Earthen plaster offers a natural, breathable finish made from clay, sand, and organic fibers, promoting indoor air quality and moisture regulation. Synthetic plaster, often composed of acrylics or cement-based materials, provides enhanced durability and faster drying times but may trap moisture and emit VOCs. Choosing between earthen and synthetic plaster depends on priorities such as environmental impact, aesthetics, and long-term maintenance.
Table of Comparison
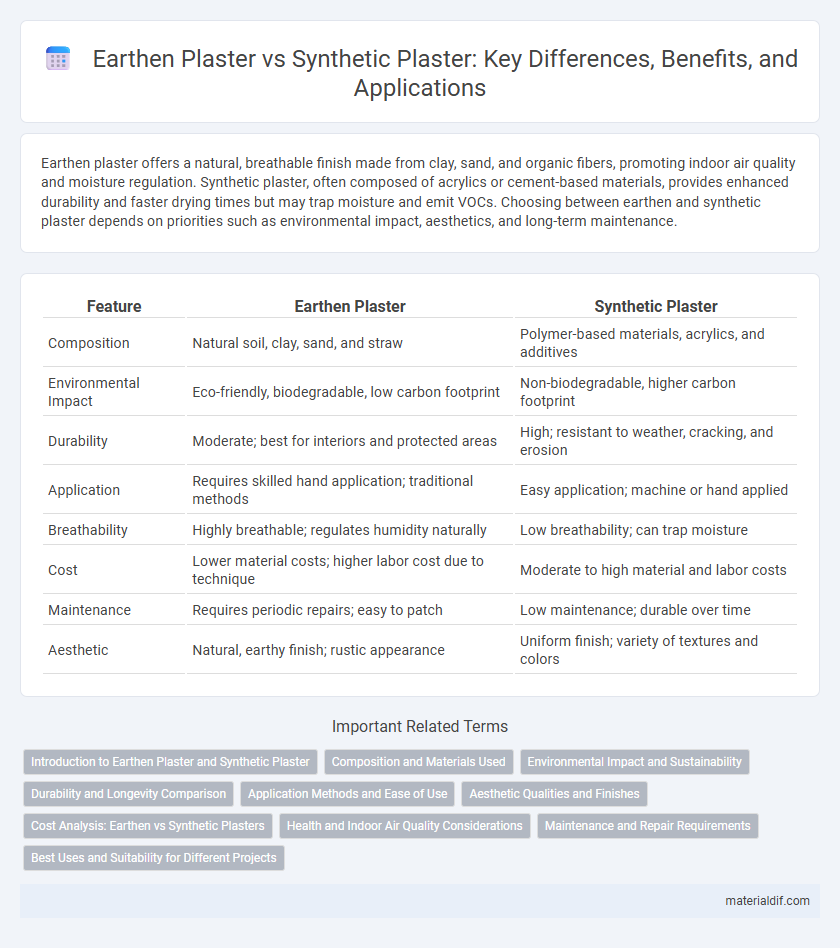
| Feature | Earthen Plaster | Synthetic Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural soil, clay, sand, and straw | Polymer-based materials, acrylics, and additives |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Durability | Moderate; best for interiors and protected areas | High; resistant to weather, cracking, and erosion |
| Application | Requires skilled hand application; traditional methods | Easy application; machine or hand applied |
| Breathability | Highly breathable; regulates humidity naturally | Low breathability; can trap moisture |
| Cost | Lower material costs; higher labor cost due to technique | Moderate to high material and labor costs |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic repairs; easy to patch | Low maintenance; durable over time |
| Aesthetic | Natural, earthy finish; rustic appearance | Uniform finish; variety of textures and colors |
Introduction to Earthen Plaster and Synthetic Plaster
Earthen plaster is a natural wall finishing material made primarily from clay, sand, and fiber, offering breathable, eco-friendly properties and excellent moisture regulation. Synthetic plaster, often composed of acrylics, polymers, and additives, provides enhanced durability, water resistance, and faster drying times for modern construction needs. Choosing between earthen and synthetic plasters depends on environmental goals, building requirements, and desired aesthetic outcomes.
Composition and Materials Used
Earthen plaster consists primarily of natural materials such as clay, sand, and straw, offering breathability and eco-friendliness due to its organic composition. Synthetic plaster, on the other hand, is made from chemical compounds like acrylics, vinyl, or cement-based materials, providing increased durability and moisture resistance. The choice between earthen and synthetic plaster impacts environmental sustainability, indoor air quality, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Earthen plaster, made from natural materials like clay, sand, and straw, offers a low environmental impact due to its biodegradability and minimal energy-intensive processing. Synthetic plaster typically relies on petrochemical ingredients and involves higher carbon emissions during production, contributing to environmental degradation. Choosing earthen plaster supports sustainable building practices by enhancing indoor air quality and reducing landfill waste.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Earthen plaster, composed mainly of natural clay, sand, and fibers, offers moderate durability but may require regular maintenance to prevent erosion and cracking in moist environments. Synthetic plaster, often made from polymers and additives, provides enhanced longevity with strong resistance to weathering, cracking, and water damage. The durability gap favors synthetic plaster for long-term structural integrity, especially in harsh or variable climates.
Application Methods and Ease of Use
Earthen plaster is applied using trowels or hands, requiring skilled labor for proper consistency and layering, which can make the process labor-intensive but allows for customization and breathability in walls. Synthetic plaster, often premixed, offers ease of use with faster drying times and simpler application methods such as spraying or rolling, making it suitable for large-scale projects and less experienced applicators. The choice between earthen and synthetic plaster depends on the desired finish, environmental impact, and application speed.
Aesthetic Qualities and Finishes
Earthen plaster offers a natural, textured aesthetic with warm, earthy tones that blend seamlessly into rustic and eco-friendly designs, allowing for unique, hand-applied finishes that age gracefully over time. Synthetic plaster provides a smooth, uniform surface with a wide range of colors and finishes, including glossy and matte options, which ensures consistent appearance and durability in modern architectural applications. The choice between earthen and synthetic plaster hinges on desired visual impact, with earthen emphasizing organic charm and synthetic focusing on precision and variety in finishes.
Cost Analysis: Earthen vs Synthetic Plasters
Earthen plaster generally offers a lower material cost compared to synthetic plaster, especially when sourced locally, making it an economical choice for sustainable construction. Synthetic plasters, although higher in price due to chemical formulations and manufacturing expenses, often require less maintenance and faster application, potentially reducing labor costs. Evaluating overall expenses involves considering initial investment, longevity, and environmental impact associated with both earthen and synthetic plaster options.
Health and Indoor Air Quality Considerations
Earthen plaster naturally regulates indoor humidity by absorbing and releasing moisture, reducing mold growth and improving overall air quality compared to synthetic plaster. Synthetic plasters often contain VOCs and chemicals that can off-gas over time, potentially triggering allergies and respiratory issues. Choosing earthen plaster promotes a healthier indoor environment by minimizing toxic emissions and supporting natural air purification.
Maintenance and Repair Requirements
Earthen plaster requires regular maintenance such as periodic reapplication and moisture control to prevent cracking and erosion, but repairs are simple and involve patching with compatible materials. Synthetic plaster tends to be more durable and resistant to weathering, reducing maintenance frequency, yet repairs may require specialized products and techniques to ensure proper adhesion and appearance. Both types demand prompt attention to damages to maintain structural integrity and aesthetic quality over time.
Best Uses and Suitability for Different Projects
Earthen plaster excels in eco-friendly building projects and historic restorations due to its natural breathability and moisture regulation properties, making it ideal for interior walls in sustainable homes. Synthetic plaster offers enhanced durability and water resistance, suitable for exterior surfaces or high-traffic commercial spaces where weather exposure and impact resistance are critical. Choosing between earthen and synthetic plaster depends on project requirements such as environmental impact, durability needs, and the specific conditions of the installation site.
Earthen plaster vs Synthetic plaster Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com