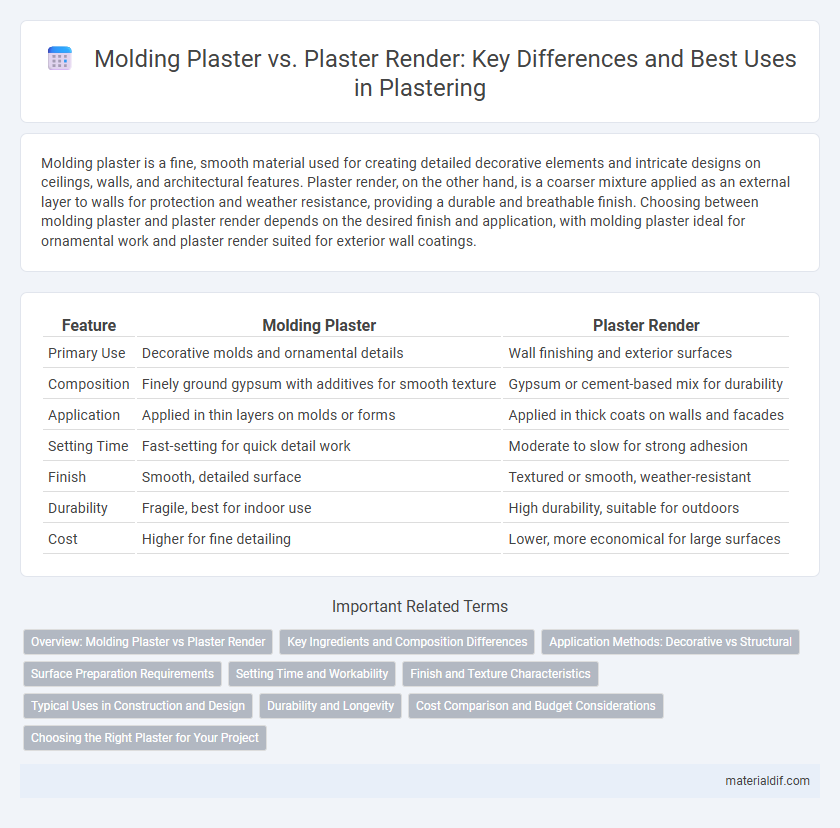
Molding plaster is a fine, smooth material used for creating detailed decorative elements and intricate designs on ceilings, walls, and architectural features. Plaster render, on the other hand, is a coarser mixture applied as an external layer to walls for protection and weather resistance, providing a durable and breathable finish. Choosing between molding plaster and plaster render depends on the desired finish and application, with molding plaster ideal for ornamental work and plaster render suited for exterior wall coatings.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Molding Plaster | Plaster Render |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Decorative molds and ornamental details | Wall finishing and exterior surfaces |
| Composition | Finely ground gypsum with additives for smooth texture | Gypsum or cement-based mix for durability |
| Application | Applied in thin layers on molds or forms | Applied in thick coats on walls and facades |
| Setting Time | Fast-setting for quick detail work | Moderate to slow for strong adhesion |
| Finish | Smooth, detailed surface | Textured or smooth, weather-resistant |
| Durability | Fragile, best for indoor use | High durability, suitable for outdoors |
| Cost | Higher for fine detailing | Lower, more economical for large surfaces |
Overview: Molding Plaster vs Plaster Render
Molding plaster is a fine, fast-setting material primarily used for creating detailed decorative elements and sculptural forms due to its smooth finish and high strength. Plaster render, on the other hand, is a coarser mix applied as an exterior or interior coating to walls for protection and aesthetic texture, designed to resist weathering and improve surface durability. The key differences lie in their composition, application techniques, and intended function, with molding plaster focusing on precision and detail, while plaster render emphasizes coverage and environmental resilience.
Key Ingredients and Composition Differences
Molding plaster primarily consists of fine calcium sulfate hemihydrate, which allows for smooth detail capture and quick setting, making it ideal for intricate mold work. Plaster render combines lime, cement, and sand, providing durability and weather resistance suitable for exterior wall finishes. The difference in composition results in molding plaster being softer and more workable, while plaster render is harder and more resilient for structural applications.
Application Methods: Decorative vs Structural
Molding plaster is primarily applied in thin layers using hand tools or molds to create intricate decorative elements like cornices, ceiling roses, and ornamental details. Plaster render is applied in thicker coats with trowels or spray machines to provide a protective, structural finish on exterior or interior walls, enhancing durability and weather resistance. The precision required in molding plaster contrasts with the broad, robust application techniques of plaster render, reflecting their distinct decorative and structural roles.
Surface Preparation Requirements
Molding plaster requires a smooth, clean surface free from dust, grease, and loose particles to ensure proper adhesion and fine detail capture in molds. Plaster render demands a rough or keyed substrate, often achieved by scratching or using a bonding agent, to enhance mechanical grip on walls or ceilings. Proper surface preparation for both types directly influences the durability and finish quality of the applied plaster.
Setting Time and Workability
Molding plaster typically sets faster than plaster render, with a setting time of about 10 to 20 minutes, enabling quicker detailing and shaping for decorative applications. Plaster render offers extended workability, generally setting between 30 minutes to an hour, which is ideal for larger surface coverage and finishing. The quick setting time of molding plaster demands efficient manipulation, while plaster render allows more time for smoothing and texturing.
Finish and Texture Characteristics
Molding plaster typically provides a smooth, fine finish ideal for detailed ornamental work and intricate designs, offering a dense, consistent texture that sets hard and durable. Plaster render, on the other hand, features a coarser texture designed for exterior walls, enhancing weather resistance and allowing better adhesion to substrates. The finish of plaster render is generally rougher and more porous, optimizing breathability and durability for external applications.
Typical Uses in Construction and Design
Molding plaster is primarily utilized for creating detailed architectural ornaments, decorative cornices, and intricate ceiling medallions in interior design, offering smooth finishes suitable for fine craftsmanship. Plaster render is typically applied on exterior walls to provide a protective, weather-resistant coating that improves durability and insulation while allowing breathability in construction. Both materials enhance structural aesthetics, but molding plaster is favored for ornamental purposes, whereas plaster render is essential for exterior wall protection and surface uniformity.
Durability and Longevity
Molding plaster, composed primarily of gypsum, offers a smooth finish ideal for detailed ornamental work but tends to be less durable and more prone to cracks over time compared to plaster render. Plaster render, typically a mix of cement, sand, and lime, provides a robust protective coating for exterior walls, delivering superior resistance to weathering and extended longevity. The choice between molding plaster and plaster render hinges on application needs, with plaster render favored for structural durability and molding plaster for intricate interior designs.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Molding plaster typically costs more than plaster render due to its finer texture and specialized composition designed for detailed decorative work, often priced around $15-$20 per 25kg bag compared to plaster render's approximate $8-$12 per 25kg bag used for wall finishes. Budget considerations should include not only the material costs but also labor expenses, as molding plaster requires skilled artisans for intricate application while plaster render involves more straightforward, faster techniques. Choosing between molding plaster and plaster render depends on the project's detail requirements and available budget, with plaster render being more economical for large surface areas and molding plaster suited for precision work despite its higher price point.
Choosing the Right Plaster for Your Project
Molding plaster offers a fine, smooth finish ideal for intricate decorative work, making it perfect for detailed molds and ornamental applications. Plaster render provides a robust, weather-resistant coating, suited for exterior walls where durability and protection against moisture are essential. Selecting the right plaster hinges on project requirements: choose molding plaster for precision and detail, and plaster render for structural strength and environmental resilience.
Molding Plaster vs Plaster Render Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com