooth finishes. Exterior plaster is prone to weather-related damage such as erosion, mold growth, and efflorescence caused by rain, freeze-thaw cycles, and UV exposure, necessitating periodic cleaning, sealing, and patching to preserve protective integrity. Proper maintenance for both types includes addressing underlying moisture problems, using compatible repair materials, and applying protective coatings to extend the lifespan and aesthetic appeal of plaster surfaces.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Interior plaster generally costs less than exterior plaster due to differences in material durability and weather resistance requirements, with average prices ranging from $2 to $6 per square foot versus $4 to $10 per square foot for exterior applications. Budget considerations must include factors such as surface preparation, labor intensity, and long-term maintenance, as exterior plaster requires enhanced formulations like cement-based mixes to withstand environmental exposure. Selecting between interior and exterior plaster impacts overall project expenditure significantly, making precise cost estimation crucial for effective financial planning.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Interior plaster typically uses lime-based or gypsum materials that offer excellent breathability and low VOC emissions, contributing to healthier indoor air quality and reduced environmental impact. Exterior plaster often incorporates cement-based mixtures designed for durability and weather resistance, but these can have higher embodied carbon due to cement production. Sustainable plaster choices prioritize natural, locally-sourced ingredients and formulations that minimize energy consumption and carbon footprint throughout their lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Plaster for Your Project
Interior plaster is formulated for smooth finishes and moisture regulation, making it ideal for walls and ceilings inside homes where breathability and aesthetic appeal are crucial. Exterior plaster, composed with weather-resistant additives, provides durability against rain, wind, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring long-lasting protection on building facades. Selecting the right plaster depends on your project's environment, exposure to elements, and desired texture finish for optimal performance and longevity.
Interior Plaster vs Exterior Plaster Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com