Woven jute features interlaced fibers that create a durable and breathable texture ideal for pet beds and accessories, offering enhanced strength and longevity. Non-woven jute, made from bonded fibers, provides a softer and more flexible material but lacks the same durability and structural integrity as woven jute. Choosing between woven and non-woven jute depends on the required balance of toughness and comfort for specific pet products.
Table of Comparison
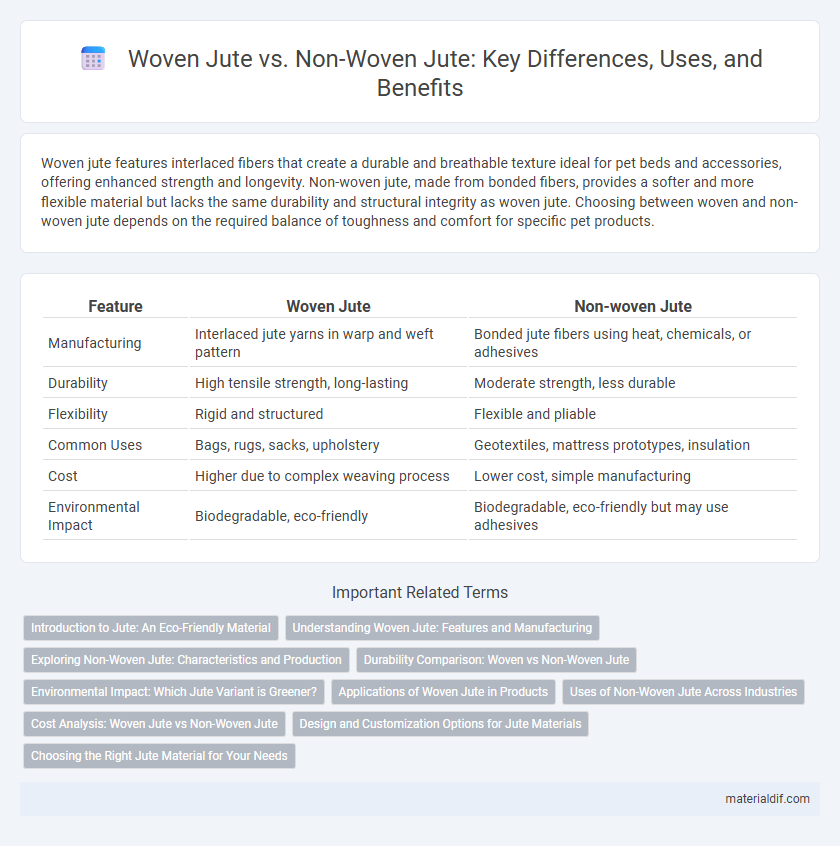
| Feature | Woven Jute | Non-woven Jute |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Interlaced jute yarns in warp and weft pattern | Bonded jute fibers using heat, chemicals, or adhesives |
| Durability | High tensile strength, long-lasting | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Flexibility | Rigid and structured | Flexible and pliable |
| Common Uses | Bags, rugs, sacks, upholstery | Geotextiles, mattress prototypes, insulation |
| Cost | Higher due to complex weaving process | Lower cost, simple manufacturing |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Biodegradable, eco-friendly but may use adhesives |
Introduction to Jute: An Eco-Friendly Material
Woven jute features interlaced fibers creating a strong, durable fabric commonly used for sacks, rugs, and upholstery, highlighting its natural breathability and biodegradability. Non-woven jute, formed by bonding fibers without weaving, offers a lightweight, flexible option ideal for geotextiles, erosion control, and disposable products. Both forms capitalize on jute's renewable, biodegradable nature, making it a sustainable alternative to synthetic materials in various eco-friendly applications.
Understanding Woven Jute: Features and Manufacturing
Woven jute fabric is created by intertwining jute fibers in a crisscross pattern, resulting in a strong, durable textile commonly used for sacks, bags, and upholstery. Its manufacturing involves spinning jute fibers into yarns followed by weaving these yarns on looms, which enhances tensile strength and flexibility compared to non-woven jute. Woven jute's breathability, biodegradability, and cost-effectiveness contribute to its widespread application in eco-friendly packaging and home decor industries.
Exploring Non-Woven Jute: Characteristics and Production
Non-woven jute is manufactured using fibers bonded together through mechanical, chemical, or thermal processes without weaving, resulting in a fabric that is lightweight, porous, and highly absorbent. It offers superior flexibility and shock absorption compared to woven jute, making it ideal for applications in geotextiles, packaging, and upholstery. The production process involves techniques such as needle punching, hydroentangling, or adhesive bonding, which enhance its uniformity and strength while maintaining biodegradability.
Durability Comparison: Woven vs Non-Woven Jute
Woven jute fibers are interlaced tightly, providing superior strength and durability compared to non-woven jute, which is bonded through adhesives or heat without a structured weave. This structural integrity makes woven jute ideal for heavy-duty applications such as sacks and carpets, where resistance to wear and tear is crucial. Non-woven jute generally offers less tensile strength and degrades faster under stress, limiting its use to lighter applications like insulation and disposable products.
Environmental Impact: Which Jute Variant is Greener?
Woven jute products offer superior durability and reusability, reducing the frequency of replacement and lowering overall environmental waste. Non-woven jute, often produced with adhesives and synthetic binders, may have a higher environmental footprint due to chemical usage and limited recyclability. Sustainable sourcing and manufacturing methods play a critical role in determining the true ecological benefits of each jute variant.
Applications of Woven Jute in Products
Woven jute fabric is predominantly used in products requiring durability and strength such as sacks, bags, and upholstery due to its tightly interlaced fibers providing enhanced tensile strength and dimensional stability. This makes woven jute ideal for packaging agricultural goods, creating eco-friendly shopping bags, and manufacturing home decor items like rugs and curtains, which benefit from its natural texture and breathability. Its versatility in applications contrasts with non-woven jute, which is more suited for insulation, cushioning, and geotextiles where flexibility and cushioning properties are prioritized over structural strength.
Uses of Non-Woven Jute Across Industries
Non-woven jute is extensively utilized in agriculture for erosion control mats and seed blankets, enhancing soil stability and moisture retention. In automotive manufacturing, non-woven jute serves as eco-friendly interior padding and sound insulation, promoting sustainability in vehicle production. The textile and furniture industries employ non-woven jute in upholstery and carpet backing, offering durable and biodegradable alternatives to synthetic materials.
Cost Analysis: Woven Jute vs Non-Woven Jute
Woven jute generally incurs higher production costs due to the intricate weaving process and extended labor requirements, resulting in a more durable and high-quality textile ideal for premium applications. Non-woven jute, produced through needle-punching or bonding techniques, offers a cost-effective alternative with faster manufacturing speeds and reduced material waste, making it suitable for disposable or less demanding products. Price differences between woven and non-woven jute reflect their manufacturing complexities and product longevity, with woven jute typically commanding a 20-40% higher market price.
Design and Customization Options for Jute Materials
Woven jute offers a structured texture with high durability, making it ideal for intricate patterns and tailored designs in bags, rugs, and upholstery. Non-woven jute, characterized by its softer, flexible fiber matrix, allows for greater versatility in shape and size customization but typically features simpler, uniform aesthetics. Both types support eco-friendly printing techniques, yet woven jute excels in detailed embossing and multi-layered weaves for premium products.
Choosing the Right Jute Material for Your Needs
Woven jute features interlaced yarns creating a durable, breathable fabric ideal for bags, rugs, and upholstery, offering strength and flexibility. Non-woven jute consists of bonded fibers producing a denser, more rigid material suited for packaging, insulation, and geotextiles requiring structural integrity. Selecting woven or non-woven jute depends on application demands, balancing durability, texture, and cost-effectiveness.
Woven Jute vs Non-woven Jute Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com