Gypsum plaster offers a smooth finish and faster drying time compared to cement plaster, making it ideal for interior walls and ceilings. Cement plaster is more durable and water-resistant, suitable for exterior surfaces and areas exposed to moisture. Choosing between gypsum and cement plaster depends on the specific application, durability requirements, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
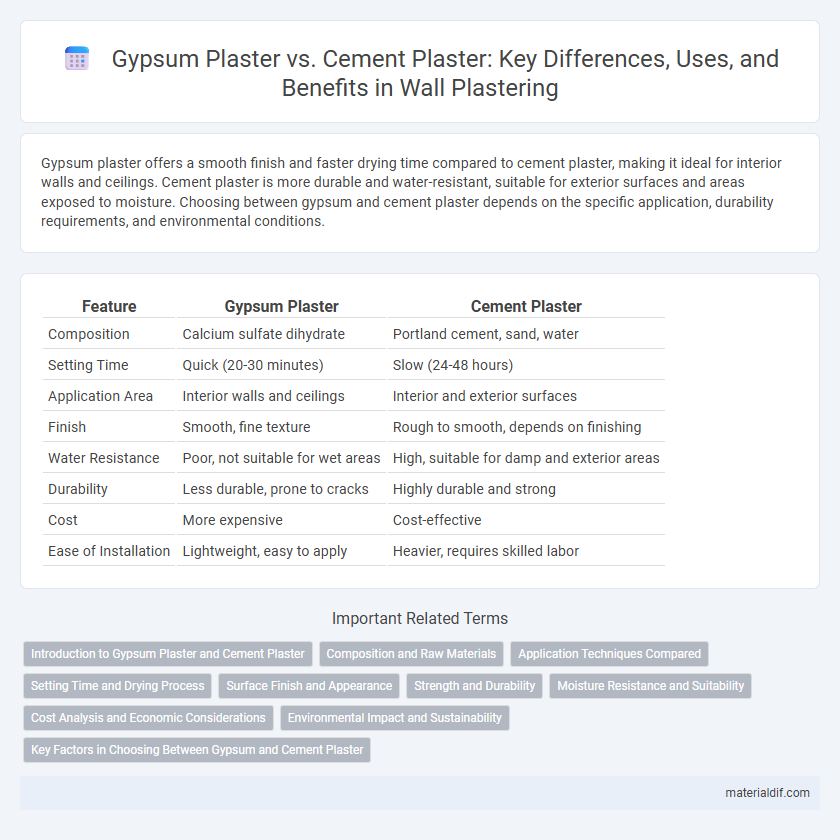
| Feature | Gypsum Plaster | Cement Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate | Portland cement, sand, water |
| Setting Time | Quick (20-30 minutes) | Slow (24-48 hours) |
| Application Area | Interior walls and ceilings | Interior and exterior surfaces |
| Finish | Smooth, fine texture | Rough to smooth, depends on finishing |
| Water Resistance | Poor, not suitable for wet areas | High, suitable for damp and exterior areas |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to cracks | Highly durable and strong |
| Cost | More expensive | Cost-effective |
| Ease of Installation | Lightweight, easy to apply | Heavier, requires skilled labor |
Introduction to Gypsum Plaster and Cement Plaster
Gypsum plaster is a lightweight, quick-setting material primarily composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, widely used for smooth interior wall finishes due to its excellent workability and fire-resistant properties. Cement plaster, made from a mixture of cement, sand, and water, offers superior strength and durability, making it suitable for both interior and exterior applications, especially in harsh weather conditions. The choice between gypsum plaster and cement plaster depends on factors such as surface type, environmental exposure, and desired finish quality.
Composition and Raw Materials
Gypsum plaster primarily consists of calcium sulfate dihydrate derived from natural gypsum, offering lightweight and smooth finishing properties. Cement plaster is composed of a mixture of Portland cement, sand, and water, providing durability and strong bonding for exterior and interior surfaces. The raw materials for gypsum plaster allow quicker setting times, while cement plaster's raw materials result in higher moisture resistance and structural strength.
Application Techniques Compared
Gypsum plaster offers smooth finishes and quick setting times, ideal for interior walls and ceilings, applied using trowels or spray machines with minimal curing requirements. Cement plaster suits exterior surfaces, providing durability and moisture resistance, applied in multiple coats through manual troweling or mechanical spraying followed by adequate curing periods. Both techniques demand surface preparation, but gypsum plaster requires less water and results in lighter finishes compared to the heavier, more robust layers formed by cement plaster.
Setting Time and Drying Process
Gypsum plaster sets rapidly, typically within 20 to 30 minutes, allowing faster application but requiring quick work before it hardens, whereas cement plaster takes approximately 24 to 48 hours to set due to its chemical hydration process. The drying process of gypsum plaster is faster owing to its water retention properties and lower thickness requirements, reducing overall curing time compared to cement plaster, which demands prolonged moist curing to achieve optimal strength. Gypsum plaster's quicker setting and drying make it ideal for interior finishes, while cement plaster's longer drying time supports durability for exterior and structural applications.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Gypsum plaster provides a smooth, fine-textured surface that enhances interior wall aesthetics with a clean, white finish, ideal for decorative painting and wallpapers. Cement plaster offers a rougher, coarser texture suited for exterior walls, delivering sturdy protection against weather while requiring additional finishing layers for a refined appearance. The choice between gypsum and cement plaster significantly impacts the final surface quality, influencing both visual appeal and functional durability.
Strength and Durability
Gypsum plaster offers a smoother finish but has lower strength and durability compared to cement plaster, making it suitable primarily for interior applications. Cement plaster, composed of cement, sand, and water, provides superior strength and resistance to weathering, ideal for both interior and exterior surfaces exposed to harsh conditions. Due to its hydraulic setting properties, cement plaster can withstand moisture and mechanical stress better than gypsum plaster, ensuring long-term durability.
Moisture Resistance and Suitability
Gypsum plaster offers excellent moisture resistance for interior walls and ceilings, making it ideal for dry, sheltered environments. Cement plaster provides superior durability and water resistance, suitable for exterior surfaces and high-moisture areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Choosing between gypsum and cement plaster depends on the specific moisture conditions and structural requirements of the application.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Gypsum plaster generally costs less than cement plaster due to lower raw material and production expenses, making it a budget-friendly option for interior applications. Cement plaster has higher durability and weather resistance but involves greater initial investment and labor costs. Choosing between them depends on project scope, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum plaster has a lower carbon footprint compared to cement plaster due to its production requiring less energy and emitting fewer greenhouse gases. It is biodegradable and often made from industrial by-products, enhancing sustainability and reducing landfill waste. Cement plaster involves significant CO2 emissions from cement manufacturing, contributing more heavily to environmental degradation and resource depletion.
Key Factors in Choosing Between Gypsum and Cement Plaster
Gypsum plaster offers superior workability, faster drying times, and excellent smooth finishes, making it ideal for interior walls, while cement plaster provides greater durability, moisture resistance, and strength suited for exterior applications. Key factors in choosing between gypsum and cement plaster include the environmental conditions, desired surface finish, and structural requirements of the project. Cost considerations and application speed also influence the decision, with gypsum typically being more cost-effective for indoor use.
Gypsum Plaster vs Cement Plaster Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com