Mesh lath offers superior flexibility and corrosion resistance compared to traditional wood lath, making it ideal for modern plaster applications. Wood lath provides a natural, breathable base that enhances plaster adhesion but may be prone to rot and insect damage over time. Choosing between mesh and wood lath depends on the desired durability, moisture exposure, and structural requirements of the plaster project.
Table of Comparison
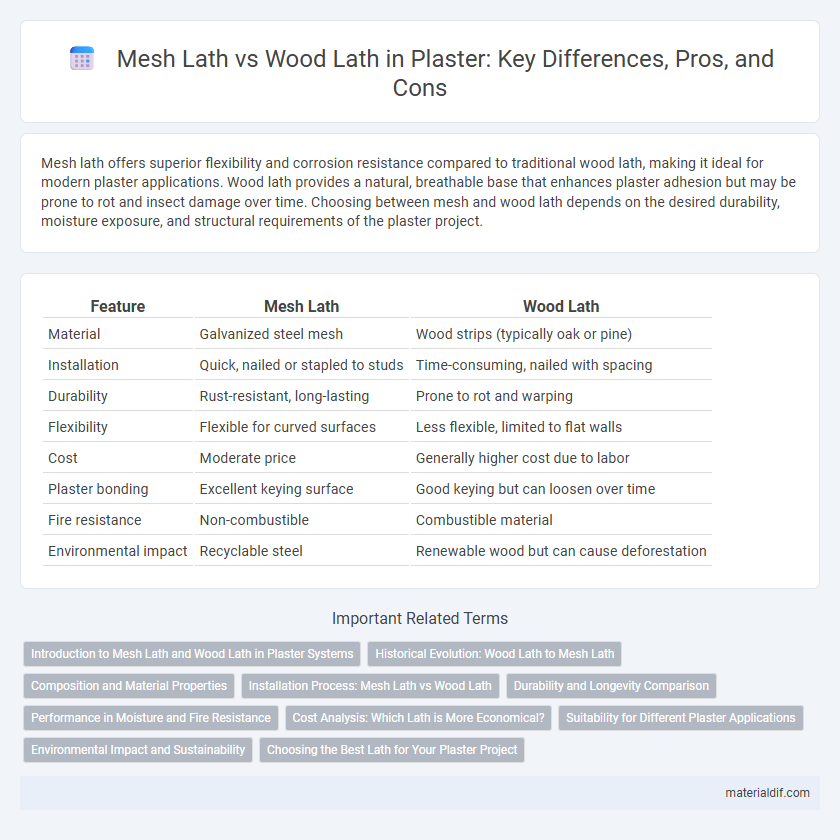
| Feature | Mesh Lath | Wood Lath |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Galvanized steel mesh | Wood strips (typically oak or pine) |
| Installation | Quick, nailed or stapled to studs | Time-consuming, nailed with spacing |
| Durability | Rust-resistant, long-lasting | Prone to rot and warping |
| Flexibility | Flexible for curved surfaces | Less flexible, limited to flat walls |
| Cost | Moderate price | Generally higher cost due to labor |
| Plaster bonding | Excellent keying surface | Good keying but can loosen over time |
| Fire resistance | Non-combustible | Combustible material |
| Environmental impact | Recyclable steel | Renewable wood but can cause deforestation |
Introduction to Mesh Lath and Wood Lath in Plaster Systems
Mesh lath in plaster systems is a galvanized metal mesh that provides a strong, flexible base for plaster application, promoting durability and crack resistance. Wood lath consists of narrow wooden strips fastened horizontally to wall studs, creating a keying surface for traditional plaster but is more prone to moisture damage and less flexible than mesh. Mesh lath offers improved longevity and ease of installation compared to the historical wood lath method, making it a popular choice in modern plaster applications.
Historical Evolution: Wood Lath to Mesh Lath
Wood lath, used extensively since ancient times, provided a flexible and breathable base for traditional plaster applications, allowing for structural adhesion and moisture regulation. Mesh lath, introduced in the 20th century, revolutionized plastering by offering a corrosion-resistant, uniform surface ideal for modern construction methods and enhanced durability. The transition from wood lath to mesh lath reflects advancements in material science and building codes focused on fire resistance, ease of installation, and long-term maintenance.
Composition and Material Properties
Mesh lath is composed of galvanized steel or fiberglass materials, offering high corrosion resistance and flexibility, while wood lath consists of thin, narrow strips of wood known for natural breathability and thermal insulation. Mesh lath provides superior tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for modern plaster applications, whereas wood lath's organic composition allows for better moisture regulation but is susceptible to rot and insect damage. Material properties of mesh lath contribute to longer lifespan and consistent plaster adherence, contrasting with wood lath's variable density and potential for warping over time.
Installation Process: Mesh Lath vs Wood Lath
Mesh lath installation involves stapling or fastening metal or fiberglass sheets directly to framing, creating a uniform base for plaster application with minimal labor. Wood lath installation requires nailing individual wooden strips horizontally with precise spacing to allow plaster to key into the gaps, which is more time-consuming and labor-intensive. Mesh lath offers a faster, more consistent installation process compared to the traditional, meticulous wood lath method.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Mesh lath offers enhanced durability compared to traditional wood lath due to its corrosion-resistant galvanized steel composition, which resists moisture damage and prevents rusting over time. Wood lath, while historically popular, is prone to warping, rot, and insect damage, leading to shorter lifespan and increased maintenance. The longevity of mesh lath installations often exceeds that of wood lath by several decades, making it a superior choice for modern plaster applications requiring long-term structural integrity.
Performance in Moisture and Fire Resistance
Mesh lath offers superior moisture resistance compared to wood lath, as its galvanized metal composition prevents water absorption and reduces the risk of mold and rot. In terms of fire resistance, mesh lath outperforms wood lath by providing a non-combustible barrier that enhances overall fire protection for plastered surfaces. This makes mesh lath a more durable and safer option for environments prone to moisture exposure and fire hazards.
Cost Analysis: Which Lath is More Economical?
Mesh lath typically offers a more cost-effective solution compared to wood lath due to its lower material and labor expenses, as it is easier and faster to install. Wood lath involves higher costs stemming from the price of lumber and the increased time required for precise nailing and alignment. For large-scale or budget-sensitive plaster projects, mesh lath presents a more economical choice while maintaining sufficient durability.
Suitability for Different Plaster Applications
Mesh lath offers superior corrosion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for exterior or damp environments where moisture exposure is frequent. Wood lath provides excellent mechanical keying for traditional lime or gypsum plasters, preferred in historic restorations or interior applications with lower moisture risk. Selection depends on the plaster type, environmental conditions, and desired durability for the finished surface.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mesh lath offers improved environmental sustainability compared to traditional wood lath due to its composition from recyclable metal materials and longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Wood lath, sourced from timber, contributes to deforestation and has a higher carbon footprint linked to harvesting and transportation processes. Choosing mesh lath supports eco-friendly construction practices by minimizing resource depletion and promoting material reuse.
Choosing the Best Lath for Your Plaster Project
Selecting the right lath is crucial for achieving a durable plaster finish, with mesh lath offering enhanced rust resistance and flexibility compared to traditional wood lath. Mesh lath, typically galvanized metal, provides superior support for modern plaster mixes and moisture resistance, making it ideal for humid environments. Wood lath, favored for historic restorations, offers natural breathability but requires careful installation to prevent warping and deterioration over time.
Mesh lath vs Wood lath Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com